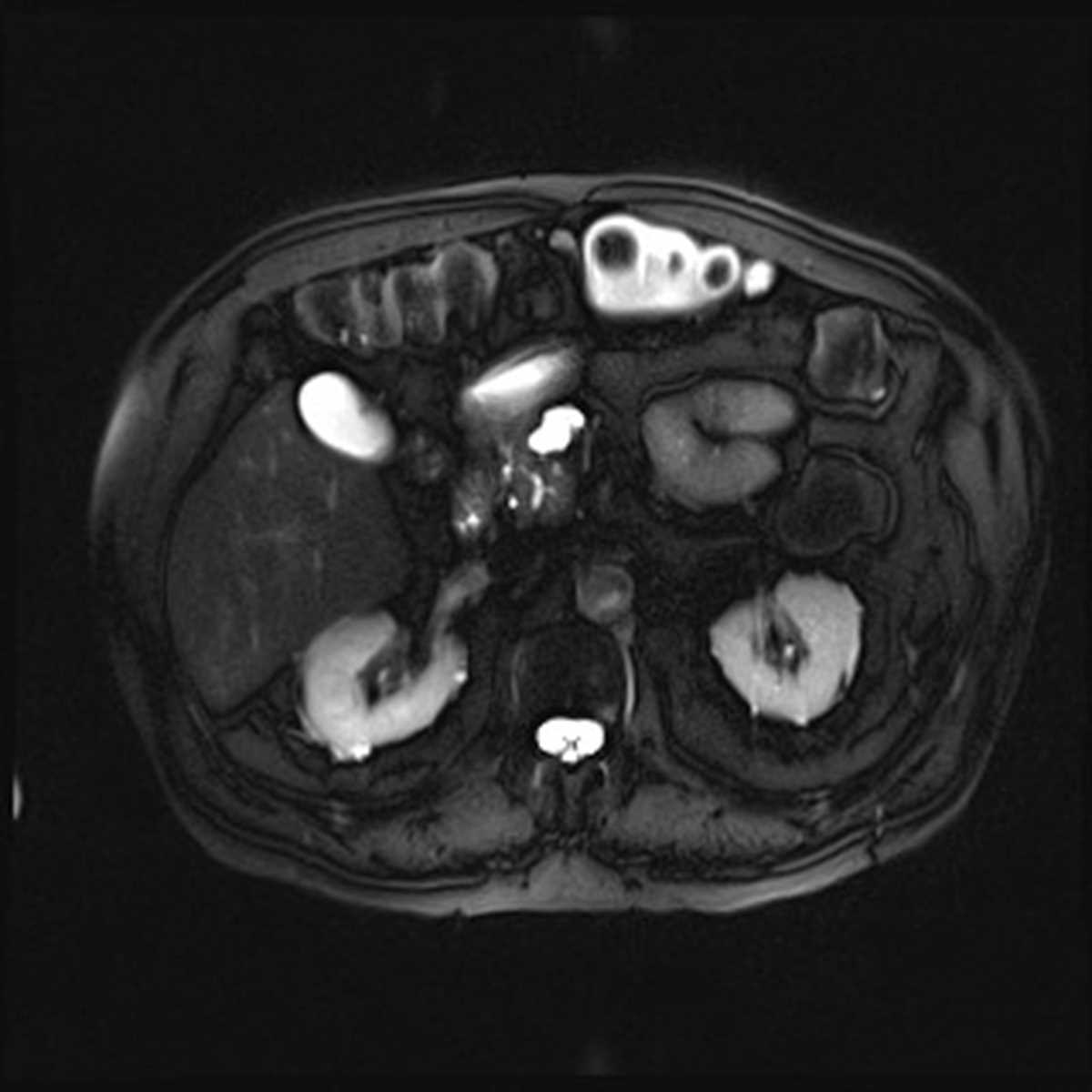
Sidebranch Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) Body MR Case Studies CTisus CT
Objectives Current guidelines base the management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN) on several well-established resection criteria (RC), including cyst size. However, malignancy may occur in small cysts. Since branch-duct (BD) IPMN are not perfect spheres, volumetric and morphologic analysis might better correlate with mucin production and grade of dysplasia. Nonetheless.
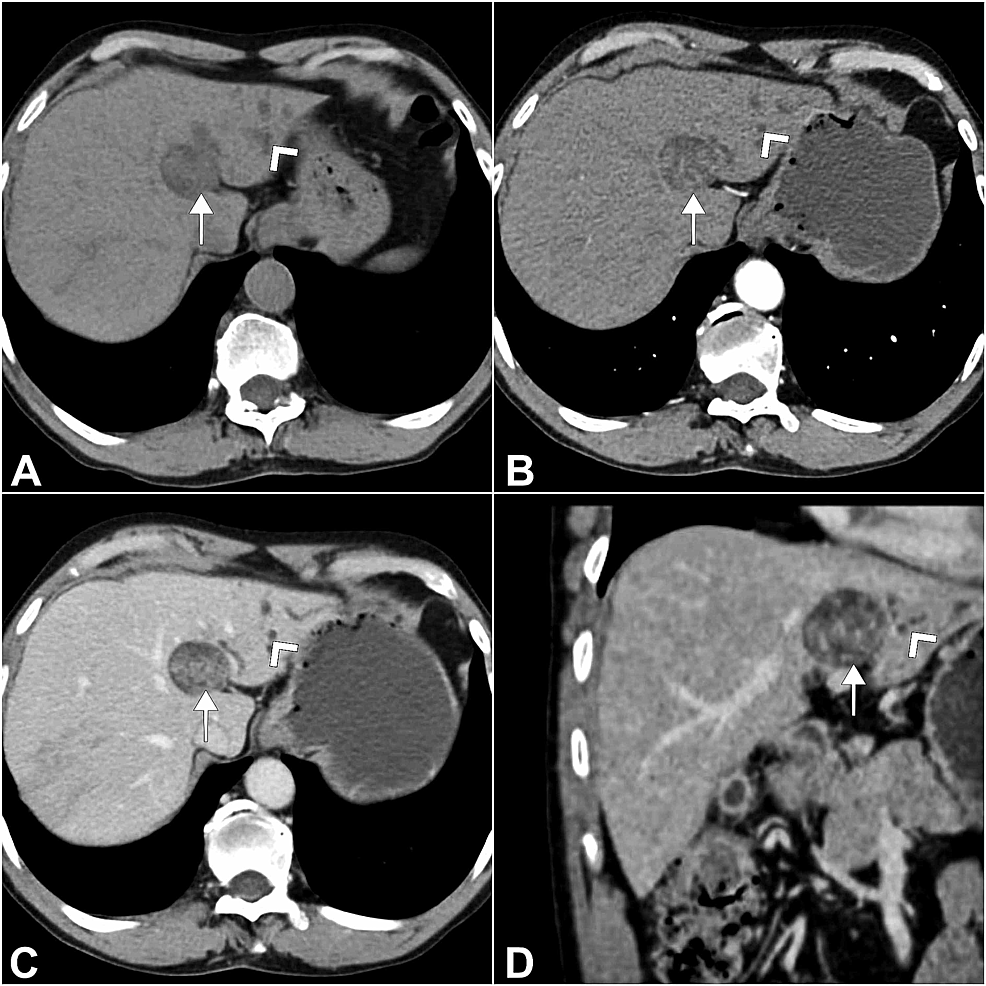
Cureus Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of the Bile Duct A Rare Case of Intrahepatic Space
Introduction. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) of the pancreas is a fascinating entity caused by proliferation of mucin-producing neoplastic epithelia and characterized by cystic or saccular dilation of the branch duct (BD-IPMN) and/or main duct (MD-IPMN) ().IPMN with macroscopic features of both BD-IPMN and MD-IPMN is called mixed type at present (Figure 1A-C).

A Case of HighGrade Panin (Carcinoma In Situ) with Intraductal Papillary Mucinous
There have been many publications detailing imaging features of malignant transformation of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN), management and recommendations for imaging follow-up of diagnosed or presumed IPMN. However, there is no consensus on several practical aspects of imaging IPMN that could serve as a clinical guide for radiologists and enable future data mining for.
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms Radiology Key
Mucin-producing intraductal papillary neoplasm (adenocarcinoma/adenoma) in the bile duct is becoming recognized as a specific type of neoplasm. Since, it bears a striking similarity to intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas with regard to its histopathologic features, the term "intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the bile duct" (IPMN-B) is frequently used.
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) Radiology Key
Terminology. Biliary papillary adenoma and non-invasive papillary carcinoma of the biliary tract were terms used to refer to localized low-grade and high-grade intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile ducts 1.Whereas biliary papillomatosis was used to describe what is now known as diffuse intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile ducts 1..
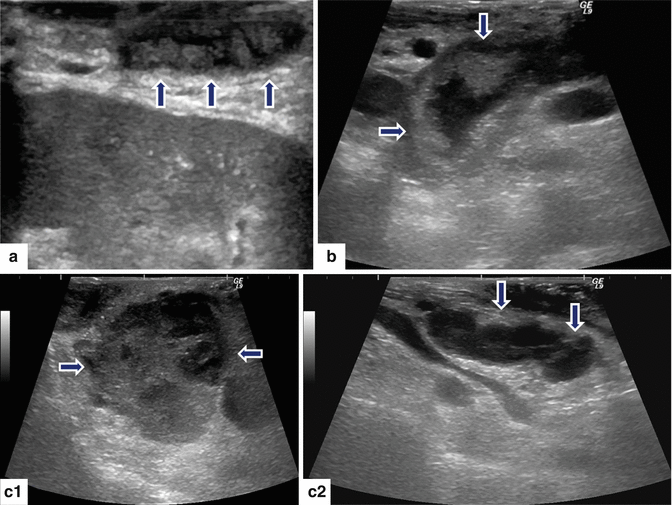
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) Radiology Key
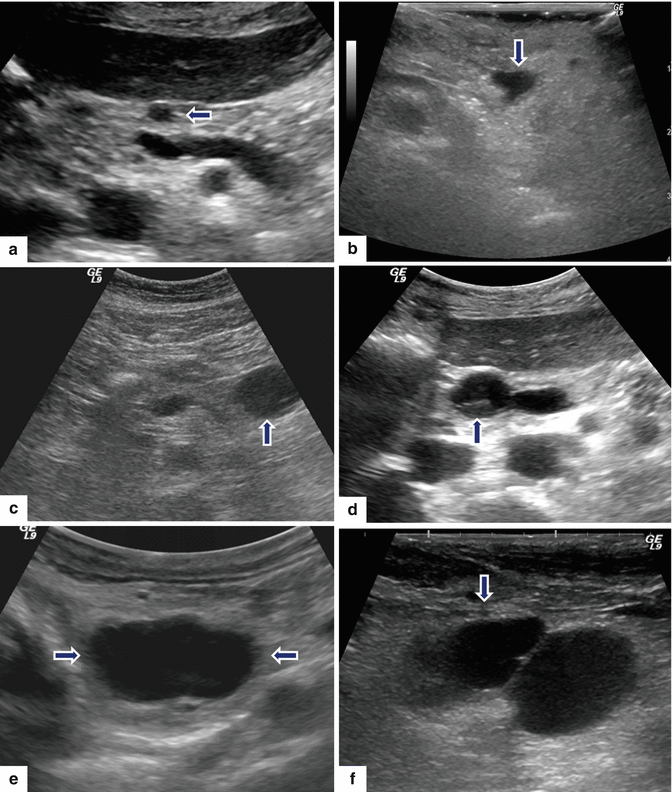
IPMN gross appearance. Intraoperative photographs with proven diagnosis of IPMNs demonstrate: a: a tortuous mass of multiple, small cysts in the body of the pancreas (arrows). b: a large, unilocular mass in the head of the pancreas adjacent to the duodenum (arrows).Photographs of a surgical specimen from a Whipple procedure (c) demonstrates a multilobulated mass in the head of the pancreas.

Mixed Type Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) With Moderate Grade Dysplasia / CTisus
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN) are common and one of the main precursor lesions of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). PDAC derived from an IPMN is called intraductal papillary mucinous carcinoma (IPMC) and defines a subgroup of patients with ill-defined specificities. As compared to conventional PDAC, IPMCs have been.

Lessons learned from hepatocellular carcinoma may cause a paradigm shift in intraductal
IPMNs have cysts filled with a jelly-like substance called mucin. When benign cystic tumors become cancerous, they secrete more mucin. Mucin can block your pancreatic ducts. The ducts are tiny tubes that help you digest food. Blocked ducts can cause pancreatitis, a painful condition that may be a symptom of an intraductal papillary mucinous.

Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the intrahepatic bile ducts a case report and
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms are one of a number of mucinous tumors of the pancreas and can be further divided both histologically and with respect to their macroscopic appearance 5. They are uncommon ductal epithelial tumors comprising 10-15% of cystic pancreatic neoplasms. Location. Reported locations of IPMN include 15: head ~50%.

Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) Radiology Key
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a grossly visible noninvasive mucinous epithelial neoplasm arising from main pancreatic duct or branch ducts. Menu. Chapters By Subspecialty . Autopsy & forensics; Bone, joints & soft tissue . Bone & joints;. Radiology description. CT:

Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas Image
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the biliary tract (B-IPMN) is an intraductal growing mucin producing tumor that is precursor of cholangiocarcinoma. Dilation of both upstream and downstream biliary ducts is the radiological key feature that is respectively caused by intraductal obstructive growth and massive mucin production.
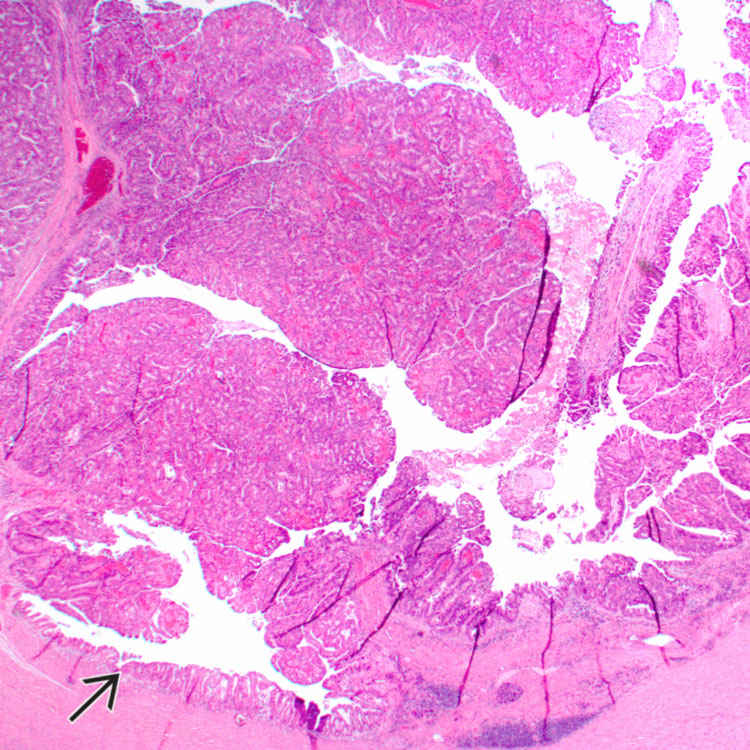
Intraductal Oncocytic Papillary Neoplasm Basicmedical Key
OBJECTIVE. We outline the concept of intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct (IPNB), discuss the morphologic features of IPNB and the differential diagnoses, and describe the radiologic approaches used in multidisciplinary management. CONCLUSION. The concept of IPNB has been evolving. Because the imaging features of IPNB can be variable, different mimickers according to IPNB subtype.
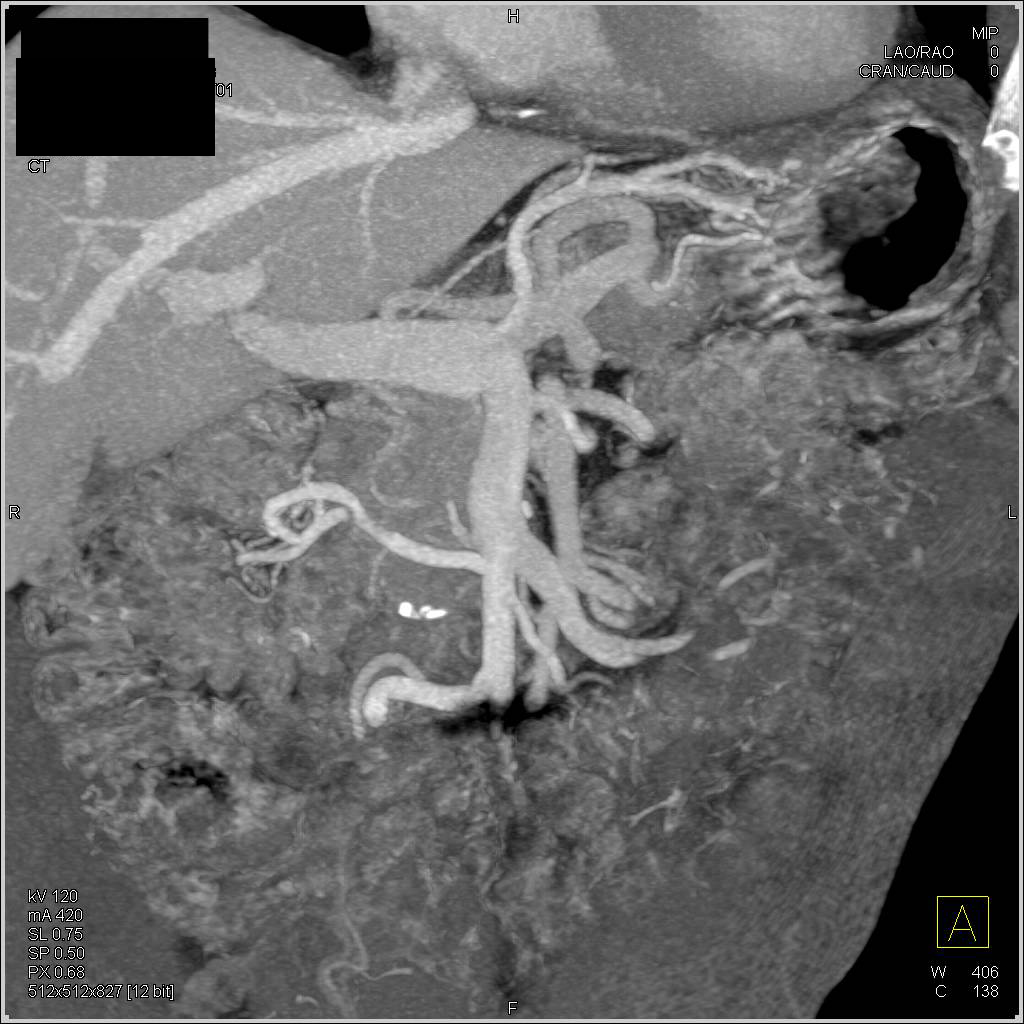
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) Pancreas Case Studies CTisus CT Scanning
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) are a group of exocrine mucin-producing tumors, diagnosed at a mean age of 60 years, with male prevalence [1, 2].Improvements in imaging techniques have led to an increasing incidental detection of IPMNs: in several studies, the prevalence of incidental cystic pancreatic lesions can be up to 19.6%, with MRI being the most sensitive imaging.
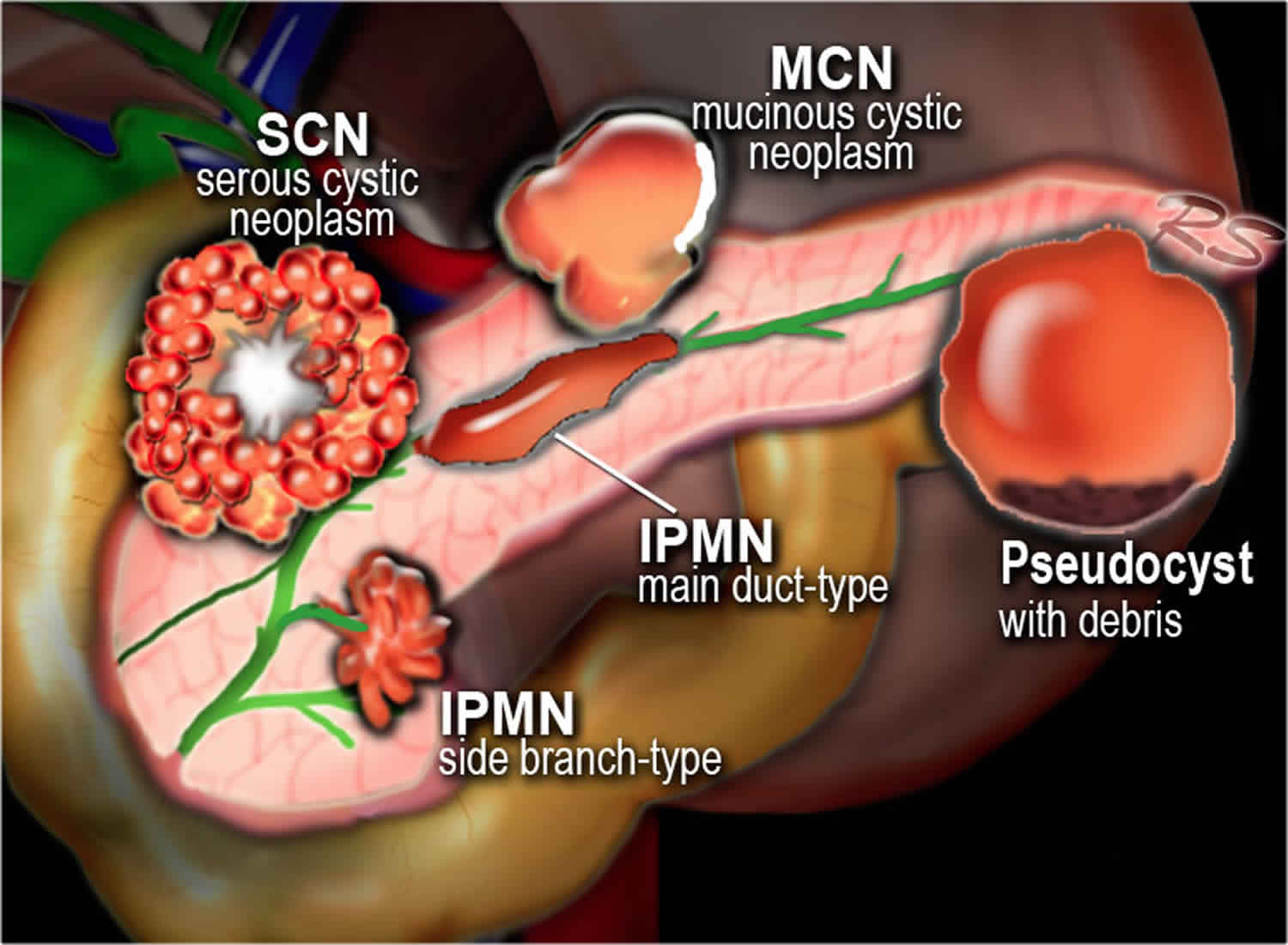
Mucinous cystic neoplasm pancreas causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) have become a very common diagnosis and represent a spectrum of disease that ranges from benign to ma…
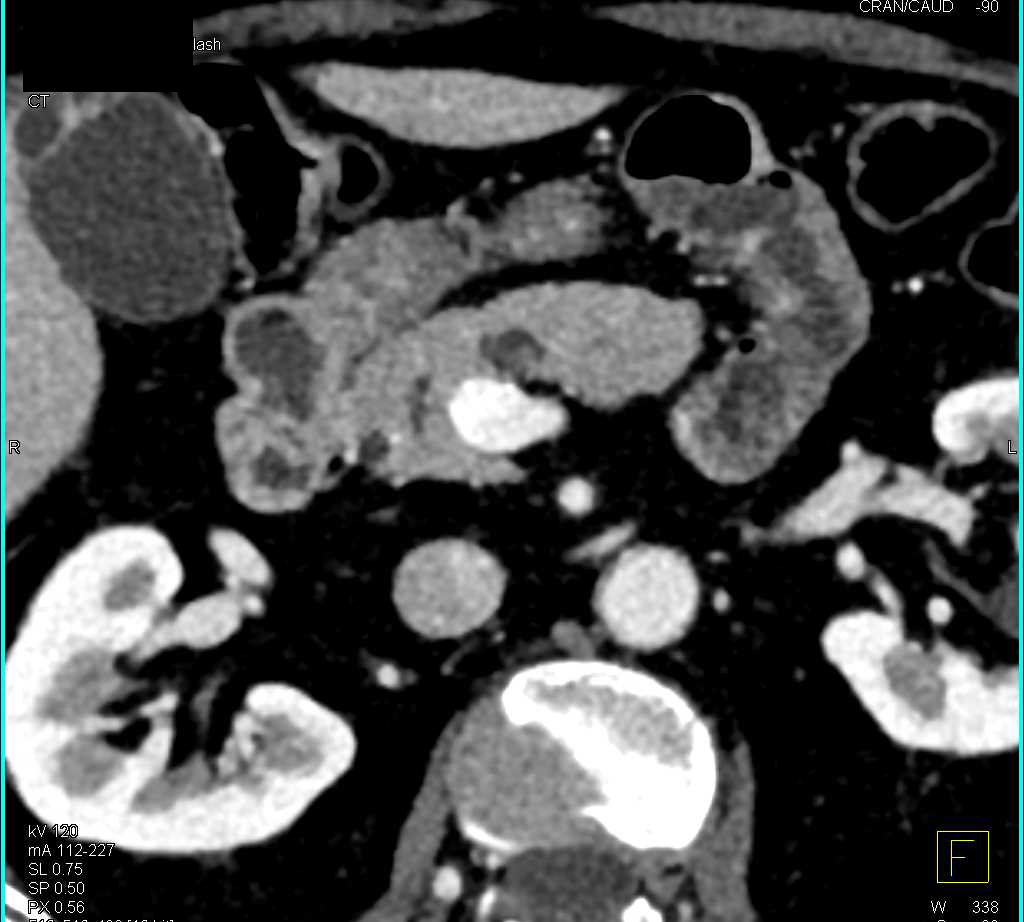
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) with a Small Nodule in the Cystic Lesion
Background Several changes have been made to the revised 2017 international consensus guidelines for management of pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs). However, the diagnostic performance is yet to be verified. Purpose To evaluate the revised guidelines for predicting malignant potential of pancreatic IPMNs and to compare diagnostic performance and intermodality.

Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm Radiology Case
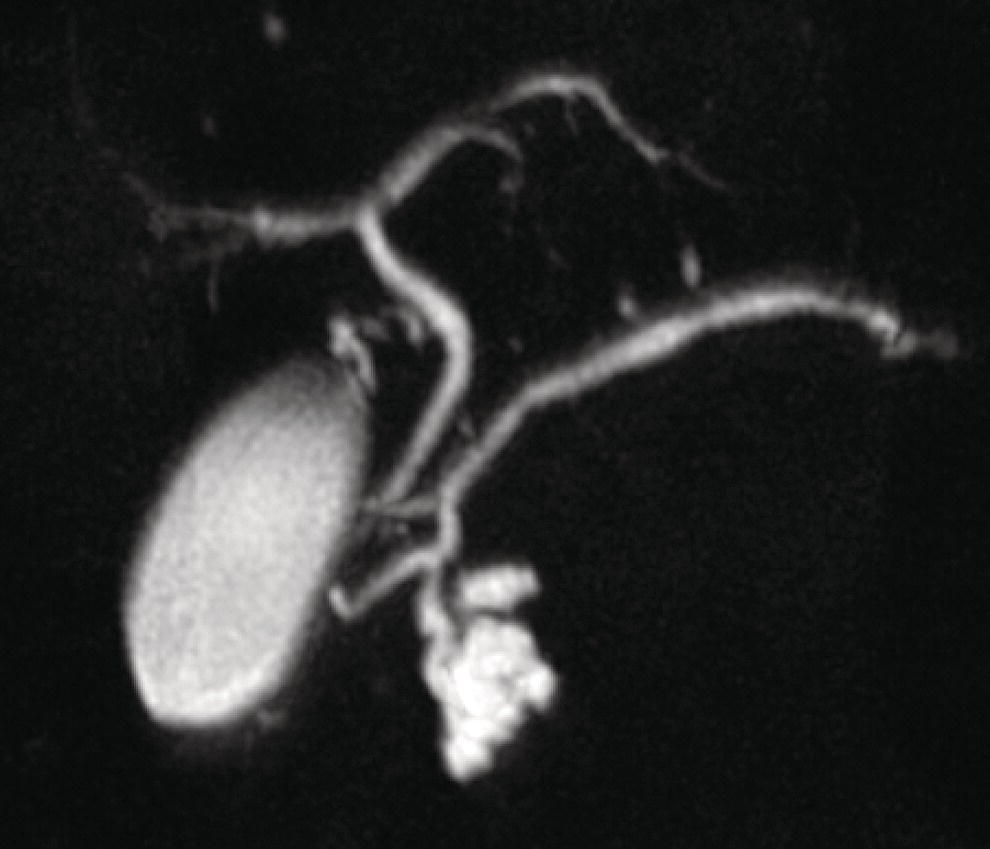
Figure 26.2 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography demonstrating a side‐branch intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm in the head of the pancreas. Endoscopic ultrasound evaluation It is also helpful in cases where surgical risk is high, and verification of malignancy is needed before resection, such as in older patients or those with.