Azure HDInsight Azure සරළව (2 කොටස) Windows Geek Magazine
The 5 V's of Big Data: Velocity, Volume, Value, Variety, and Veracity. September 6, 2019. 6 min read. Cameron Downs. Database Hosting. One of the greatest innovations of the technological age has been the ability for individuals and businesses to collect large amounts of data about themselves and their organizations.

The 5 Vs of big data AuraQuantic
In recent years, Big Data was defined by the " 3Vs " but now there is "6 Vs " of Big Data which are also termed as the characteristics of Big Data as follows: 1. Volume: The name 'Big Data' itself is related to a size which is enormous. Volume is a huge amount of data. To determine the value of data, size of data plays a very.

5 Vs of Big Data and security related properties of Veracity, Variety
The term "big data" refers to extremely large and complex datasets that are challenging to store, process, and analyze using traditional data management and processing techniques. Big data is typically characterized using 5 key attributes known as the "5 Vs" - Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity and Value. This article provides an.
The 5 V’s of big data BPI The destination for everything process
Attend our Data and Generative AI Events and Webinars. Acuvate Digital Framework. Insights. Discover the 5Vs of big data analytics - volume, velocity, variety, veracity, and value. Learn how they impact big data.

Big Data Overview Types, Advantages, Characteristics
Their in-house Big Data team applies machine learning to recommend the 97% of products customers view without buying. Algorithms detect 10,000+ fraudulent transactions daily by revealing anomalous.

The five V’s of Big Data (Adapted from (“IBM big data platform
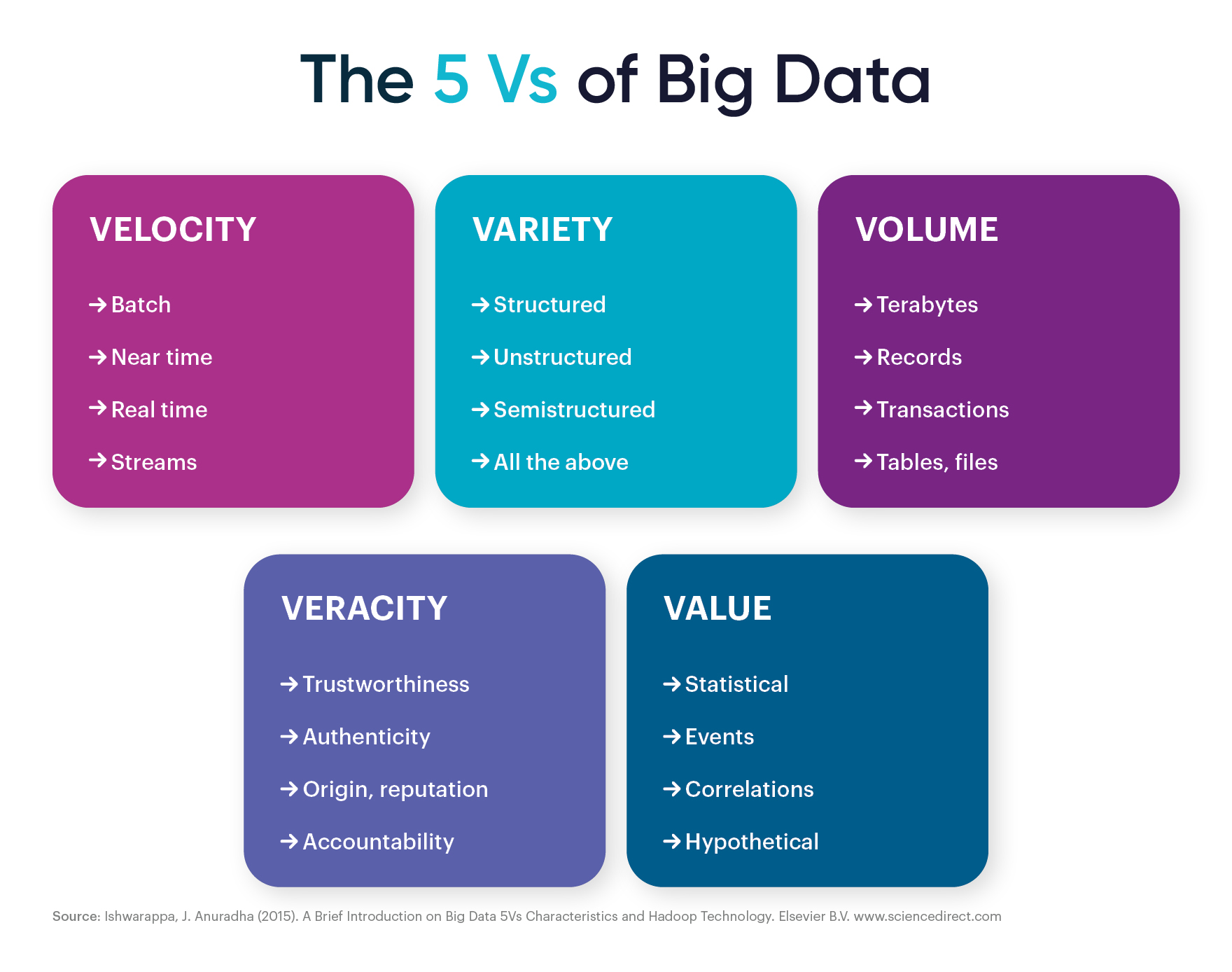
These 2Vs are Value and Veracity. Following are the details of all 5 V's: 1. Volume. Volume in Big data represents the amount of data. In today's world data is being processed in various formats like word, excel, pdf format, and sometimes in audio and video. These data can be structured or unstructured format.
RealTime Big Data Integration Solutions and Platform Don
Verdict. Understanding the 5 Vs of big data provides a comprehensive framework for unlocking its potential. Volume, velocity, variety, veracity and value collectively shape the world of big data, empowering organizations to make informed decisions, enhance customer experiences and gain a competitive edge in an increasingly data-driven world.
Big Data Analytics What is Big Data Definitions of Big Data
The 5 Vs of Big Data are interconnected. For instance, high velocity can impact data volume, as rapid data generation leads to larger datasets. Similarly, data veracity influences the value extracted from data. Final Words. Understanding the 5 Vs of Big Data - Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity, and Value - is super important for doing.
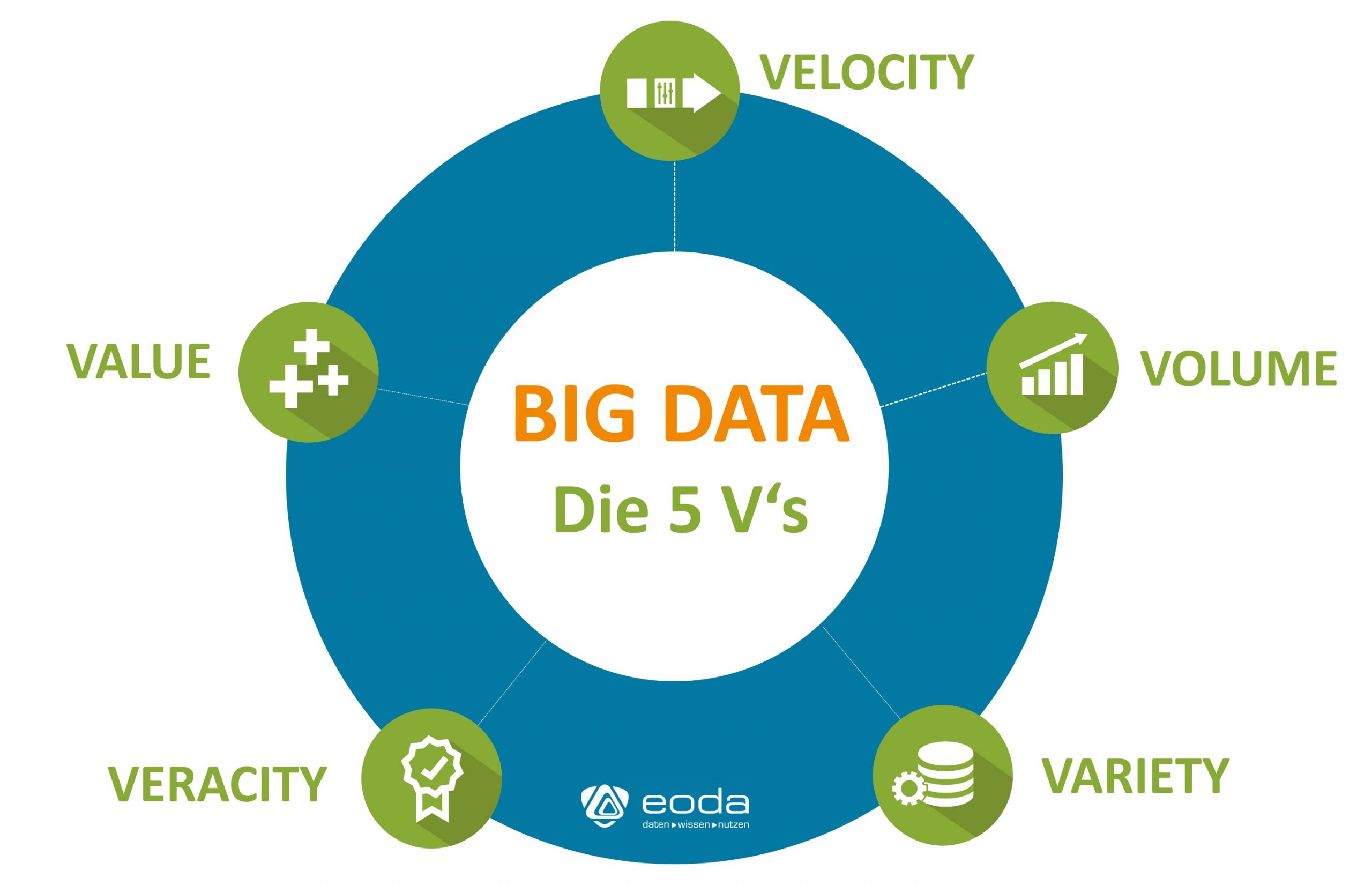
Veracity Sinnhaftigkeit und Vertrauenswürdigkeit von Big Data als
Variability: the changing nature of the data companies seek to capture, manage and analyze - e.g., in sentiment or text analytics, changes in the meaning of key words or phrases. Big data is often discussed or described in the context of 5 V's: value, variability, variety, velocity, veracity, and volume.

What are 5V’s of Big Data (Study Blog) Smart Edge
The 5 Vs in Big Data refer to five fundamental characteristics that describe the challenges of handling vast amounts of data. The digital world is in a constant state of expansion, where every action we take generates data. These data, when collected and analyzed, are known as Big Data.

Infographic The Four V's of Big Data IBM Big Data & Analytics Hub
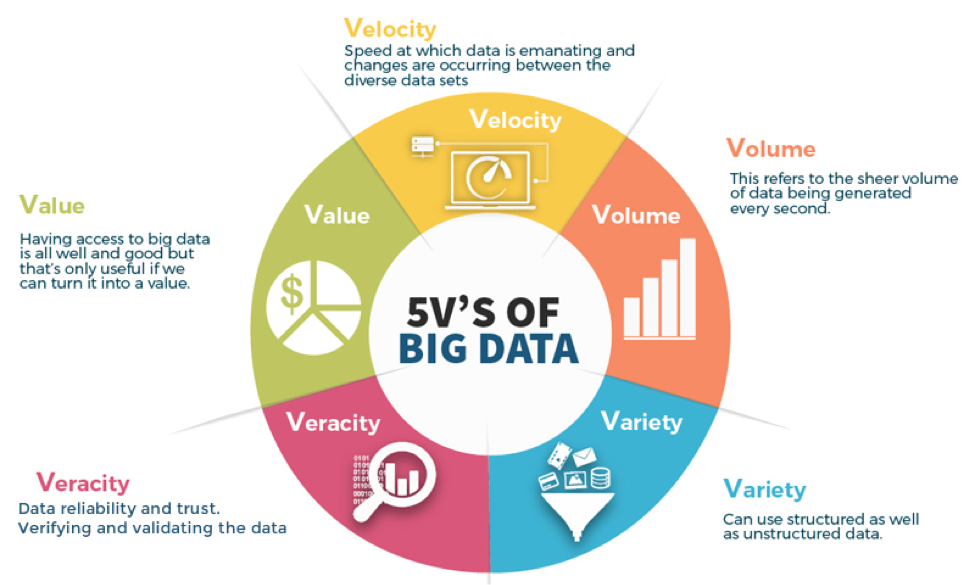
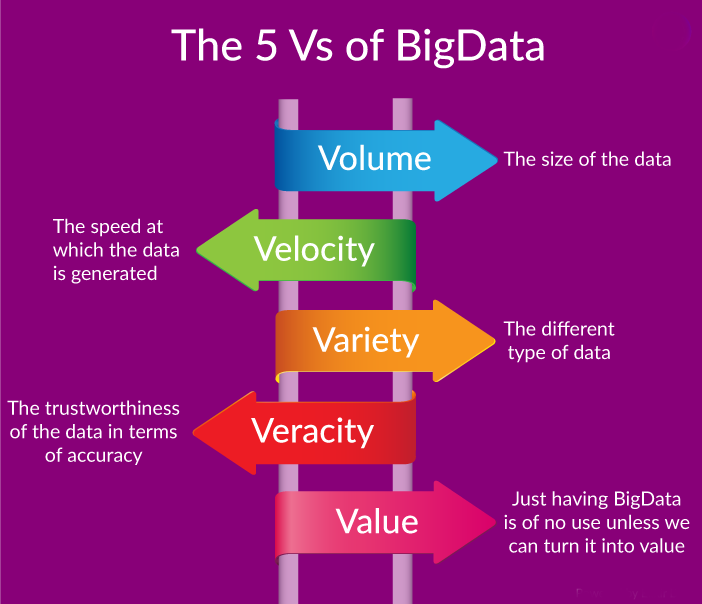
What are the 5 V's? The 5 V's are defined as follows: Velocity is the speed at which the data is created and how fast it moves.; Volume is the amount of data qualifying as big data.; Value is the value the data provides.; Variety is the diversity that exists in the types of data.; Veracity is the data's quality and accuracy.; Velocity. Velocity refers to how quickly data is generated and how.
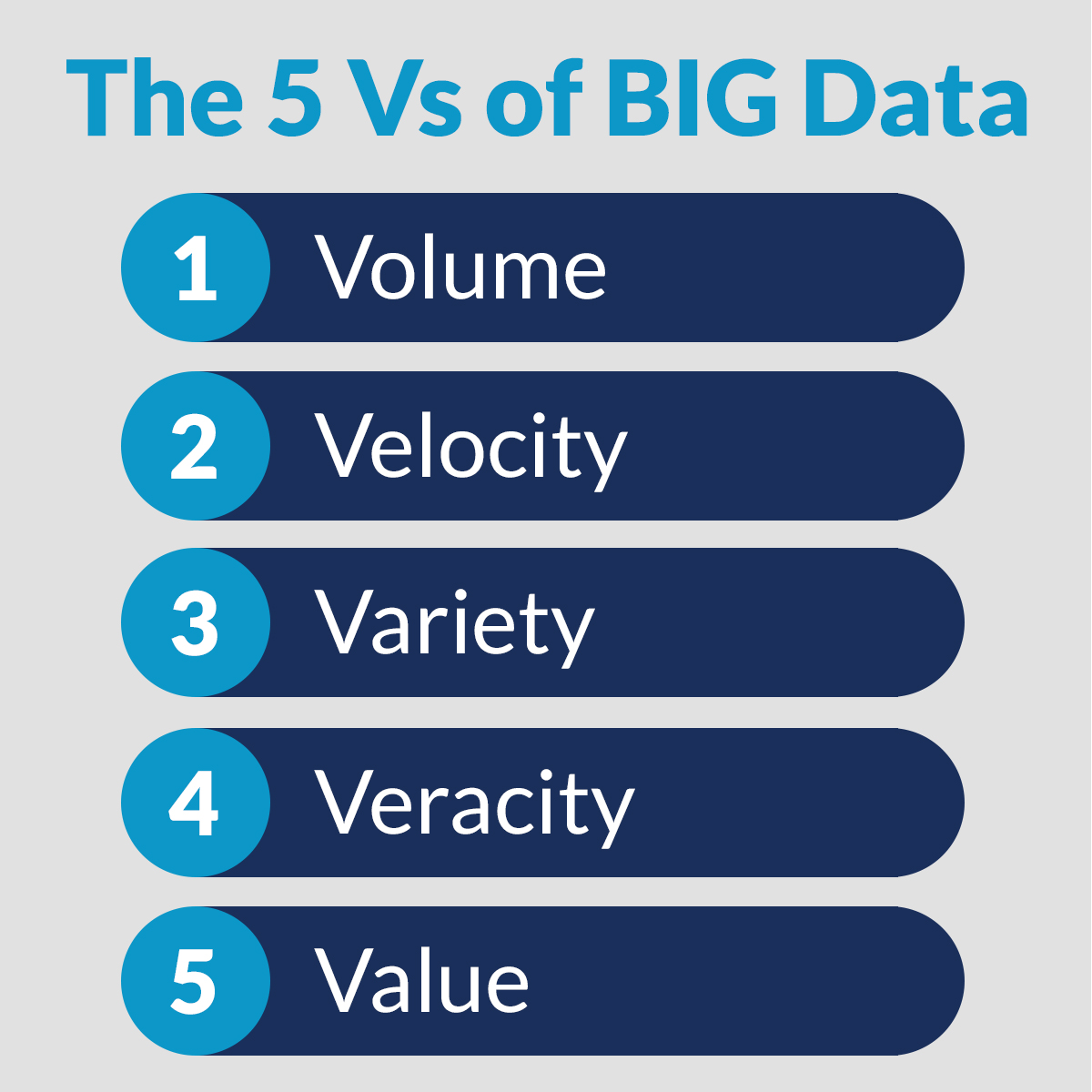
Understanding Big Data The 3 (or 5) Vs Far Reach Blog
Using Big Data Management Tools to Optimize the 5 V's. Savvy companies use robust big data management tools to maximize the value of their big data. Tools like Hadoop help companies store that massive data, clean it, and rapidly process it real time. Such data management tools also help leaders handle unstructured data and extract insights to.

Big Data and its Applications Civilsdaily
While the model is accurate and vital, now two crucial factors need to be added. So, now there are '5Vs' of Big Data, also called characteristics of Big Data, and they are as follows- Volume, Variety, Veracity, Value, and Velocity. This zenith of Software Engineering is designed to handle the enormous data being generated every second, and.

Big Data (5 Vs) YouTube
The main goal of Big Data isn't just to collect and store large volumes of data but to extract meaningful and actionable insights from it. Example: E-commerce companies like Amazon use Big Data analytics to understand customer preferences, buying patterns, and market trends. This information is invaluable in personalizing the shopping.

Representation of the five V's of big data. Download Scientific Diagram
The 5 Vs of Big Data are the fundamental pillars supporting a concept that goes beyond the simple processing and systematic collection of data sets that are too large or difficult for traditional data processing software to handle.. An example is found in a report published by the McKinsey Global Institute, belonging to the consulting firm.
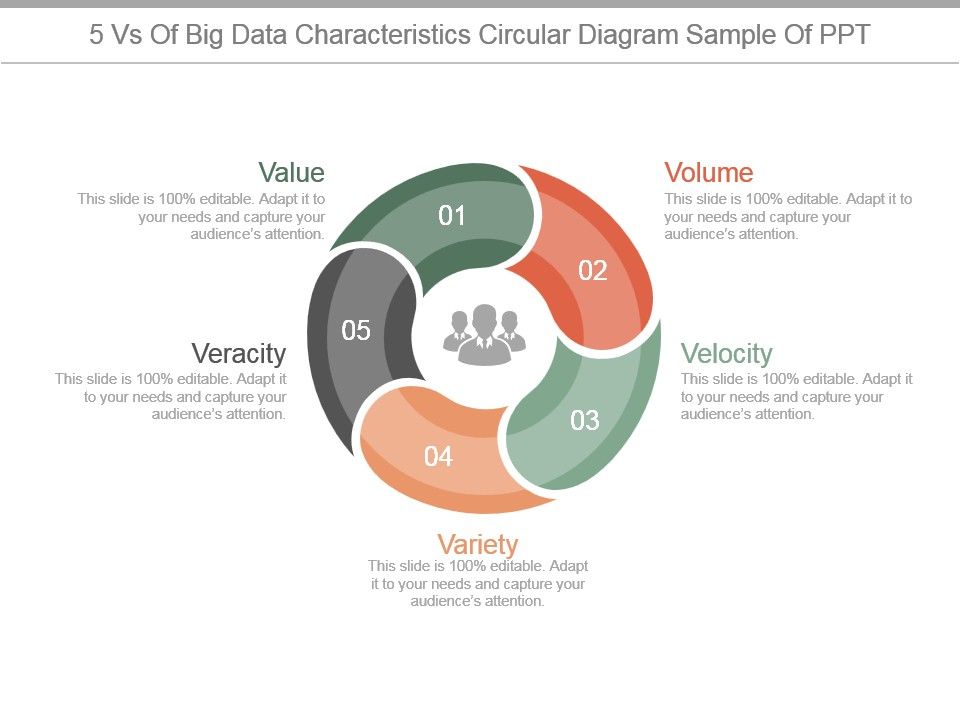
5 Vs Of Big Data Characteristics Circular Diagram Sample Of Ppt
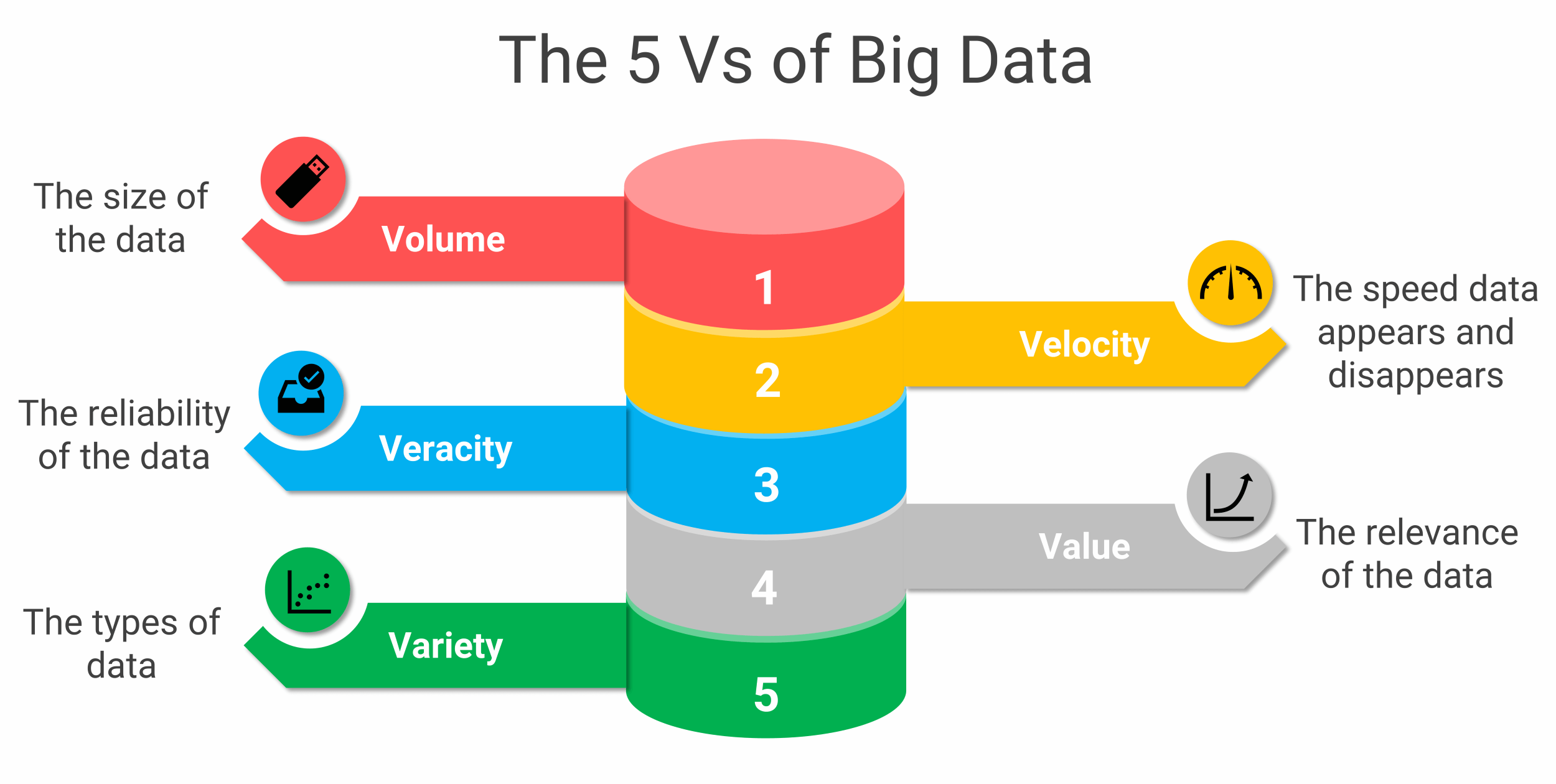
The 5 Vs of big data. Understanding the qualities of big data can help you find the right tools for analysis and interpretation. In general, you can characterize big data by the "five Vs." Read more: Big Data Examples: 6 Ways Big Data Can Change Your Business. Volume "Volume" refers to the high amount of data points in big data.