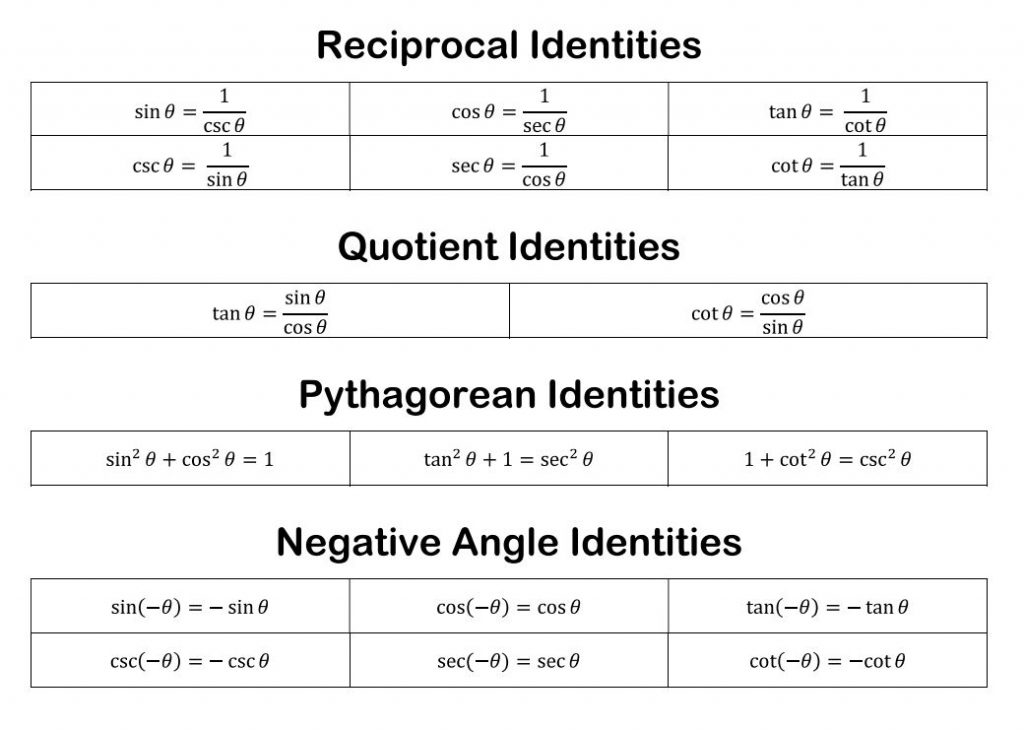
Calculus 1 trig cheat sheet peerrewa
You'll learn how to use trigonometric functions, their inverses, and various identities to solve and check equations and inequalities, and to model and analyze problems involving periodic motion, sound, light, and more. Inverse trigonometric functions Learn Intro to arcsine Intro to arctangent Intro to arccosine
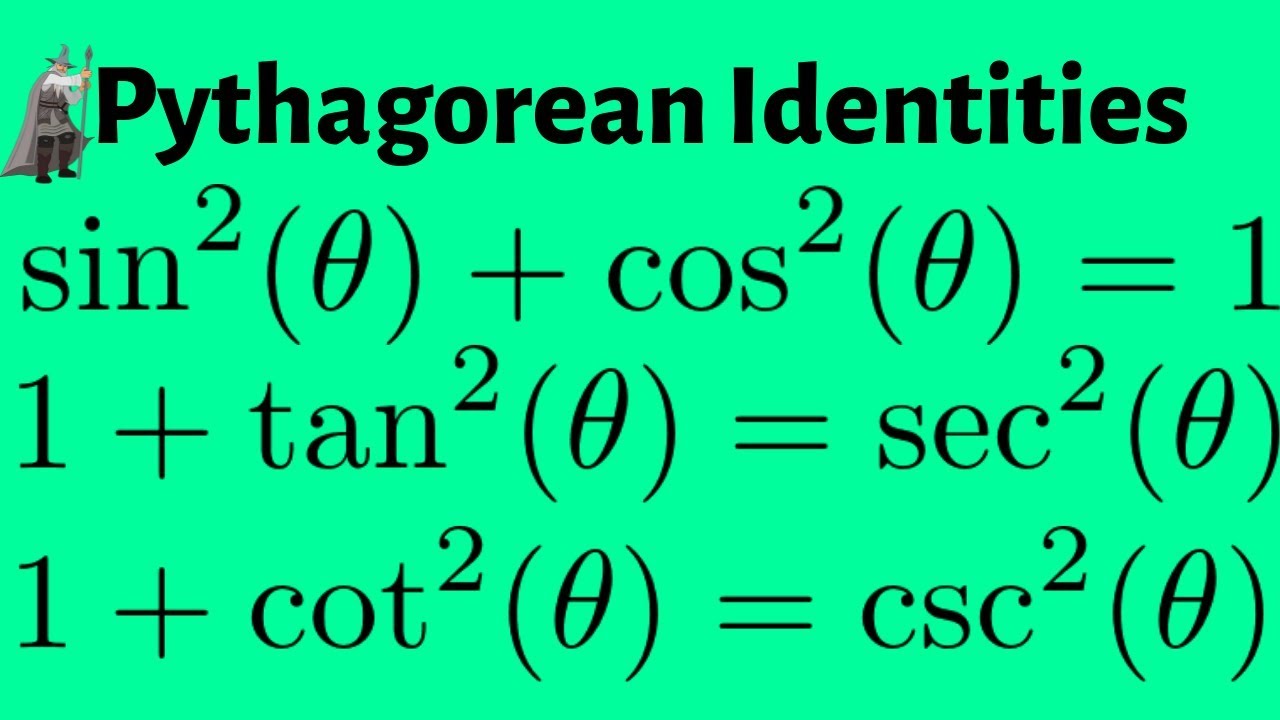
The Pythagorean Identities for Trigonometric Functions YouTube
Identities expressing trig functions in terms of their supplements. Sum, difference, and double angle formulas for tangent. The half angle formulas. The ones for sine and cosine take the positive or negative square root depending on the quadrant of the angle θ /2. For example, if θ /2 is an acute angle, then the positive root would be used.
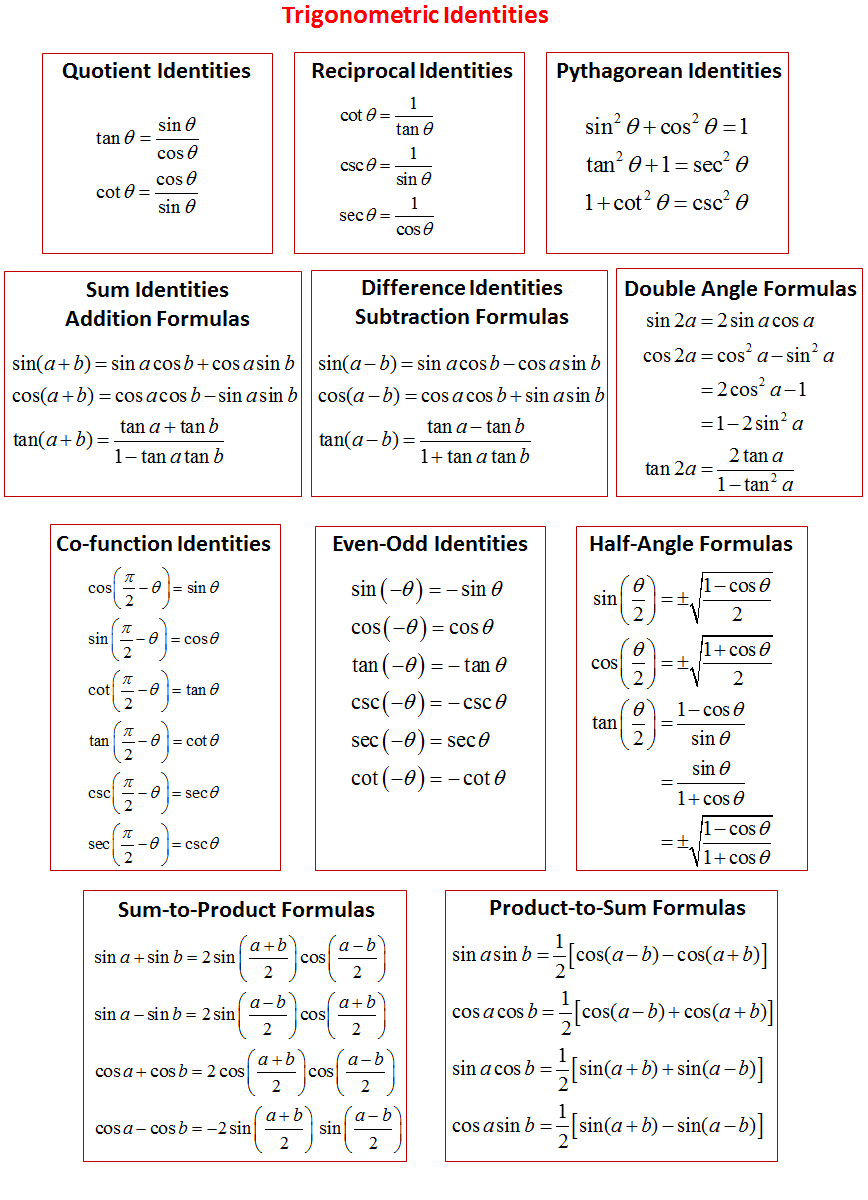
Trigonometric Identities (solutions, examples, videos)
21 Trig Identities Every Calculus Student Should Know! { 6. sin 1 = csc 2 1 csc cos 1 = sin . p 3 = sec Two Special Triangles sec = cos tan 7.{ 8. sin = cos cot 9. sin2 + cos2 10. 11. 12. sin( cos = sin 1 = cot 2 1 = tan = 1 (Pythagorean Identity) . 1 tan2 + 1 = sec2 cot2 1 = csc2 ) = sin 13. 14. sin( cos( cos

Trig Identities for PreCalculus dummies
Trig identities are trigonometry equations that are always true, and they're often used to solve trigonometry and geometry problems and understand various mathematical properties. Knowing key trig identities helps you remember and understand important mathematical principles and solve numerous math problems. The 25 Most Important Trig Identities
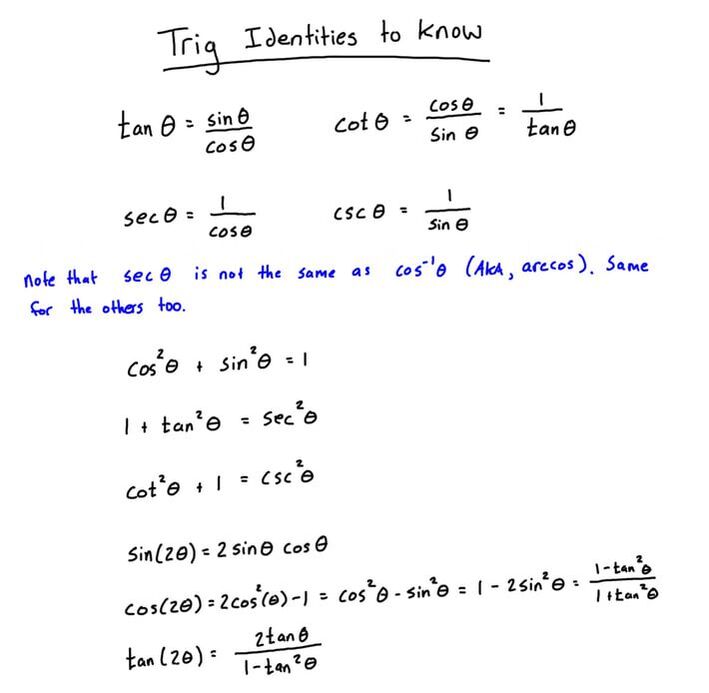
Integral Table and Trigonometric Identities Engineer4Free The 1
7 years ago. The easiest way is to see that cos 2φ = cos²φ - sin²φ = 2 cos²φ - 1 or 1 - 2sin²φ by the cosine double angle formula and the Pythagorean identity. Now substitute 2φ = θ into those last two equations and solve for sin θ/2 and cos θ/2.
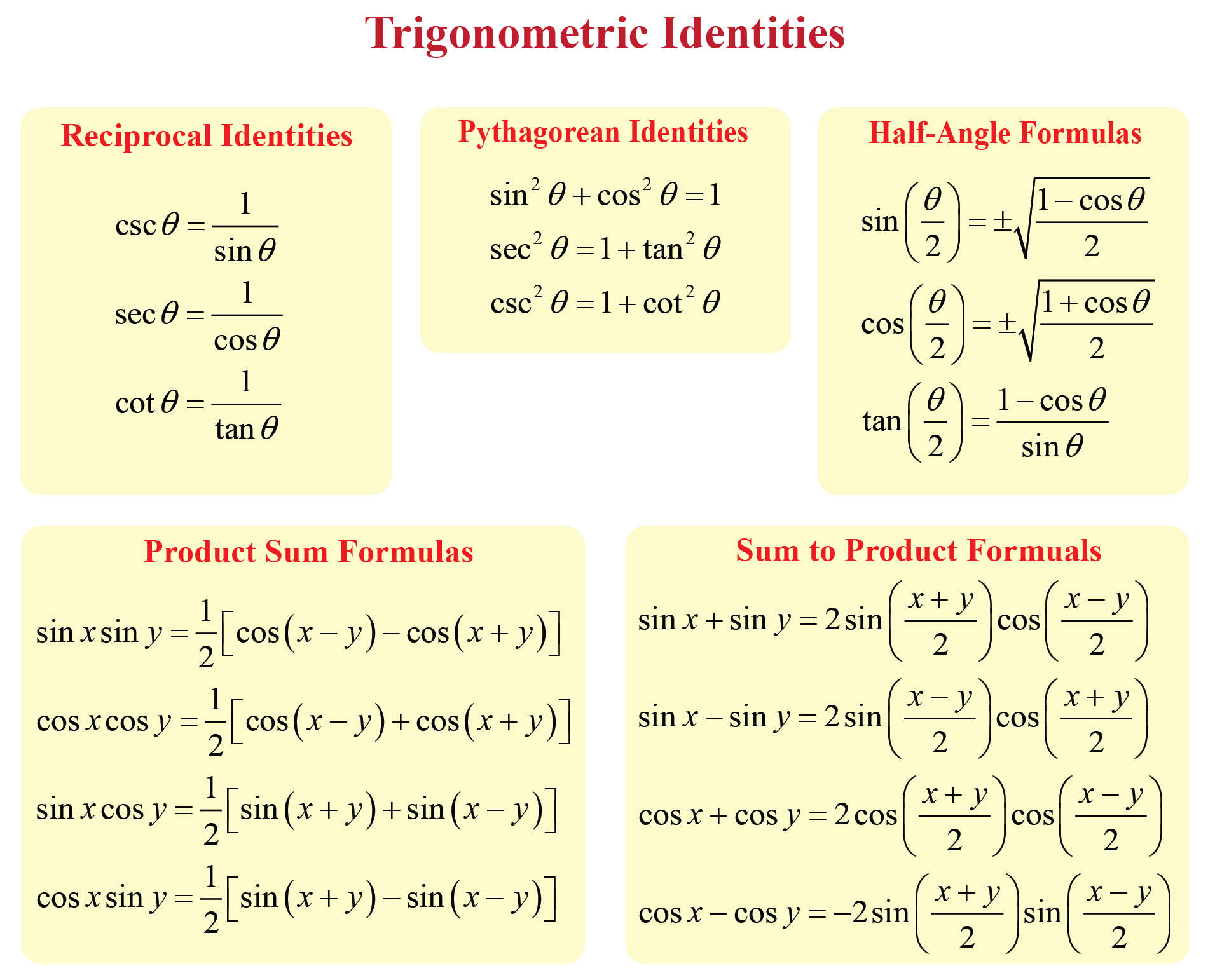
Trigonometric Formula Chart
The Essential Trigonometric Identities. Fortunately, you do not have to remember absolutely every identity from Trig class. Below is a list of what I would consider the essential identities. 1. Quotient Identities. The quotient identities are useful for re-expressing the trig functions in terms of sin and/or cos. 2.
Trigonometric Functions NEW Classroom Trig School Math POSTER
In our example of equation (1) we might begin with the expression tan2(x) + 1 tan 2 ( x) + 1. Example 4.1.1 4.1. 1: Verifying a Trigonometric Identity. To verify that equation (1) is an identity, we work with the expression tan2(x) + 1 tan 2 ( x) + 1. It can often be a good idea to write all of the trigonometric functions in terms of the cosine.

Proving Trigonometric Identities Calculator
Algebra (all content) 20 units · 412 skills. Unit 1 Introduction to algebra. Unit 2 Solving basic equations & inequalities (one variable, linear) Unit 3 Linear equations, functions, & graphs. Unit 4 Sequences. Unit 5 System of equations. Unit 6 Two-variable inequalities. Unit 7 Functions. Unit 8 Absolute value equations, functions, & inequalities.

Trig Identities Calculator Math Is Fun
Trigonometric identities are equations that are used to describe the many relationships that exist between the trigonometric functions. Among other uses, they can be helpful for simplifying trigonometric expressions and equations. The following shows some of the identities you may encounter in your study of trigonometry.

Trigonometric Identities Very Interesting
What are Trigonometric Identities? Trigonometric Identities are the equalities that involve trigonometry functions and holds true for all the values of variables given in the equation. There are various distinct trigonometric identities involving the side length as well as the angle of a triangle.
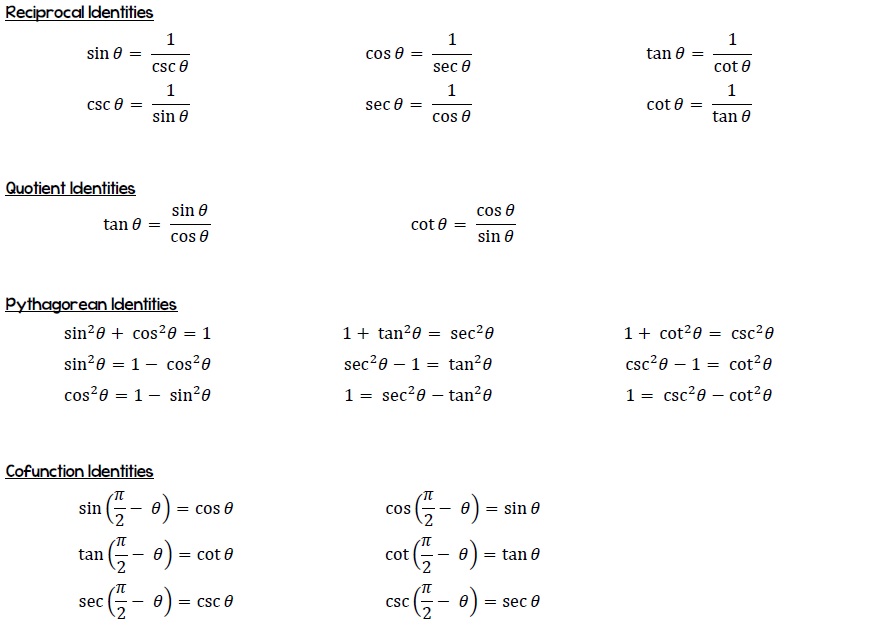
Trig Identities AP Calculus AB & BC
Free trigonometric identity calculator - verify trigonometric identities step-by-step

Trigonometric Values Chart Pdf
sin(π 2 − θ) = cos(π 2 − [π 2 − θ]) = cos(θ), which says, in words, that the 'co'sine of an angle is the sine of its 'co'mplement. Now that these identities have been established for cosine and sine, the remaining circular functions follow suit. The remaining proofs are left as exercises. Theorem 10.14.

Differentiation Rules Trig
In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. Geometrically, these are identities involving certain functions of one or more angles.

Lesson 5.1 Trigonometric Identities TRIG RIDGE STYLE
To sum up, only two of the trigonometric functions, cosine and secant, are even. The other four functions are odd, verifying the even-odd identities. The next set of fundamental identities is the set of reciprocal identities, which, as their name implies, relate trigonometric functions that are reciprocals of each other. (Table \(\PageIndex{3}\)).

Trig Identities Study Sheet
Trigonometric identities like sin²θ+cos²θ=1 can be used to rewrite expressions in a different, more convenient way. For example, (1-sin²θ) (cos²θ) can be rewritten as (cos²θ) (cos²θ), and then as cos⁴θ. Created by Sal Khan. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Top Voted E Man 9 years ago

Trig Identities Calc 2 slidesharetrick
TrigFormulas.dvi MATH 10560: CALCULUS II TRIGONOMETRIC FORMULAS Basic Identities The functions cos(θ) and sin(θ) are defined to be the x and y coordinates of the point at an angle of θ on the unit circle. Therefore, sin(−θ) = − sin(θ), cos(−θ) = cos(θ), and sin2(θ) + cos2(θ) = 1.