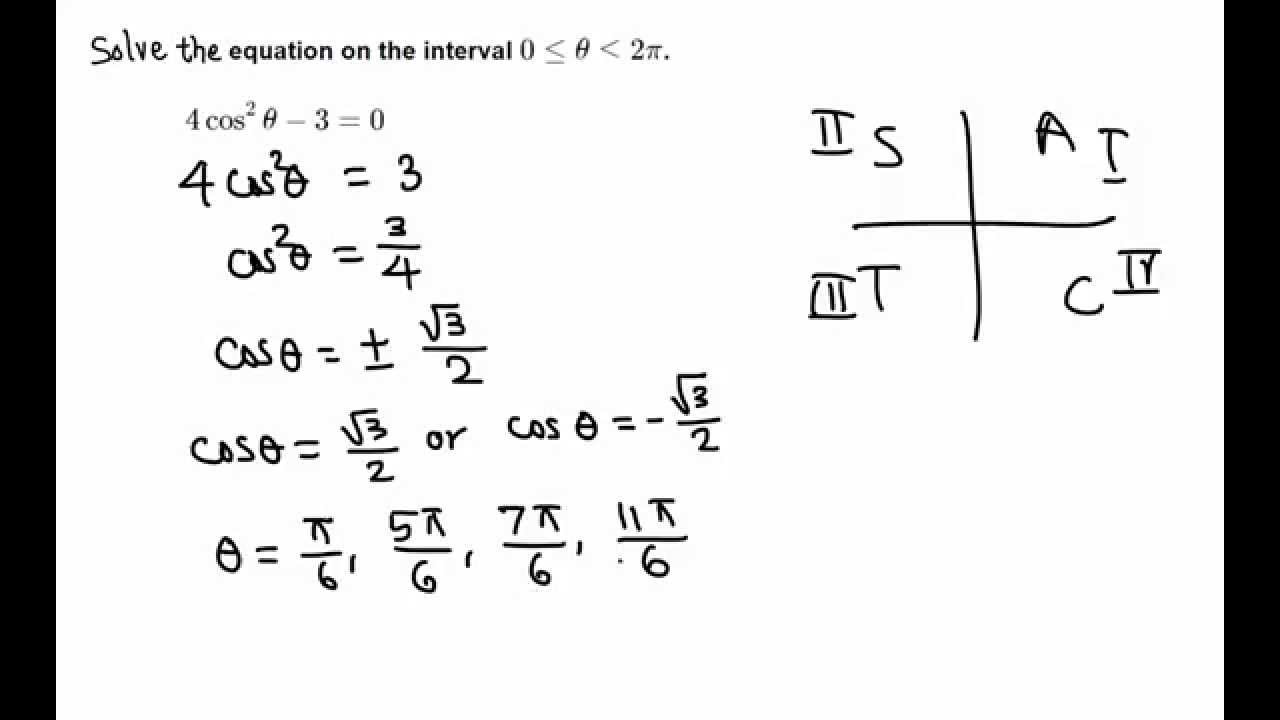
Solving Trigonometric Equation 4 cos^2 x 3 = 0 YouTube
What is cos² (x)? Asked 8 years, 11 months ago Modified 7 years ago Viewed 31k times 2 This looks odd to me. I need a definition. Is it just the square of cos(x) cos ( x) ? Like cos2(x) = cos(x) ⋅ cos(x) cos 2 ( x) = cos ( x) ⋅ cos ( x) ? Then why don't you write it like that: cos(x)2 cos ( x) 2 ? functions trigonometry notation Share Cite

HOW TO INTEGRATE COS SQUARED Definite Integrals Calculus YouTube
There are two popular cosine squared power reducing trigonometric identities in mathematics and they are used as formulas in trigonometry. When the theta represents an angle of a right triangle, the double angle and half angles are written as 2 θ and θ 2 respectively. The cosine of angle and the square of cosine of angle are written in.
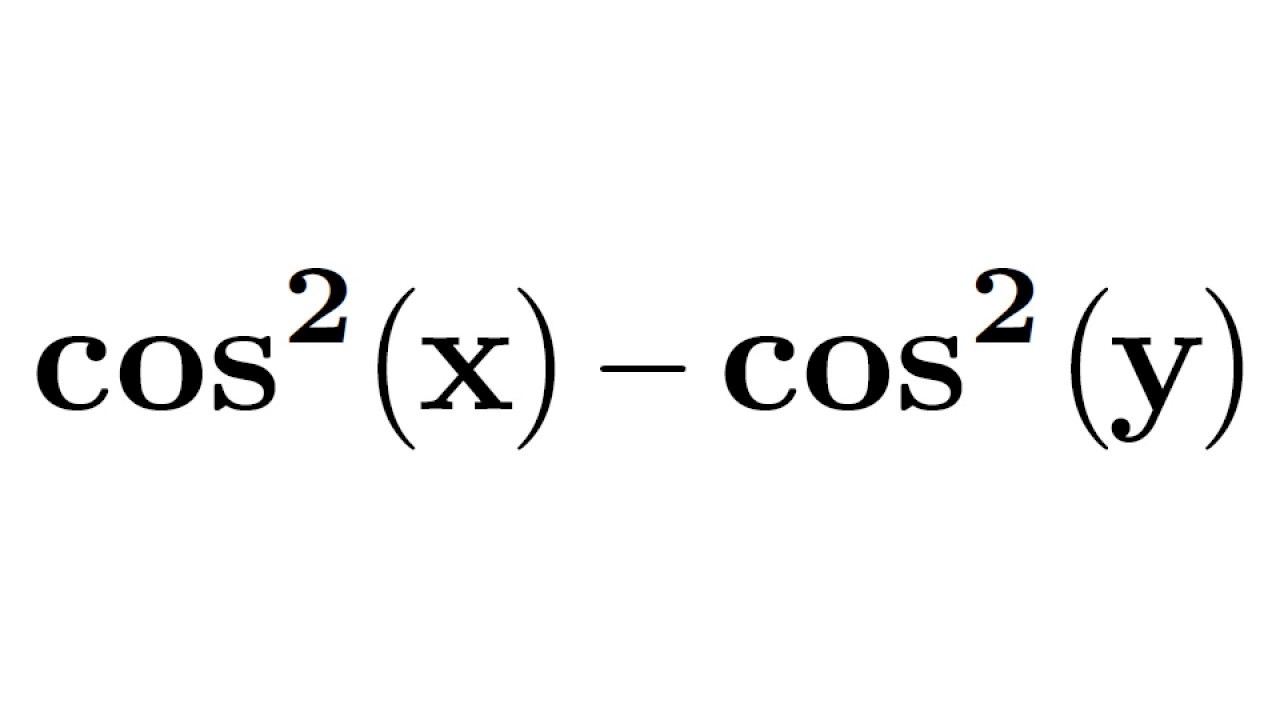
cos^2(x) cos^2(y) square of cos(x) square of cos(y) Identity for cos^2(x) cos^2(y
The square of cosine function equals to the subtraction of square of sin function from one is called the cosine squared formula. It is also called as the square of cos function identity. Introduction In trigonometric expressions and equations, the cosine functions are often involved in square form.

PPT Law of Cosines 10.5 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4307257
Cos is the cosine function, which is one of the basic functions encountered in trigonometry. It is defined for real numbers by letting be a radian angle measured counterclockwise from the axis along the circumference of the unit circle. Cos [x] then gives the horizontal coordinate of the arc endpoint. The equivalent schoolbook definition of the cosine of an angle in a right triangle is the.

Cosine_squared_graph,_or_half_of_one_plus_the_cosine_of_twice_x.svg The Story Siren
Purplemath What is an identity? In mathematics, an "identity" is an equation which is always true, regardless of the specific value of a given variable. An identity can be "trivially" true, such as the equation x = x or an identity can be usefully true, such as the Pythagorean Theorem's a2 + b2 = c2 MathHelp.com Need a custom math course?

Trigonometric Identity Square Root Cosine 67 YouTube
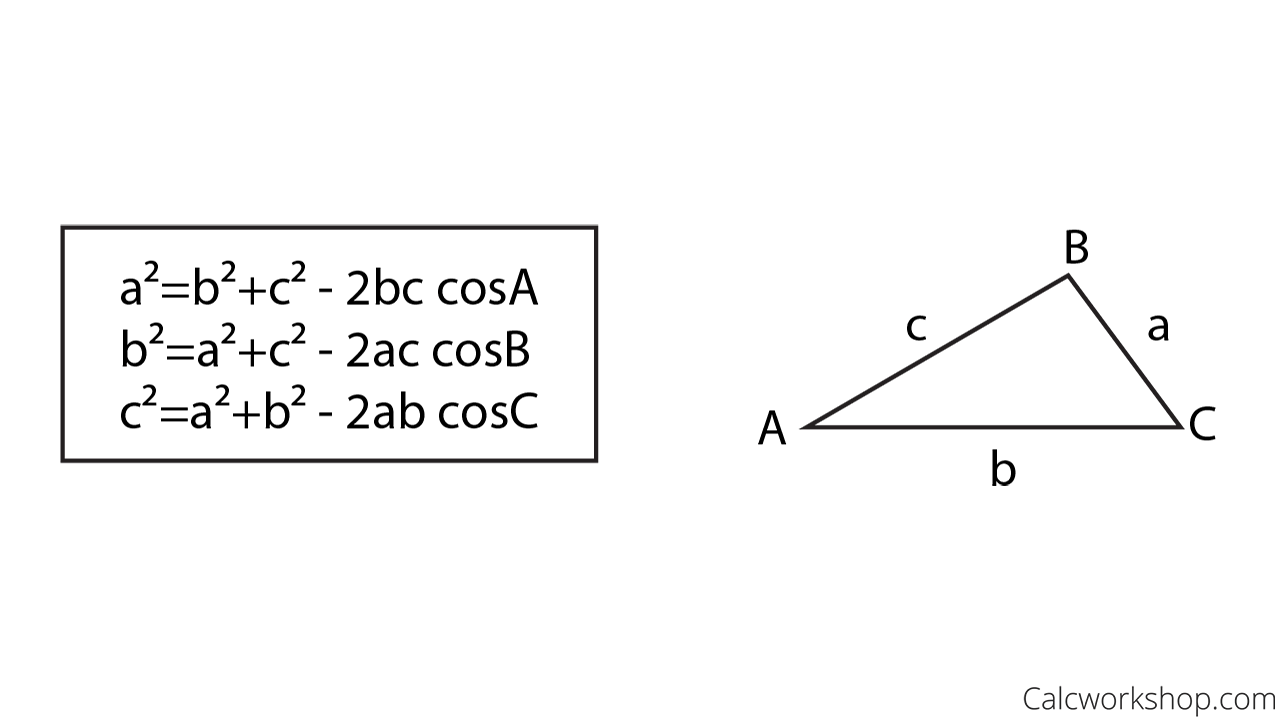
The Law of Cosines For any triangle: a, b and c are sides. C is the angle opposite side c The Law of Cosines (also called the Cosine Rule) says: c 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2ab cos (C) It helps us solve some triangles. Let's see how to use it. Example: How long is side "c". ? We know angle C = 37º, and sides a = 8 and b = 11

Law of Cosine (Cosine Law) with Examples and Proof Teachoo
Adjacent Opposite Sine, Cosine and Tangent The three main functions in trigonometry are Sine, Cosine and Tangent. They are just the length of one side divided by another For a right triangle with an angle θ : For a given angle θ each ratio stays the same no matter how big or small the triangle is When we divide Sine by Cosine we get:
What is the Law of Cosines? (Explained in 3 Powerful Examples!)
Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.

Law of Cosine (Cosine Law) with Examples and Proof Teachoo
Cosine and Sine of the Sum of Two Angles Tomas Garza; Cofunction Identities for Sine and Cosine Chris Boucher; Difference Formula for Cosine Chris Boucher; A Visual Proof of the Double-Angle Formula for Sine Chris Boucher; A Special Case of the Sum of Two Cosines Izidor Hafner; Dudeney's Proof of the Pythagorean Theorem Izidor Hafner

Law of Cosine (Cosine Law) with Examples and Proof Teachoo
Trigonometry Free math problem solver answers your trigonometry homework questions with step-by-step explanations.

MEDIAN Don Steward mathematics teaching cosine rule
Trigonometry/Sine Squared plus Cosine Squared - Wikibooks, open books for an open world [ dismiss] - Trigonometry/Sine Squared plus Cosine Squared < Trigonometry Contents 1 Pythagoras in Disguise 2 Pythagorean Trigonometric Identity 3 Using the Formula 4 This formula and Circles 5 Revision 6 References Pythagoras in Disguise [ edit | ]
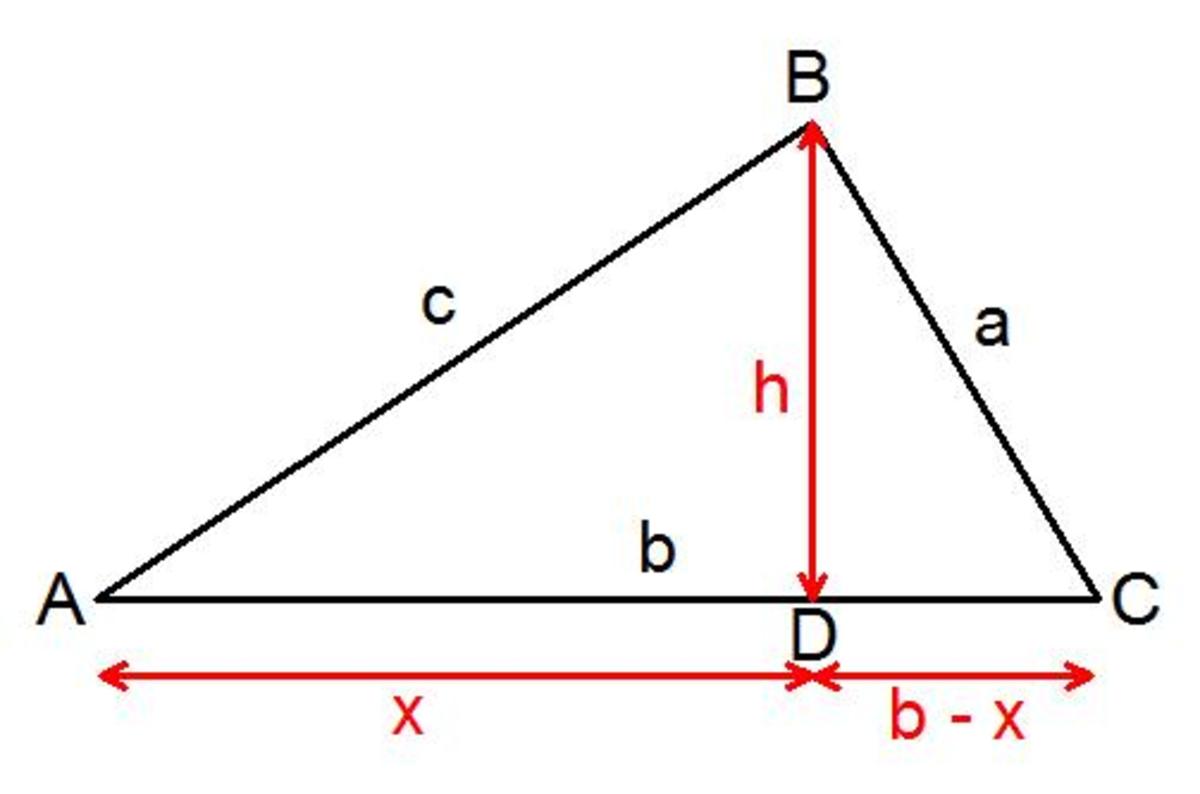
Proof of the cosine rule. Proving the cosine rule using Pythagoras and Trigonometry. HubPages
In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. Geometrically, these are identities involving certain functions of one or more angles.

Cosine Square Law calculation YouTube
The law of cosines (alternatively the cosine formula or cosine rule) describes the relationship between the lengths of a triangle's sides and the cosine of its angles. It can be applied to all triangles, not only the right triangles.

Integral Tricks cosine squared and sine squared YouTube
Free trigonometric equation calculator - solve trigonometric equations step-by-step
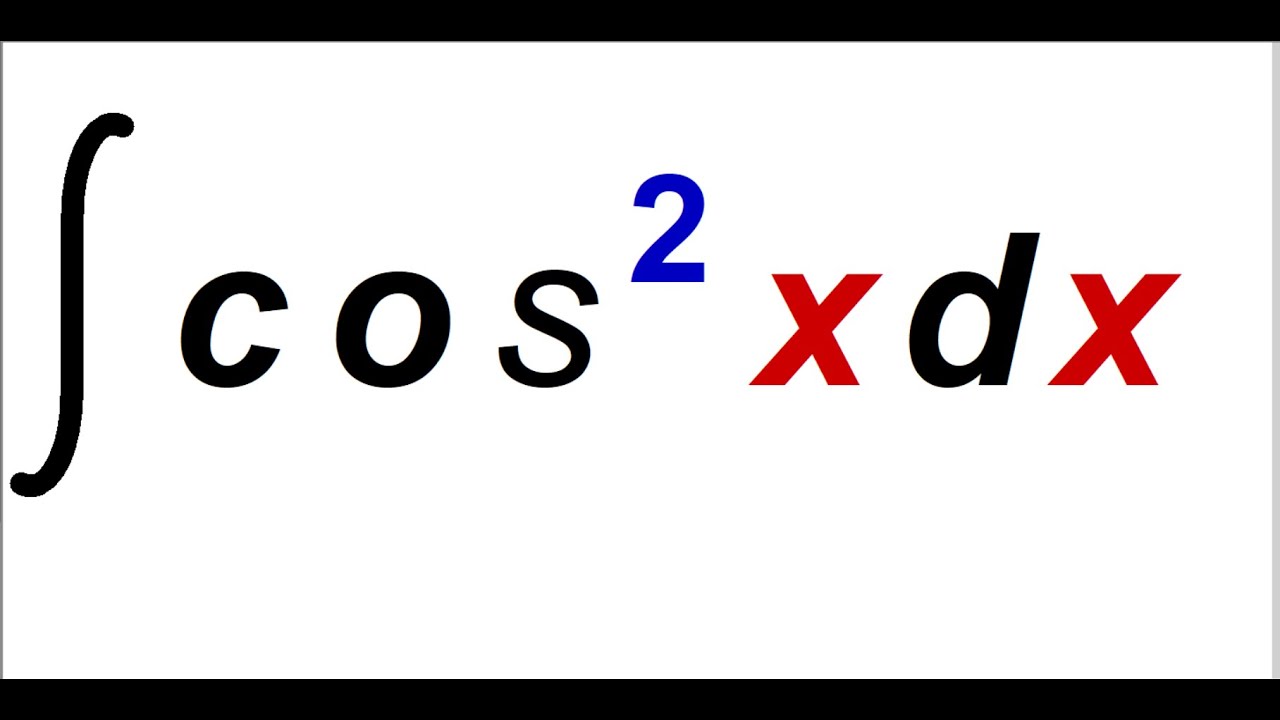
Integral of cosine squared , integral cos^2x YouTube
Cosine, written as cos(θ), is one of the six fundamental trigonometric functions.. One method that may help with memorizing these values is to express all the values of cos(θ) as fractions involving a square root. Starting from 0° and progressing through 90°, cos(0°)=1=. The subsequent values, cos(30°), cos(45°), cos(60°), and.

Law of Cosine (Cosine Law) with Examples and Proof Teachoo
Cos2x is a double angle trigonometric function that determines the value of cos when the angle x is doubled. What is Cos2x Formula in Trigonometry? Cos2x is an important identity in trigonometry which can be expressed in different ways. It can be expressed in terms of different trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent.