Internal Structure Human Stomach Stock Vector Illustration of medicine, healthy 91532703
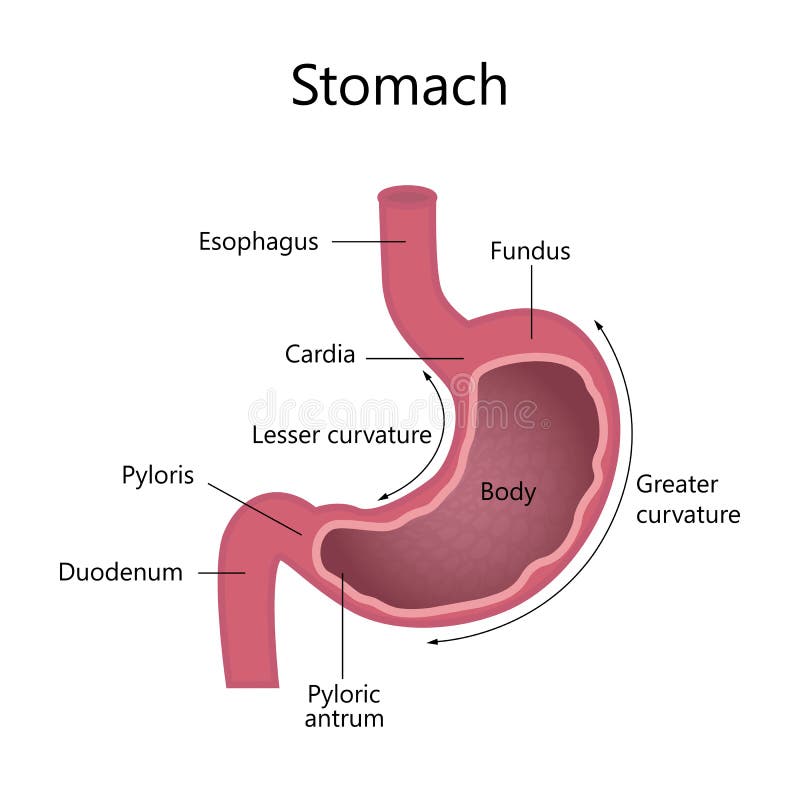
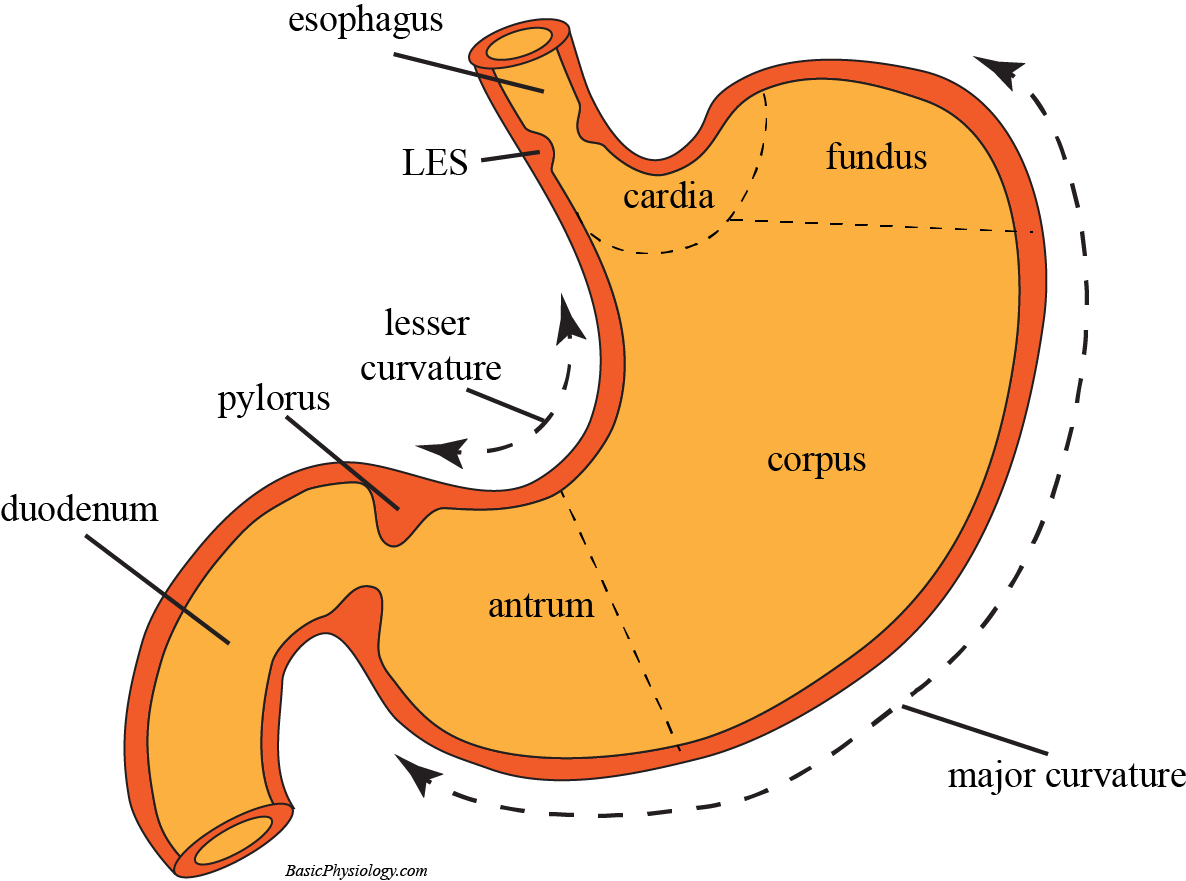
The stomach has four main anatomical divisions; the cardia, fundus, body and pylorus: Cardia - surrounds the superior opening of the stomach at the T11 level. Fundus - the rounded, often gas filled portion superior to and left of the cardia. Body - the large central portion inferior to the fundus. Pylorus - This area connects the.
How is the shape of the stomach?(a) As V(b) As J(c) As O(d) None of the above
The stomach is lined by a mucous membrane that contains glands (with chief cells) that secrete gastric juices. Two smooth muscle valves, or sphincters, keep the contents of the stomach contained: the cardiac or esophageal sphincter and the pyloric sphincter. The arteries supplying the stomach are the left gastric, the right gastric, and the.
E.4. Stomach
Indigestion Heartburn Nausea Vomiting Diarrhea Peptic Ulcers Crohn's disease Last medically reviewed on December 17, 2014 How we reviewed this article: The stomach is located in the upper-left.
Anatomy Of Chest And Stomach Human Chest Anatomy Diagram Physiology, Anatomy and The
Digestion The stomach, gallbladder, and pancreas work together as a team to perform the majority of the digestion of food. Food entering the stomach from the esophagus has been minimally processed — it has been physically digested by chewing and moistened by saliva, but is chemically almost identical to unchewed food.

Stomach (Anatomy) Definition, Function, Structure Biology Dictionary
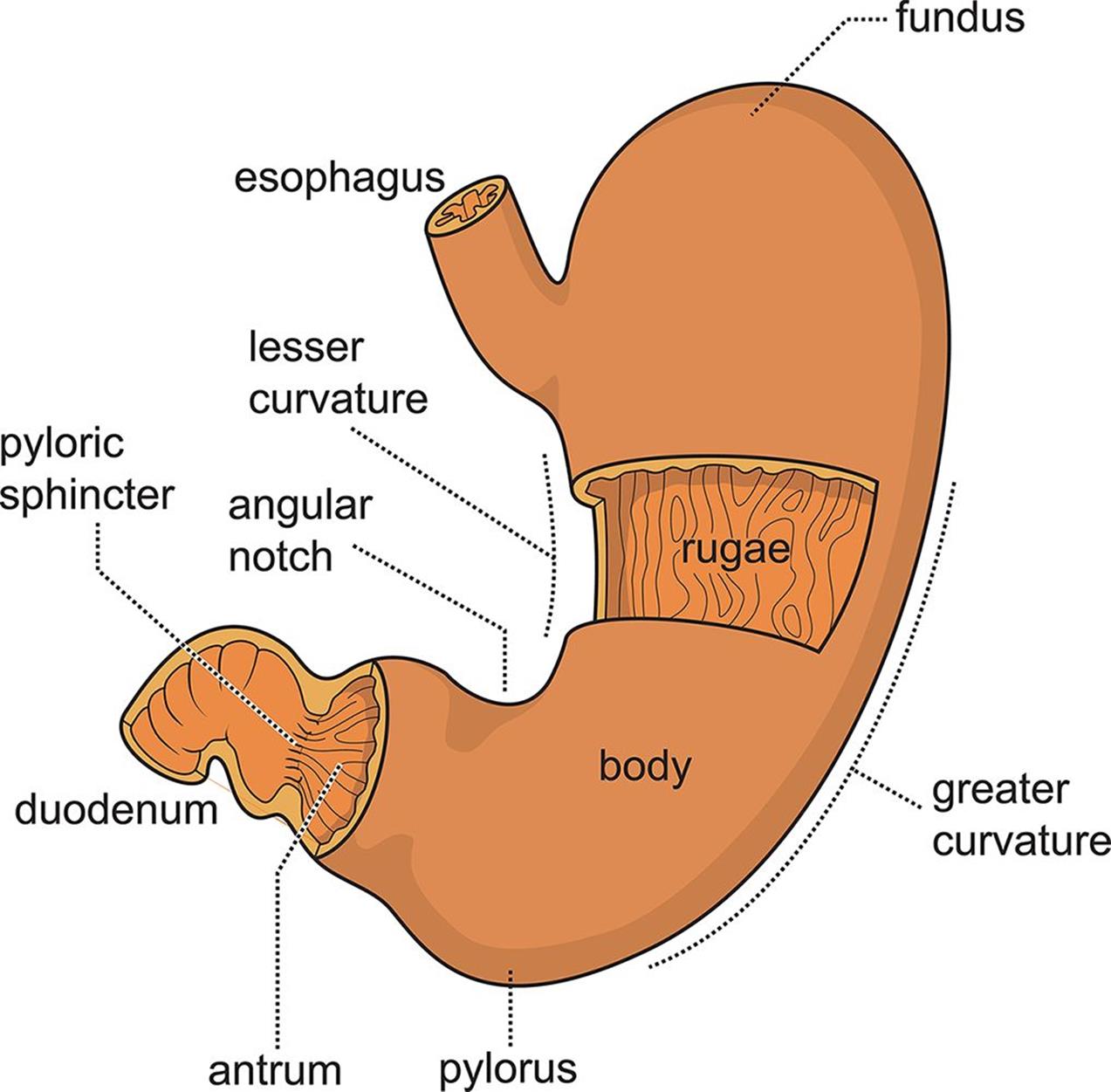
The human stomach is subdivided into four regions: the fundus, an expanded area curving up above the cardiac opening (the opening from the stomach into the esophagus); the body, or intermediate region, the central and largest portion; the antrum, the lowermost, somewhat funnel-shaped portion of the stomach; and the pylorus, a narrowing where the.
.jpeg)
Organs of the Abdominopelvic Cavity MedicTests
Picture of Abdomen The abdominal cavity is the part of the body that houses the stomach, liver, pancreas, kidneys, gallbladder, spleen, and the large and small intestines. The diaphragm marks the top of the abdomen and the horizontal line at the level of the top of the pelvis marks the bottom.
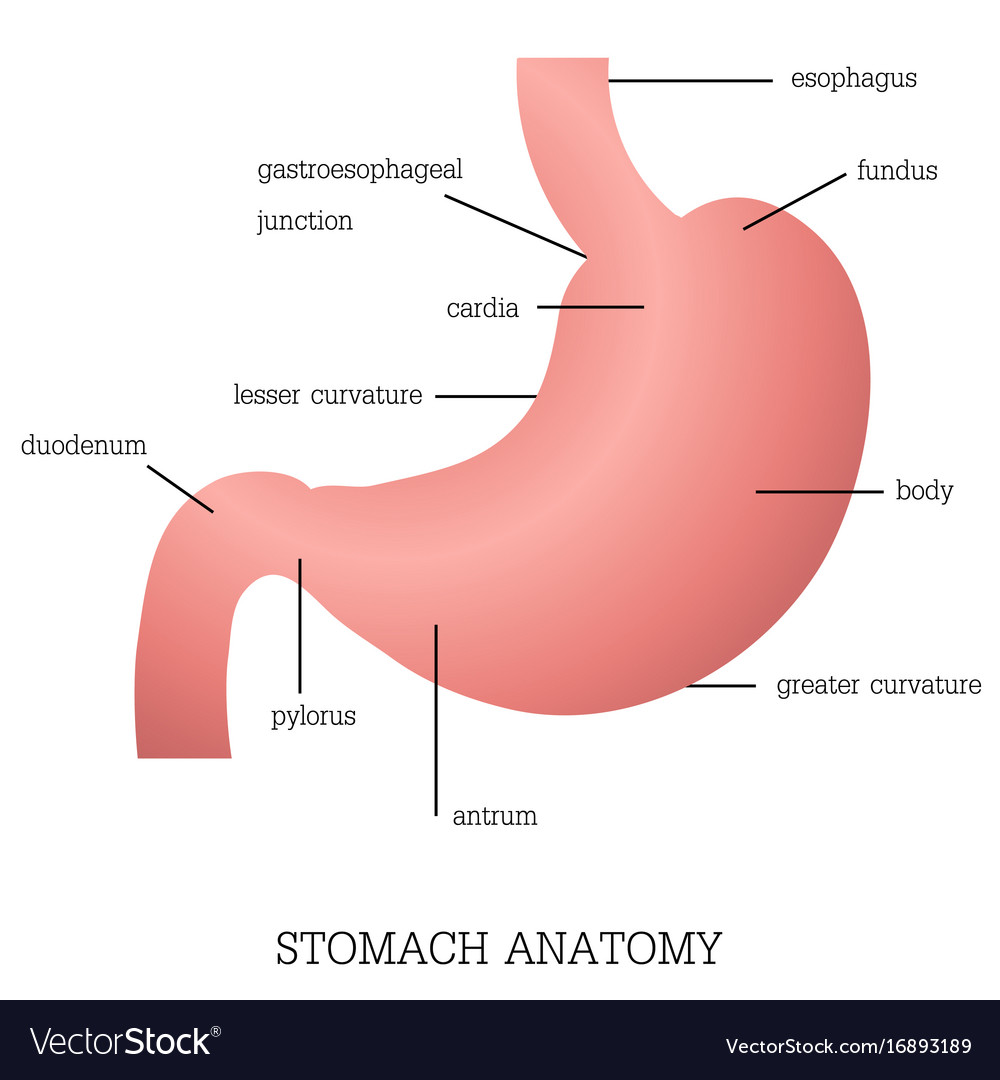
Structure and function of stomach anatomy system Vector Image
Label on a diagram the four main regions of the stomach, its curvatures, and its sphincter Identify the four main types of secreting cells in gastric glands, and their important products Explain why the stomach does not digest itself Describe the mechanical and chemical digestion of food entering the stomach
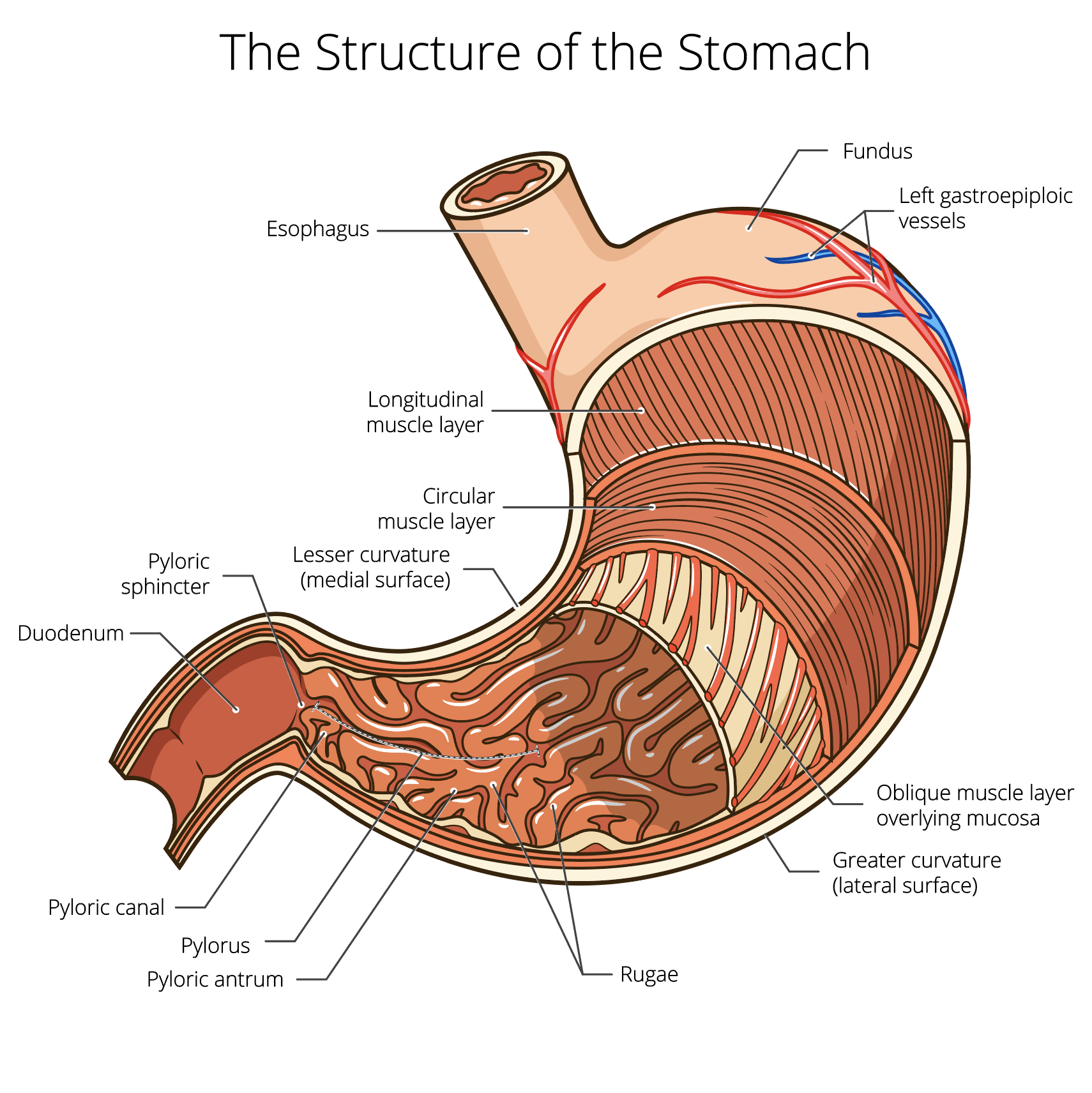
Stomach — High Plains Surgical Associates
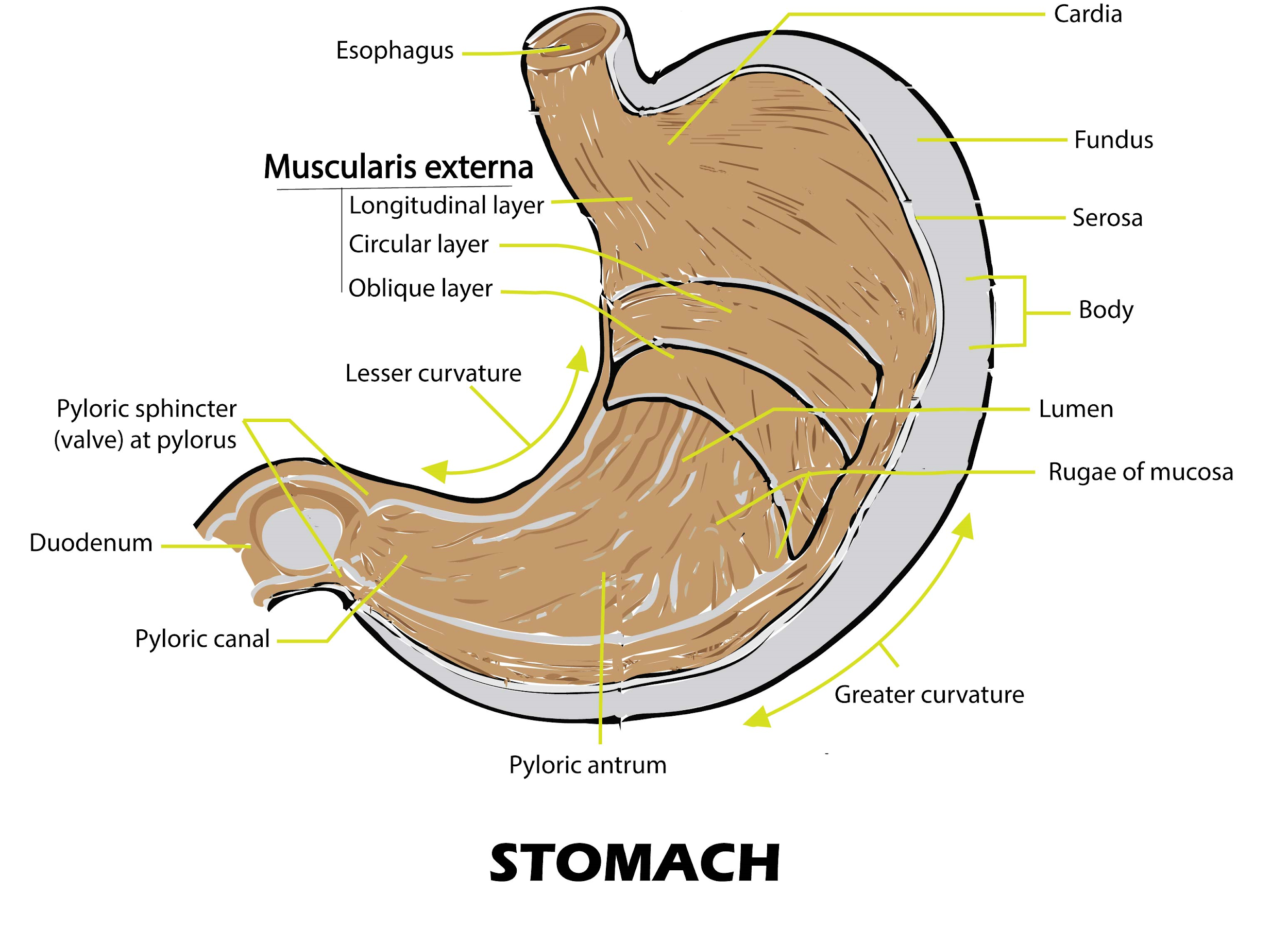
The stomach wall: A micrograph that shows a cross section of the stomach wall, in the body portion of the stomach. This consists of an epithelium, the lamina propria underneath, and a thin bit of smooth muscle called the muscularis mucosae. The submucosa lies under this and consists of fibrous connective tissue that separate the mucosa from the.

Human Stomach Anatomy Vector Illustration With Labels Stock Illustration Download Image Now
01 of 03 Anatomy of the Stomach STEVE GSCHMEISSNER/SPL/Getty Images The wall of the stomach is structurally similar to other parts of the digestive tube, with the exception that the stomach has an extra oblique layer of smooth muscle inside the circular layer, which aids in the performance of complex grinding motions.

The Stomach Organs Parts, Anatomy, Functions of the Human Stomach
Diagram Stomach Gallbladder Liver Pancreas Small intestine Large intestine How they interact Common problems Summary The stomach is located in the upper part of the abdomen. The digestive.
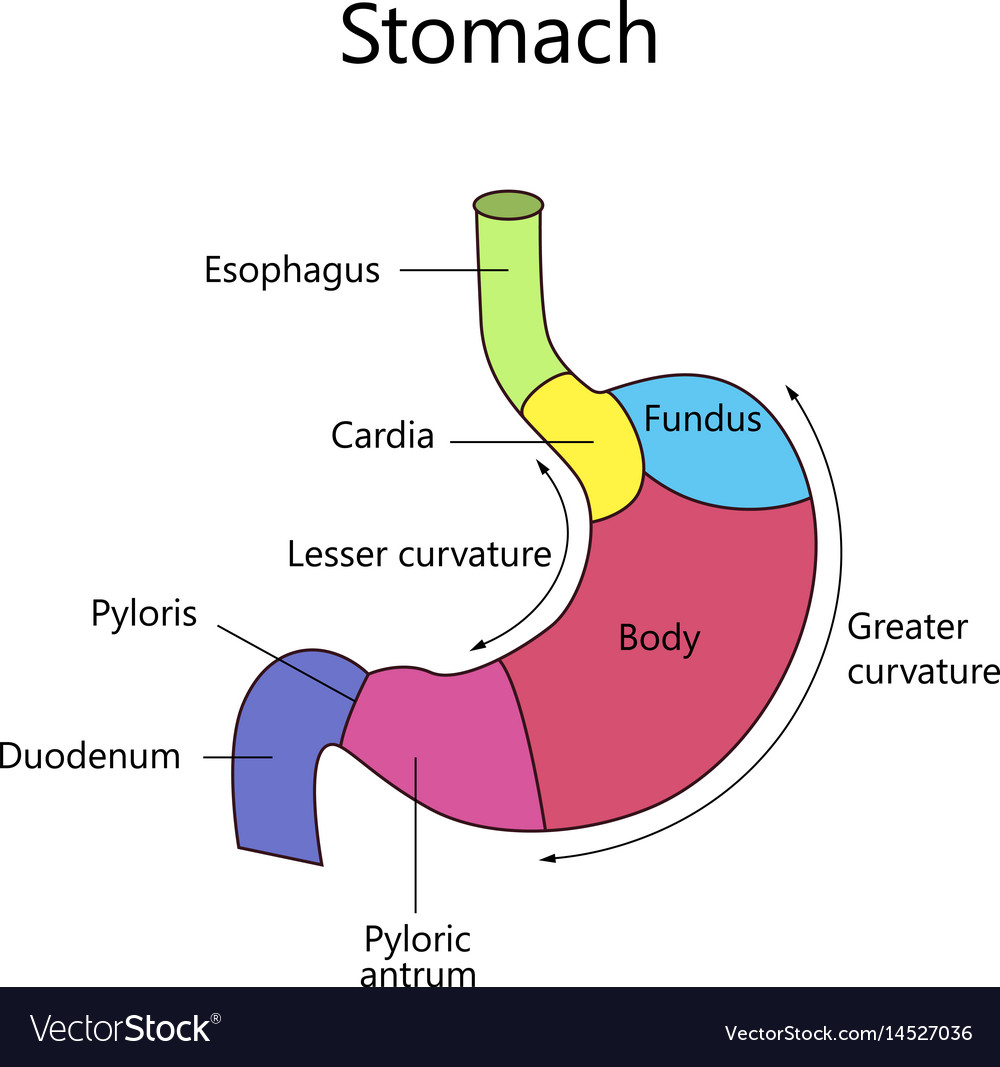
Internal structure human stomach Royalty Free Vector Image
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates.The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system.The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing.It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid.
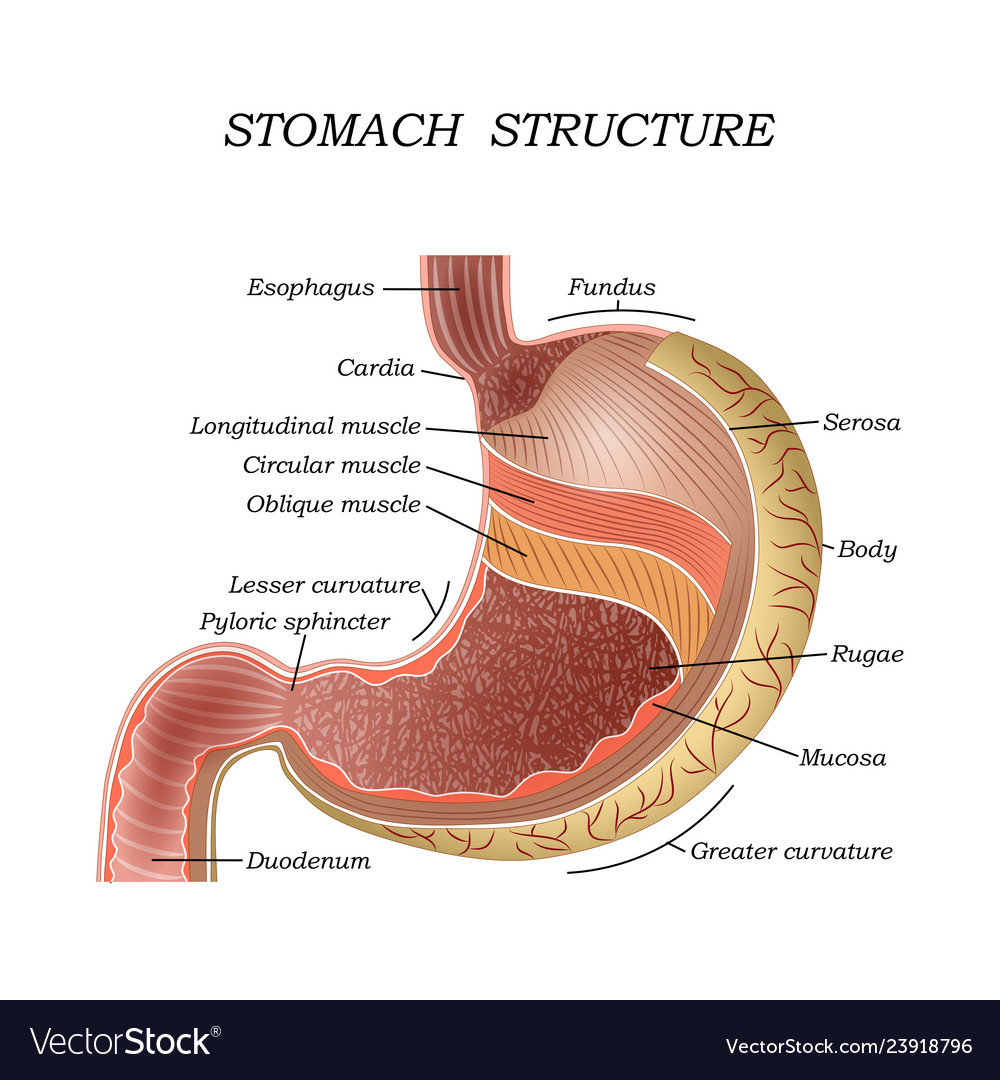
The structure of the human stomach Royalty Free Vector Image
Overview The digestive system is made up of the gastrointestinal tract-mouth, esophagus, stomach, small & large intestine, and rectum. What is the stomach? The stomach is a J-shaped organ that digests food. It produces enzymes (substances that create chemical reactions) and acids (digestive juices).

The Stomach Organs Parts, Anatomy, Functions of the Human Stomach
ISSN 2534-5079. This e-Anatomy illustrates the gross anatomy of the digestive system. We focused especially on the diagrams of the abdominal digestive system (oesophagus is described on the modules about the thorax and oral cavity/pharynx on the ENT modules). 84 anatomical diagrams and histological images with over 300 labeled anatomical parts.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11880/stomach-mucosa-and-muscular-layers_english.jpg)
Stomach Anatomy, function, blood supply and innervation Kenhub
The stomach is an important organ and the most dilated portion of the digestive system. The esophagus precedes it, and the small intestine follows. It is a large, muscular, and hollow organ allowing for a capacity to hold food. It is comprised of 4 main regions, the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus. The cardia is connected to the esophagus and is where the food first enters the stomach. The.
Human stomach diagram in detail 365742 Vector Art at Vecteezy
The innermost layer of the stomach wall is the gastric mucosa.It is formed by a layer of surface epithelium and an underlying lamina propria and muscularis mucosae. The surface epithelium is a simple columnar epithelium.It lines the inside of the stomach as surface mucous cells and forms numerous tiny invaginations, or gastric pits, which appear as millions of holes all throughout the stomach.

stomach model Google Search Anatomy models labeled, Anatomy models, Human anatomy and physiology
1/4 Synonyms: Ventriculus The stomach is an organ of the digestive system, specialized in the accumulation and digestion of food. Its anatomy is quite complex; it consists of four parts, two curvatures and receives its blood supply mainly from the celiac trunk. Innervation is provided via the vagus nerves and the celiac plexus .