
Foot Anatomy 101 A Quick Lesson From a New Hampshire Podiatrist Nagy
The foot is a part of vertebrate anatomy which serves the purpose of supporting the animal's weight and allowing for locomotion on land. In humans, the foot is one of the most complex structures in the body. It is made up of over 100 moving parts - bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments designed to allow the foot to balance the body's.

Diagrams of Foot 101 Diagrams
Foot Pain Identifier. footEducation.com was created by orthopaedic surgeons to provide patients and medical. providers with current and accurate information on foot and ankle conditions and their. treatments. The contributors to this site are all board certified orthopaedic surgeons who. specialize in treating patients with foot and ankle problems.

Sulcus
Listed below are 3 common areas of pain in the foot and their causes: Pain in the ball of the foot. Pain in the ball of the foot, located on the bottom of the foot behind the toes, may be caused by nerve or joint damage in that area. In addition, a benign (noncancerous) growth, such as Morton's neuroma, may cause the pain.

Diagram Of A Human Foot Human Foot Diagram Anatomy Organ Anatomy
Regions of the Foot. The foot is traditionally divided into three regions: the hindfoot, the midfoot, and the forefoot (Figure 2).Additionally, the lower leg often refers to the area between the knee and the ankle and this area is critical to the functioning of the foot.. The Hindfoot begins at the ankle joint and stops at the transverse tarsal joint (a combination of the talonavicular and.

Diagram Of Your Foot
Peripheral neuropathy can cause pain on the bottom of the foot paired with tingling or burning, and so on. Finding the cause of bottom-of-the-foot pain may include a physical exam and X-rays or other imaging. Treatment may involve pain relief, lifestyle changes, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgery. 18 Sources.

Diagram Of Your Foot
Bottom Of Foot Pain Diagram. This foot pain diagram looks at the common causes of pain under the foot and at the back of the heel. A. Heel Spurs. A bone spur here is called an inferior calcaneal bone spur and is usually linked with a tight plantar fascia. Causes a sharp pain under the foot that is worse with initial movement then eases to a.

Cutaneous afferent innervation of the human foot sole what can we
Tarsals. The tarsals are a group of seven bones close to the ankle. The proximal tarsal bones are the talus and the calcaneus, which is the largest bone of the foot. The talus is on top of the.
Anatomy The Bones Of The Foot
Foot. The foot is the lowermost point of the human leg. The foot's shape, along with the body's natural balance-keeping systems, make humans capable of not only walking, but also running.

Anatomy Of The Foot Bottom Anatomy Of The Bottom Of The Foot Human
Foot Pain Chart - Bottom of the foot. Bottom of the Heel: Fat Pad Atrophy - changes in the thickness of the fatty tissue protecting the heel bone. Spring Ligament Injury - a ligament spanning the bottom of the foot that plays a vital role alongside the Plantar Fascia to provide structural integrity to the foot.

Medial Muscles And Bones Of The Foot Sole Labeled Human Anatomy Diagram
The 20-plus muscles in the foot help enable movement, while also giving the foot its shape. Like the fingers, the toes have flexor and extensor muscles that power their movement and play a large.
Muscles that lift the Arches of the Feet
Summary. The foot is an intricate part of the body, consisting of 26 bones, 33 joints, 107 ligaments, and 19 muscles. Scientists group the bones of the foot into the phalanges, tarsal bones, and.
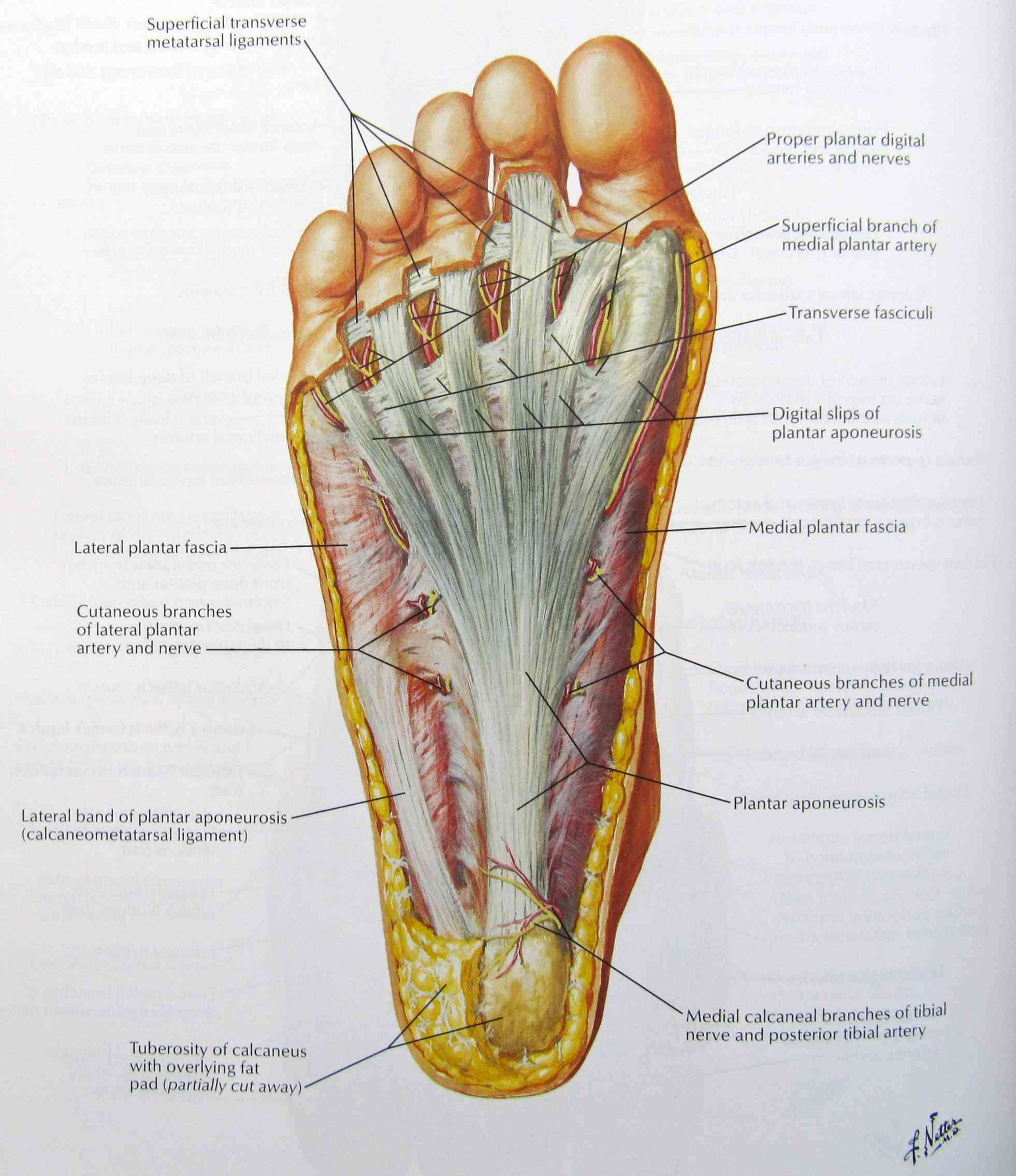
Bottom Of Foot Diagram Visual Diagram
The foot can be divided into three regions, the hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. F oot Bones Labeled Diagra m. Names of the Bones in the Foot With Basic Anatomy Tarsal Bones. The tarsals are a group of 7 irregular bones forming the hindfoot and the midfoot. These bones are arranged in two rows, proximal and distal.

What Is Turf Toe?
The navicular bone is found on the inner side of the foot. The navicular articulates with five of the other tarsal bones - at the top with the talus, talonavicular joint, laterally (outer side) with the cuboid, cubonavicular joint, and at the bottom it articulates with the three cuneiform bones. In around 10% of the population, a small extra piece of bone develops next to the navicular which.

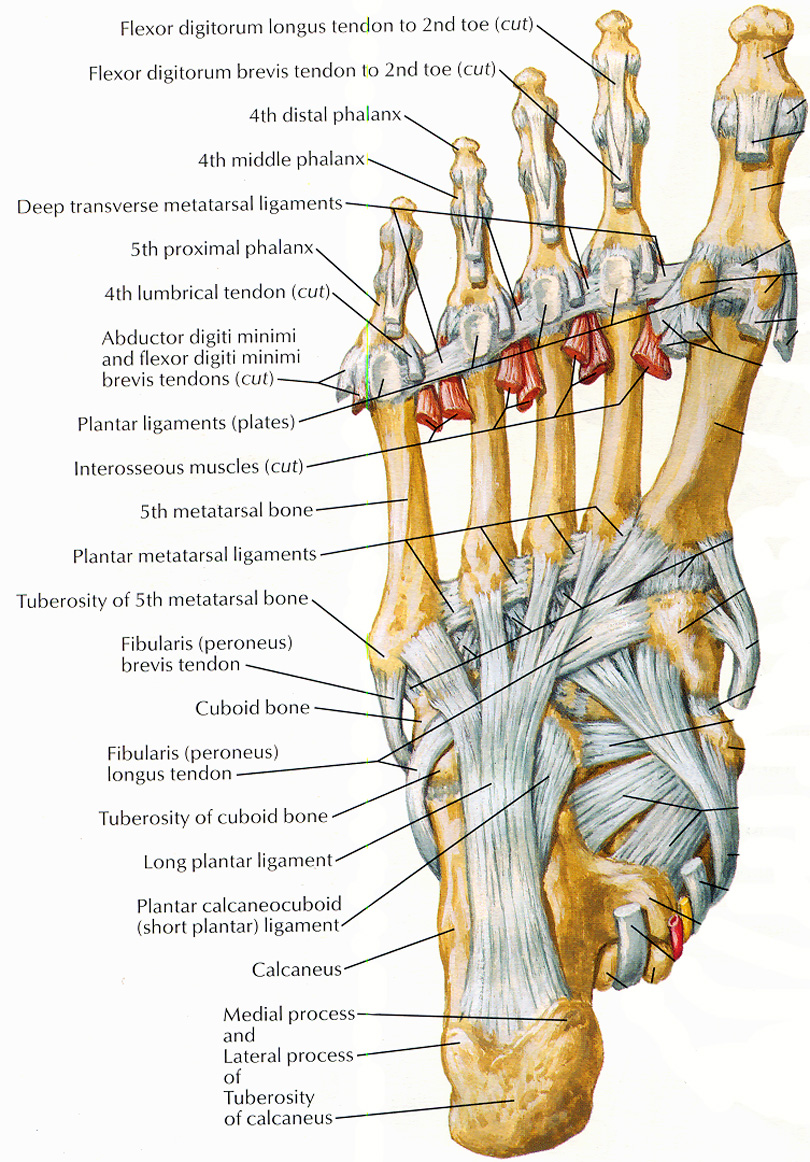
Bones of foot plantar view Diagram Quizlet
The muscles of the foot are located mainly in the sole of the foot and divided into a central (medial) group and a group on either side (lateral). The muscles at the top of the foot fan out to supply the individual toes. The tendons in the foot are thick bands that connect muscles to bones. When the muscles tighten (contract) they pull on the.
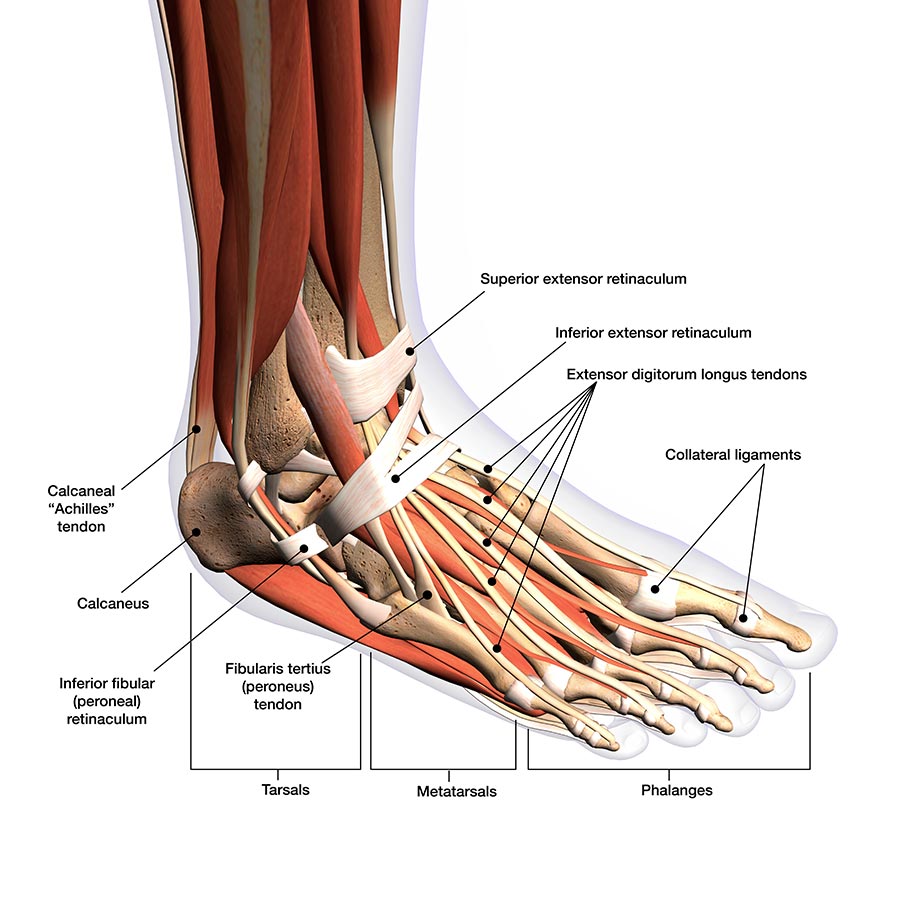
Foot and ankle anatomy, conditions and treatments
The Toes, Arch and Heel. Toes are the parts of the foot that allow people to move. They help people grip the ground and push off when they walk or run. The arch is the part of the foot that helps to absorb shock when we move around. It is located between the heel and the toes. The heel provides balance and stability.

Tendons of the Foot and Ankle TrialExhibits Inc.
The nerves of the leg and foot arise from spinal nerves connected to the spinal cord in the lower back and pelvis. As these nerves descend toward the thighs, they form two networks of crossed nerves known as the lumbar plexus and sacral plexus. The lumbar plexus forms in the lower back from the merger of spinal nerves L1 through L4 while the.