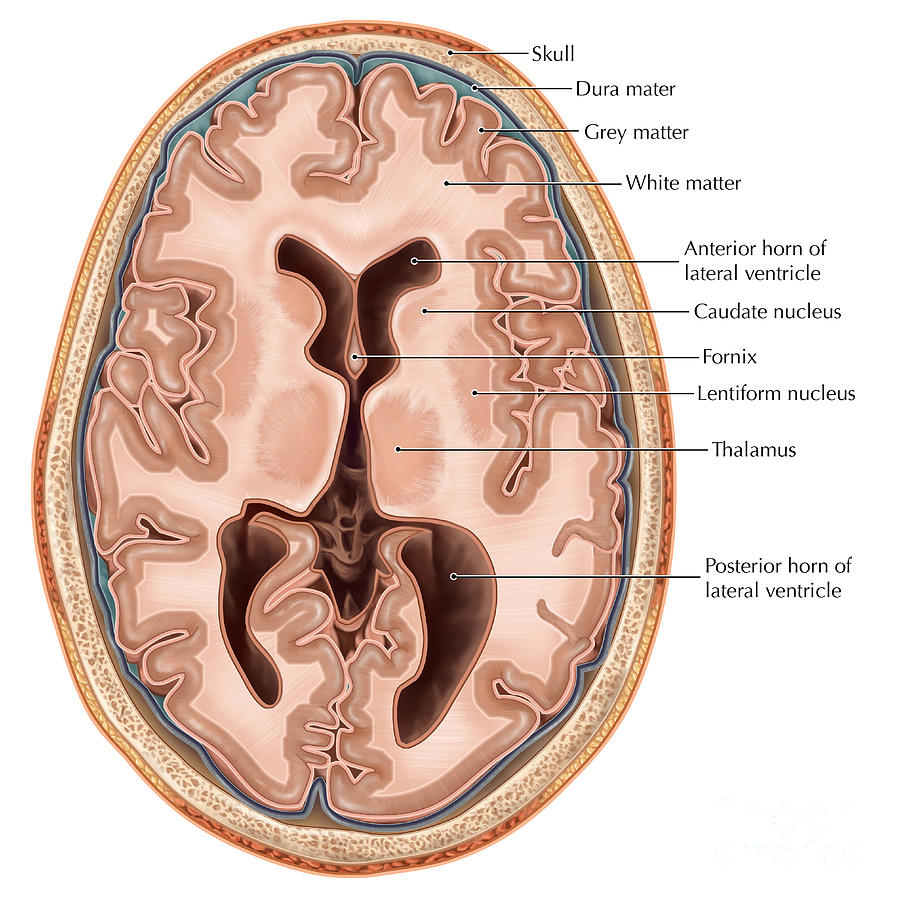
Transverse Section Of The Brain Photograph by Evan Oto Fine Art America
neocortex: The largest part of the cerebral cortex of the human brain, covering the two cerebral hemispheres.. Transverse section of a cerebellar folium, showing principal cell types and connections. The cerebellum is separated from the overlying cerebrum by a layer of leathery dura mater. Anatomists classify the cerebellum as part of the.
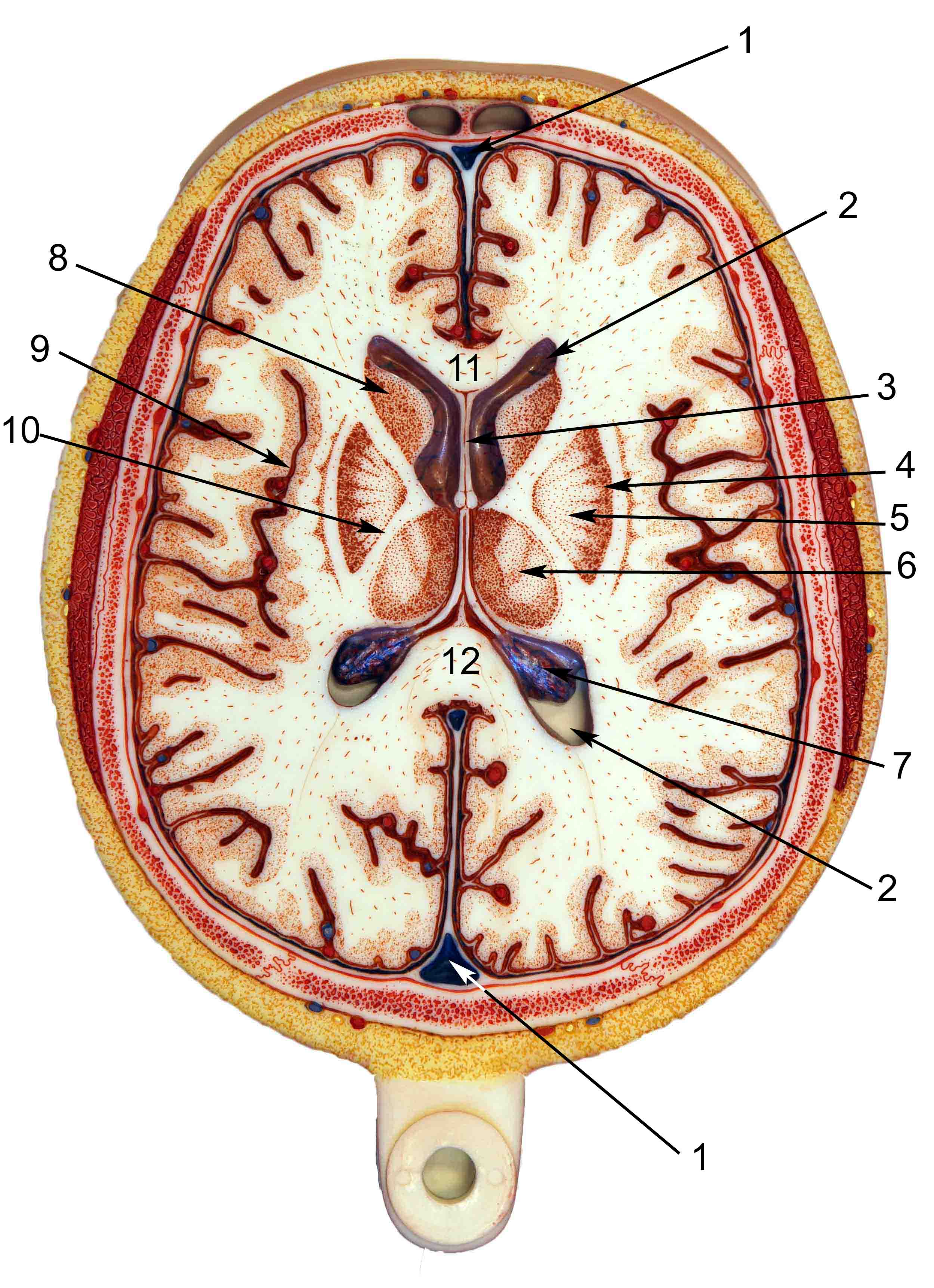
Transverse Section Of Brain Labelled slideshare
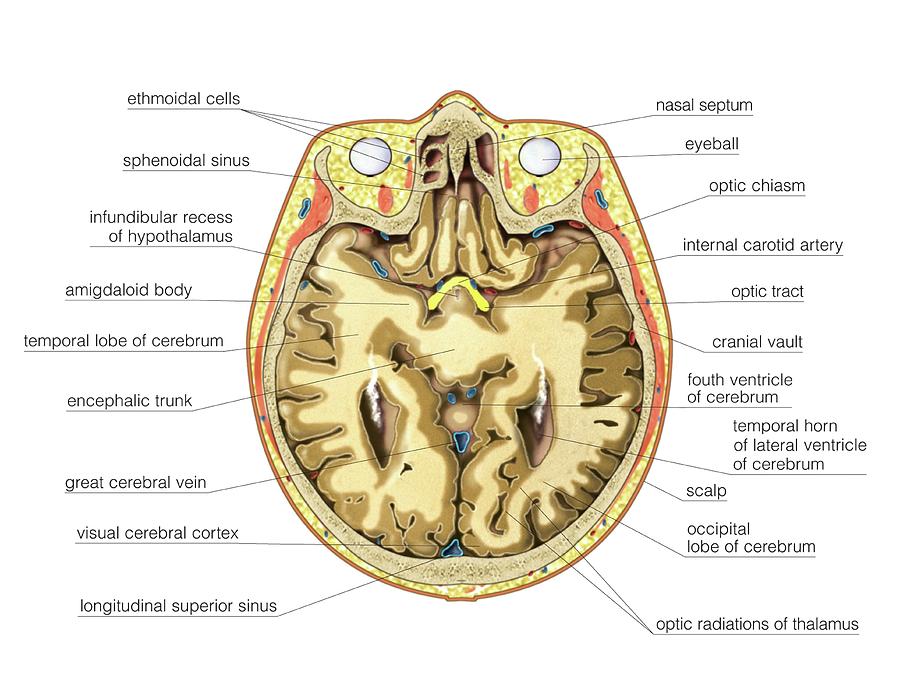
The brain is part of the central nervous system responsible for various functions, ranging from simple homeostasis to higher cognitive functions like critical thinking, memory etc. In order to appreciate the overall transverse anatomy of this organ, we'll examine an axial view through the thalamus.
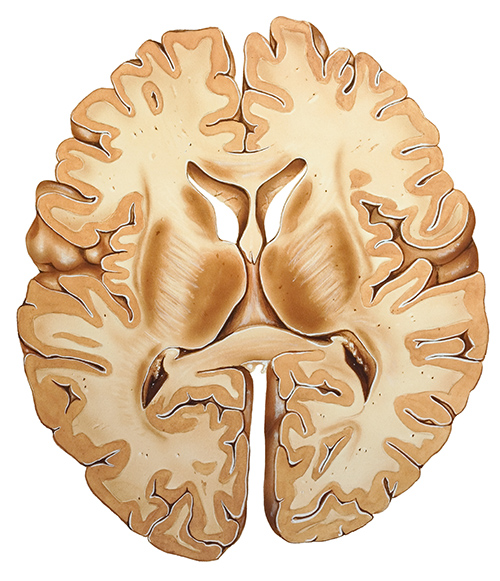
Sistema nervioso Central cerebro y médula espinal The Bay
Axial MRI Atlas of the Brain. Free online atlas with a comprehensive series of T1, contrast-enhanced T1, T2, T2*, FLAIR, Diffusion -weighted axial images from a normal humain brain. Scroll through the images with detailed labeling using our interactive interface. Perfect for clinicians, radiologists and residents reading brain MRI studies.

Transverse Section Of Brain Labelled slideshare
Welcome to Soton Brain Hub - the brain explained!Charlie is here to give you a basic tutorial on the main structures visible on a midline transverse (axial).

Human Brain Transverse Section Illustration Drawing Stock Illustration 2159805583 Shutterstock
A transverse plane, also known as an axial plane or cross-section, divides the body into cranial and caudal (head and tail) portions. A sagittal plane divides the body into sinister and dexter (left and right) portions. Body planes have several uses within the anatomy field, including in medical imaging, descriptions of body motion, and embryology.
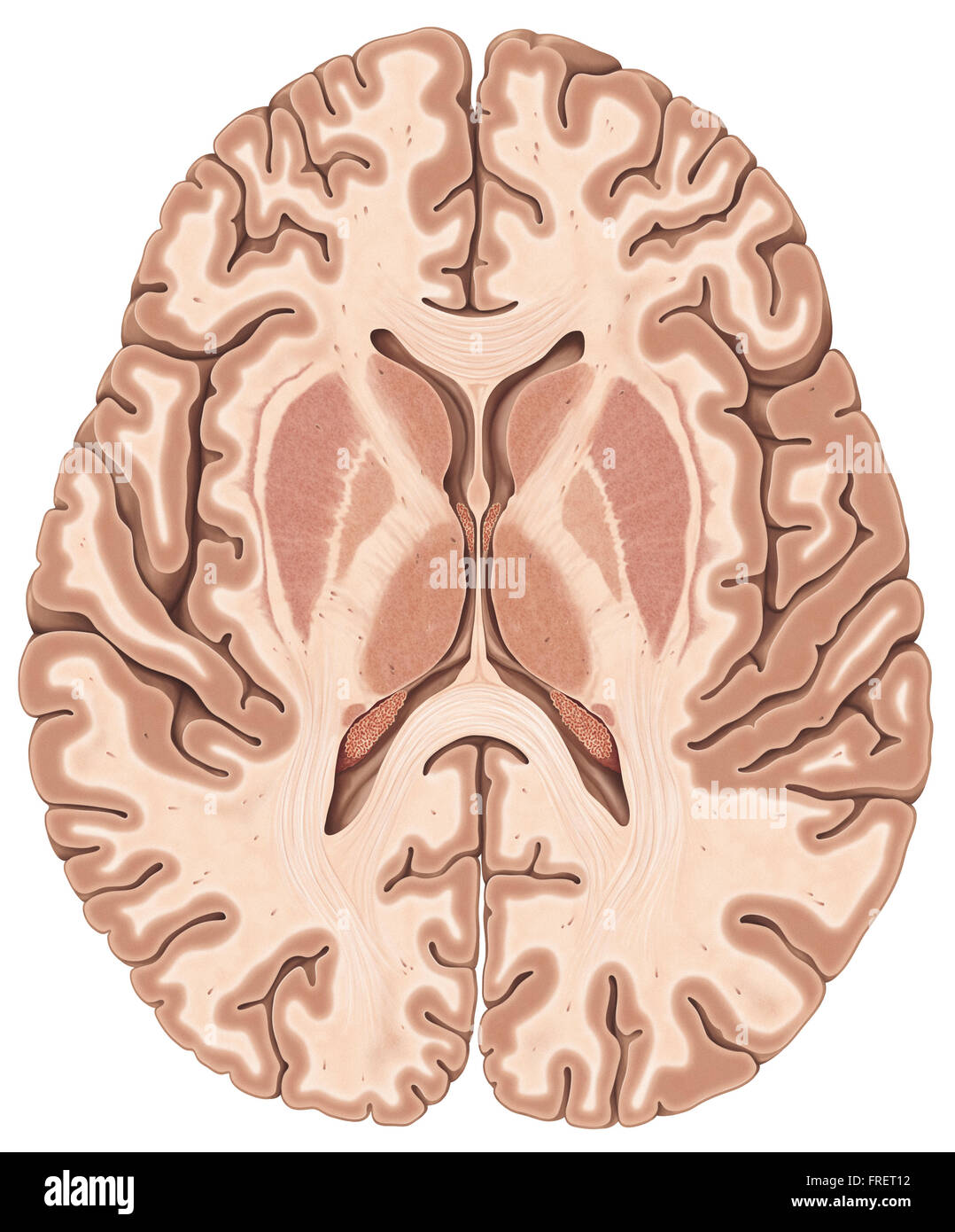
Transversesection illustration of the human brain Stock Photo Alamy
Your brain wants 3D. The human brain and mind thrives on complexity, colours and images to name a few. In other words, it loves anything that is coloured and in three dimensions. Similarly, it receives a constant stream of stimulations from a similarly elaborate 3D world.Humans automatically perceive things surrounding them in three axes: length, width/height and depth/thickness.
Transverse Section Of Brain Labelled slideshare
The brain and the spinal cord arise in early development from the neural tube, which expands in the front of the embryo to form the main three primary brain divisions: the prosencephalon (forebrain), mesencephalon (midbrain), and rhombencephalon (hindbrain) (fig. 1A).
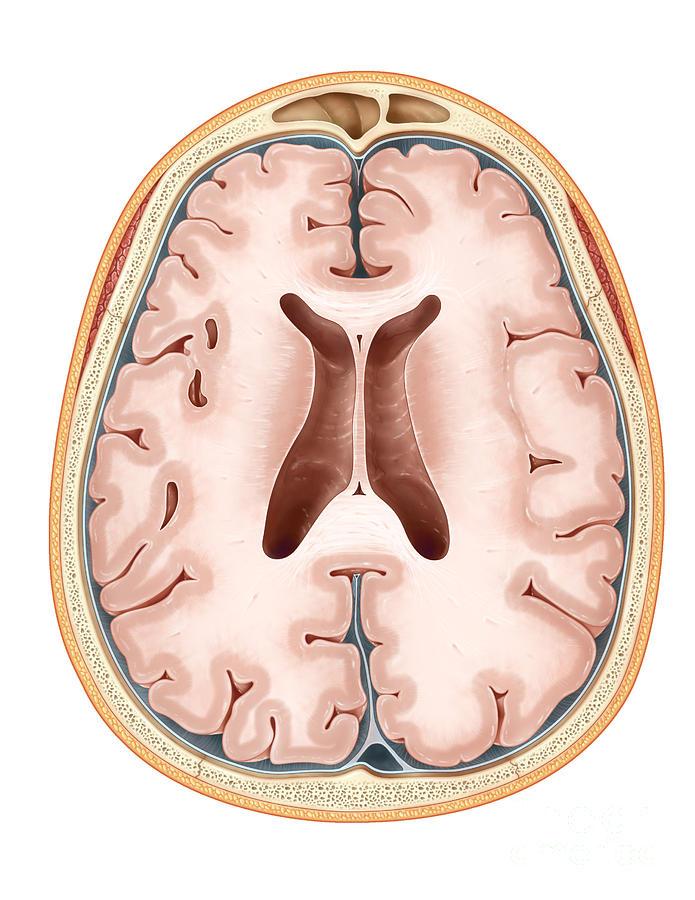
Brain, Transverse Section Photograph by Evan Oto Pixels
Sagittal section through the human head and neck. fig5.13. The section in Figure 5.13 is cut lateral to the midline in the location indicated on the insets of coronal and horizontal sections. After spending some time studying sectional views of the brain in isolation, it is worth recalling how the brain and spinal cord are related to the.

Transverse Sections of the Brainstem Neupsy Key
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum.

interpreting a transverse section through brain YouTube
Frontal lobes. At this level, the anterior portion of the section is occupied by the frontal lobes. The frontal lobes are located anterior to the central sulcus and superior to the lateral fissure. They occupy the anterior cranial fossa and are divided into four gyri by three sulci. Frontal lobe (lateral-left view)

Transverse section of the human brain Stock Image C005/5982 Science Photo Library
The midsagittal section of the brain shows the three major parts of the brain, which are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.The cerebrum (prosencephalon or forebrain) comprises the telencephalon (cerebral hemispheres) and the diencephalon.They are each also divided into subparts or regions for simplified localization of structures, for example, the brainstem is composed of the midbrain.

Transverse section of human brain Stock Image C005/5981 Science Photo Library
Neuroanatomy Video Lab: Brain Dissections -- This series of Neuroanatomy video lessons with brain dissections has two principal objectives. The first is to provide viewers access to human brain specimens, something lacking in many places. The second is to simplify the anatomy, omitting some details, and making numerous generalizations. This helps keep the focus on the localization of a patient.

Vertical transverse section of the human brain Stock Photo Alamy
Anatomy of the Ventricular System Figure 1. A. Midsagittal section of brain. B. Transverse section of midbrain. Figure 2. Midsagittal section of brain and skull showing flow of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). Figure 3. Midsagittal view showing the subarachnoid cisterns. Note: Lateral cerebellomedullary cisterns cannot be seen in this section.
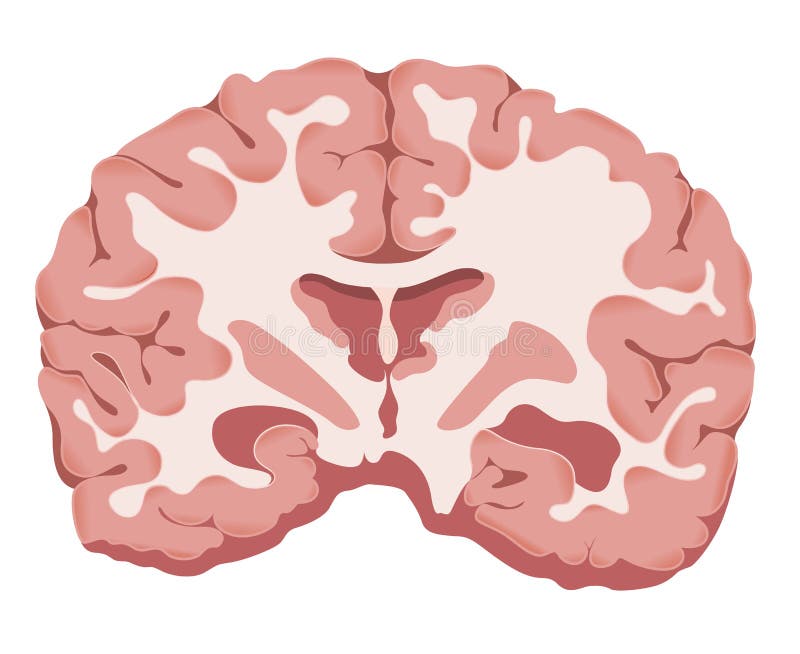
Brain Transverse Section Illustration Stock Vector Illustration of scanner, stroke 242359161
Summary Sources + Show all Level of the genu of the corpus callosum A coronal section of the head is viewed and interpreted from the point of view that the clinician is facing the patient. Therefore, the patient's left side will be on the physician's right side.

Neuromuscular The Rehabilitation Specialist's Handbook, 4e F.A. Davis PT Collection McGraw
Anatomy-Histology main menu. This tutorial has images in which the structures are labeled. You are to identify the structures by clicking on the name of the structure. The structure whose name is clicked will be identified in the image by an arrow.
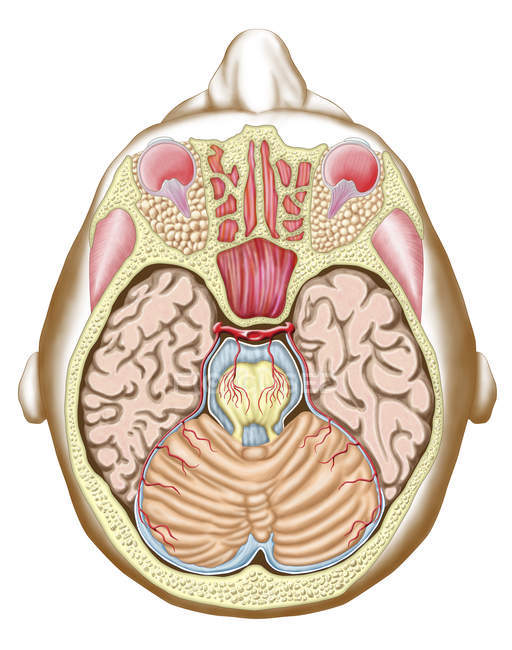
Medical illustration of the midbrain transverse section — structure, head Stock Photo 174713024
The atlas of myelin-stained sections through the central nervous system is in three planes: transverse, horizontal, and sagittal. (See Figure 1-17 for schematic views of these planes of sections.) Transverse sections through the cerebral hemispheres and diencephalon are termed coronal sections because they are approximately parallel to the coronal suture.