
Cestui Que Vie Act 1540 and 1666 With Henry VIII And The
A cestui que trust is a beneficiary who has equitable title to trust property or assets. This is known as cestui que confidence in the judicial system. This means that the recipient does not have legal ownership or control over the property, but just the right to use and benefit from it. The trustee is responsible for overseeing the management.

Cestui Que Vie Definition, History, and What It Means for a Trust
The meaning of CESTUI QUE VIE is the person whose life measures the duration of an estate.
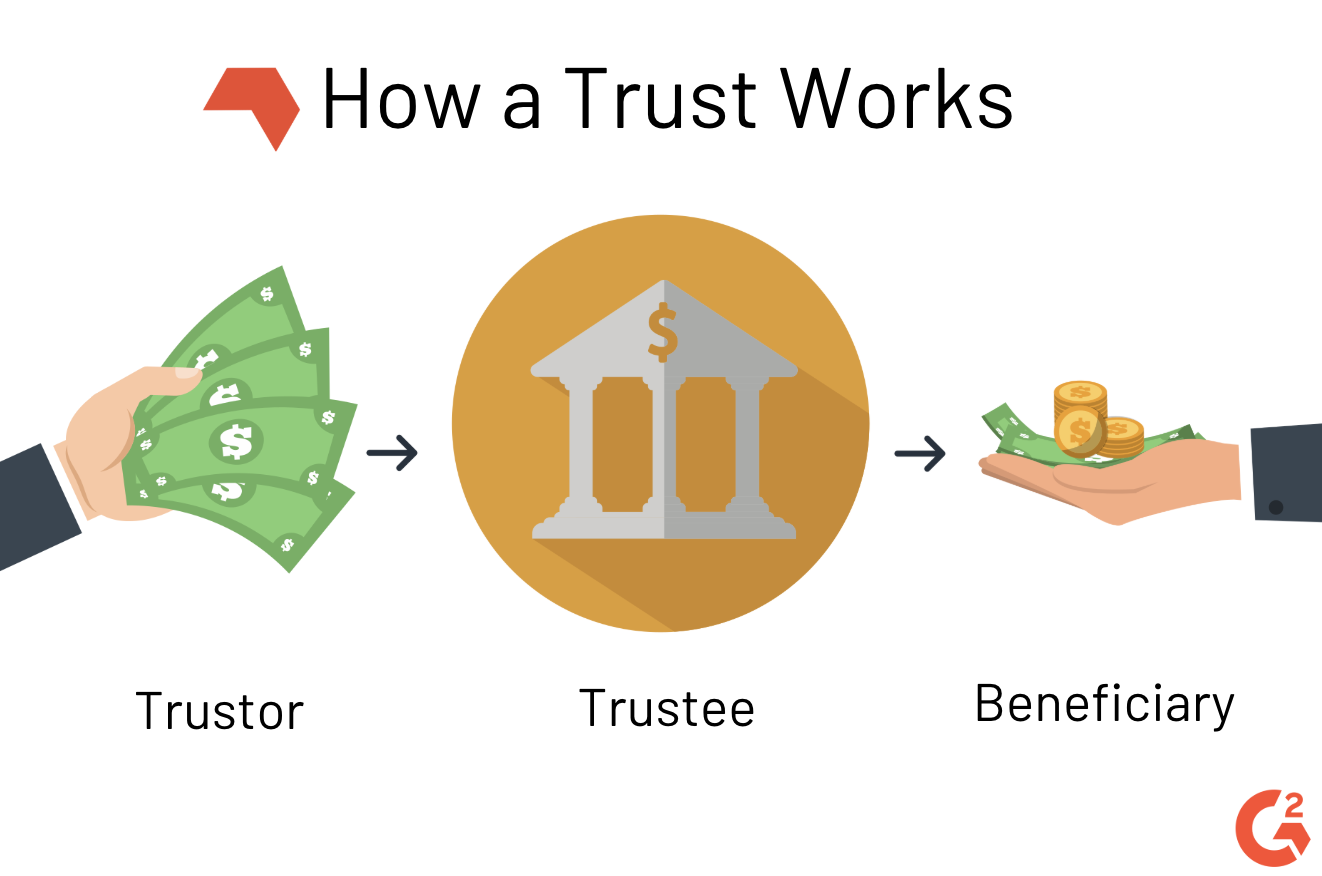
What Is a Trust? (Definition + Types)
Key takeaways. Cestui que vie, meaning "he who lives," refers to the beneficiary of a trust or insurance policy with property and income rights. Historically, it protected property during the owner's absence and was used to avoid taxation. The Cestui Que Vie Act of 1666 reinstated the legal concept after catastrophic events.

5415 (I) Knowledge Is Power_Truth About the Cestui Que Vie Trust
the cestui que trust as beneficial owner of the trust res, but because it considers that the trustee adequately represents him."2 Else-where he says, "It is submitted that the cestui que trust is not merely the owner of the equitable obligation of the trustee, but he is also the equitable ozwner of the property held by the trustee.

A Brief History of Cestui Que Vie Trust Constitution Watch
CESTUI QUE [French, He or she who.] The person for whom a benefit exists. A cestui que trust is a person for whose benefit a trust is created; a beneficiary. Although legal title of the trust is vested in the trustee, the cestui que trust is the beneficiary who is entitled to all benefits from a trust.. A cestui que use is an archaic term of property law that describes one who has a beneficial.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Cestui-que-vie_final-791c0b2e1ea9415daa7be768af173721.png)
Cestui Que Vie Definition, History, and What It Means for a Trust
It is equal in precision to the antiquated and unwieldy Norman phrase, and far better adapted to the genius of our language. Find the legal definition of CESTUI QUE TRUST from Black's Law Dictionary, 2nd Edition. He who has a right to a beneficial interest in and out of an estate the legal title to which is vested in another. 2 Waslib. Real.
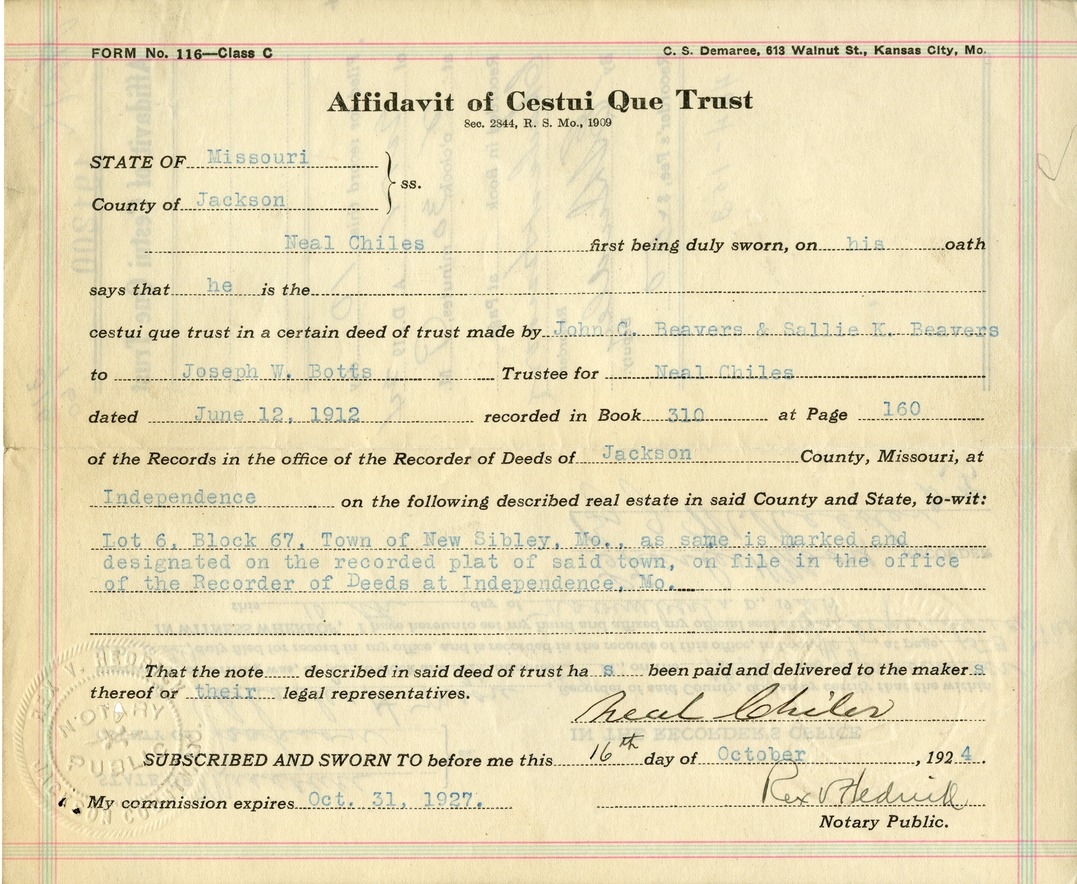
Affidavit of Cestui Que Trust of Neal Chiles Harry S. Truman
Cestui Que Vie: The individual who is the beneficiary of a trust or insurance policy that is legally attached to his or her name. Cestui que vie is used less frequently than the term.

Fillable Online Cestui Que Vie Definition, History, and What It Means
the value of the trust res, or the amount of profits which should have accrued if no breach had been committed. His right is a per-sonal right against the trustee; it is an equitable obligation. But while a trustee still holds the trust res the right of the cestui que trust is of a different nature. On the question how far it is differ-

Cestui Que Vie Trust Canon 1283 A Cestui Que Vie Trust is a fictional
noun. -kē-ˈtrəst, -ki-. plural cestuis que trust or cestuis que trustent. -ˈtrəs-tənt. : the beneficiary of a trust compare trustee.

Cestui Que Vie Trust with Tami Pepperman The Matrix Unlocked
The Trust Corpus created by a Cestui Que (Vie) is also known as the Estate from two Latin words e+statuo literally meaning "by virtue of decree, statute or judgment". However, as the Estate is held in a Temporary not permanent Trust, the ( Corporate) Person as Beneficiary is entitled only to equitable title and the use of the Property.
Cestui Que Vie Act [1666] UK.pdf Google Drive
In trust law, a beneficiary (also known by the Law French terms cestui que use and cestui que trust), is the person or persons who are entitled to the benefit of any trust arrangement.A beneficiary will normally be a natural person, but it is perfectly possible to have a company as the beneficiary of a trust, and this often happens in sophisticated commercial transaction structures.

Calaméo Evi Doc 26 Cestui Que Vie Trust Act
document that follows, plaintiff references the Cestui Que Vie Act of 1666 and includes a passage attributed to this authority related to the circumstance of a person being alive after having been presumed dead. Id. at 10-12. Plaintiff then presents a Declaration of Trust, id. at

Calaméo CESTUI QUE VIE ACT [1666]
United States v. State Bank, 96 U.S. 30 (1877) United States v. State Bank. 1. Where a trust fund has been perverted, the cestui que trust can follow it at law as far as it can be traced. 2. The United States cannot, against the claim of an innocent party, hold his money which has gone into its treasury by means of the fraud of its agent. 3.

Cestui Que Vie Act 1666 in the United States
It means "he who lives" and refers to a beneficiary of a trust. Despite the "he" part of the translation, the term isn't as sexist as it sounds though.it can refer to a woman too. Originally passed in England, the Cestui Que Vie Act of 1666 outlined how property, usually land, would be passed down to beneficiaries (without doing any.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bamburgh-castle-daytime-with-people-walking-on-beach-157193180-ae684e3e0bb04217880bbd6397665a5c.jpg)
Cestui Que Vie Definition, History, and What It Means for a Trust
Beneficiary The beneficiary, also known as the cestui que trust, is the beneficial or equitable owner of the property. The beneficiary is said to have the "use" of. Assets required By definition, a trust is a legal relationship with regard to property. Thus, the common-law rule is that a trust does not exist without a res. Am. Jur. 2d
Cestui Que Trust Definition What Does Cestui Que Trust Mean?
A Cestui Que Vie Trust, also known by several other pseudonyms such as "Term of Life or. In terms of the evidential history of the formation of Cestui Que Vie Trusts: (i) The first Cestui Que Vie Trusts formed were through an Act of Henry VIII of England in 1540 (32Hen.8 c1) and later wholly corrupted whereby the poor people of England.