Unleashing the Truth Behind Animal Testing — PULSE Magazine
The characteristics like safety, maximum dose tolerance, the time span of effect, etc., are noted by giving to a suitable animal. If this is done directly on humans without testing on animals, it could be disastrous. 2. Minimize the cost: Animal research decreases the cost of drug development significantly.

Animal Testing Pros And Cons Cosmetics Country Roads Animal
List of the Key Disadvantages of Animal Testing in Cosmetics. 1. Animal testing harms the animals - there's no getting around that fact. One of the most common animal studies is called the LD50 test. It stands for the "lethal dose 50%" test, where animals are given test substances until half of them die.

Ethical Animal Testing Pros and Cons Sigma Earth
For cosmetics, there are endless cons of animal testing. When animals are used as test subjects for cosmetics, they are forced to endure a number of painful procedures in laboratories. These tests include injecting animals with products; dropping products into animals' eyes; forcing animals to eat cosmetic ingredients; and having compounds.

What is Animal Testing Facts, Pros & Cons Propatel
One of the main advantages for animal testing is advancements in medical research. 2. Animals have physiological and biological similarities to human. Some animals share a surprisingly high amount of DNA with human beings. For instance, chimpanzees share 99% of DNA with humans, while mice share 98%.

animal testing pros and cons argumentative essay Teresia Seidel
Con 1 Animal testing is cruel and inhumane. Animals used in experiments are commonly subjected to force feeding, food and water deprivation, the infliction of burns and other wounds to study the healing process, the infliction of pain to study its effects and remedies, and "killing by carbon dioxide asphyxiation, neck-breaking, decapitation, or other means," according to Humane Society.

Animal testing facts 6 Things every animal lover should know SheKnows
Animal testing facts: Government regulations often require numerous different animal-poisoning tests to assess the hazards of a single new chemical, pesticide or medicinal product. Some tests use thousands of animals at a time, while others are repeated two or even three times using different animal species or routes of administration (oral.

Animal Testing Pros and Cons Exploring the Ethical and Scientific
Better understanding regarding certain bacteria and viruses. One important advantage of animal testing is that we will be better able to understand certain viruses and bacteria once we test their effects on animals. Even in our current state of the world, there are so many bacteria and viruses around and we know quite little about the majority.

Pros and Cons of Animal Research YouTube
Animal testing may save millions of human lives, but at the expense of the lives of animals. In the end, taking the pros and cons into consideration, animal testing highlights the fine line between ethics and practical need, and the ultimate decision is subjective to the values of each individual. Article by Sherry Jiaa. Feature Image Source.

29 Major Pros & Cons Of Animal Testing E&C
A common feature of animal research is that usually at the end of the study, the animal subjects are euthanized, either for the purposes of collecting tissue to examine an organ of interest or for some other reason. Animals are euthanized in labs the same way they are in a vet's office — a dose of an anesthetic and the animal simply goes to.

🐈 Animal experiment pros and cons. Animal Testing Pros and Cons Review
According to the UK Home Office ( 12 ), in the year 2016, 48.6% of the animal tests in medical research were conducted for genetically oriented studies. Moreover, 28.5% of the medical research involving animal testing was for basic biological research, 13.5% was for regulatory. testing, 8.6% was for translating research from animals to humans.

Animal Testing Pros and Cons, for Cosmetics and Pharmaceuticals
Pros & Cons of Animal Testing. Animal testing - taken here to mean the use of animals in research for the purpose of furthering human concerns such as drug efficacy and the safety of products such as cosmetics - is an endeavor fraught with controversy and difficult ethical arguments. Animal experimentation has clear and undeniable benefits.

animal testing pros and cons list Antony Verdin
The most common laboratory animal in biomedical research are purpose bred rats and transgenic mice. In fact, approximately 95% of all warm-blooded laboratory animals are rodents. The contributions made by these animals and other species help researchers answer questions of biological uncertainty and are necessary and critical to the advancement.
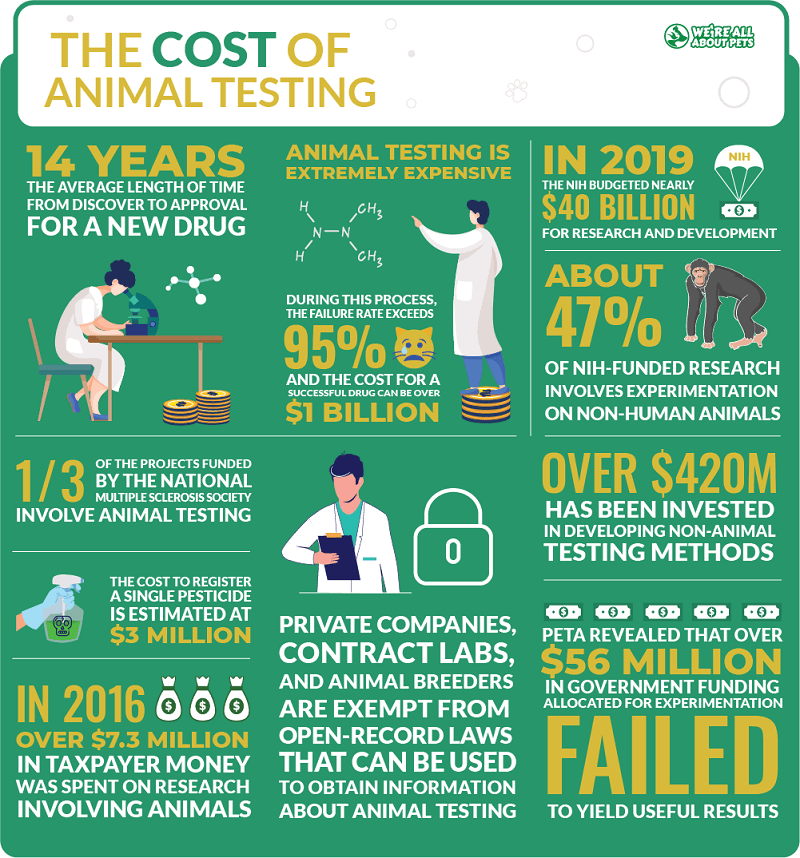
55 Powerful Animal Testing Statistics We're All About Pets
It encompasses everything from testing methods and transport. These are some of the basic tenants animal testers must follow: Refer to an animal care board. Have veterinary programs. Ensure qualifications of those practicing on animals. Have adequate safety and reporting tools for animal welfare.
Pros and Cons of Animal Testi... Mapa Mental Amostra
Ethics and Animal Testing. By Riley Black. November 02, 2007. Mark of SB's own Denialism Blog has asked other science bloggers who use animals in their research to speak up and discuss what they.

Pros And Cons Of Animal Testing
Millions of animals are used every year to test medicines. There are proponents for and opponents against using animals for testing. This article explored 12 pros and cons to using animals for medical testing.
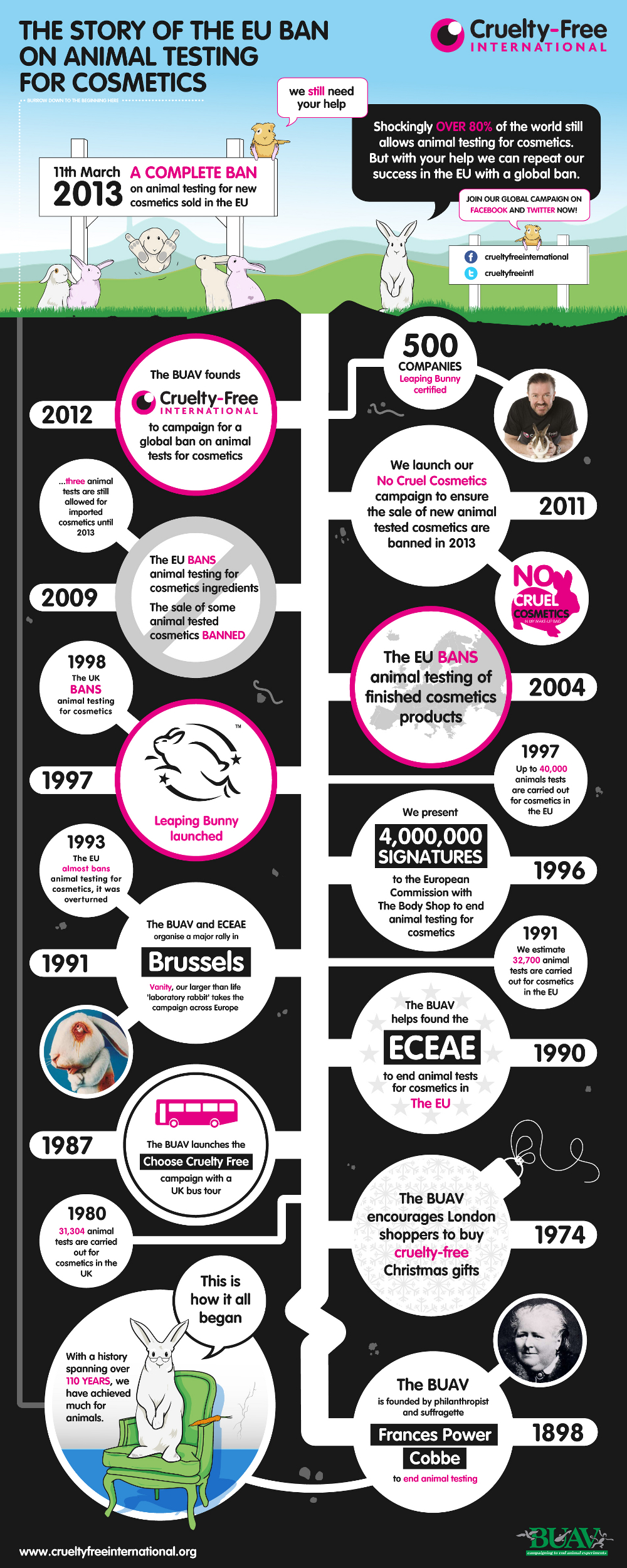
Pros and Cons of Animal Testing HRF
Facts and figures on animal testing. Millions of animals are used and killed in scientific procedures every year. Globally. We estimate that at least 192.1 million animals were used for scientific purposes worldwide in 2015. This is the world's most reliable figure to date. This includes nearly 80 million experiments on animals as well as.