
Physiology Glossary Cardiac Performance (CO, SV, Preload, and Afterload) Draw It to Know It
Cardiac output is the amount of blood the heart pumps in 1 minute, and it is dependent on the heart rate, contractility, preload, and afterload. Understanding of the applicability and practical relevance of each of these four components is important when interpreting cardiac output values.

CVS physiology lecture 11 PRELOAD vs AFTERLOAD. YouTube
The systolic performance of the heart is determined by 3 factors: preload, afterload, and contractility. The direct relationship between preload and cardiac output was formulated in the early 1900s based on the work of Otto Frank and Ernest Starling. It led to the well-known Frank-Starling curves. Gordon et al. helped to elucidate the underlying mechanism for this phenomenon in their 1966.

Ventricular PressureVolume Relationship Preload, Afterload, Stroke Volume, Wall Stress & Frank
One of the really nice things about preload and afterload is that the two have so much in common. So if you're trying to figure out afterload, then remembering what preload is about is a really good idea because the definitions are so similar. So we have volume and pressure on this graph. I'm actually going to start by sketching out very.

PPT Cardiac Muscle Contraction PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6530818
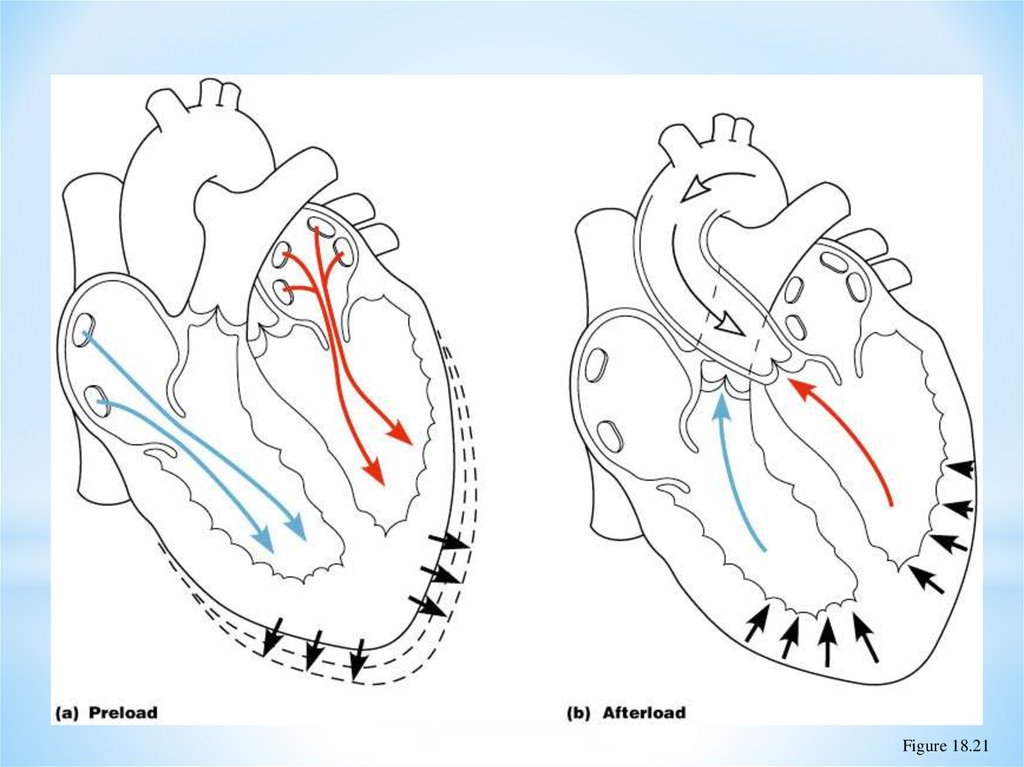
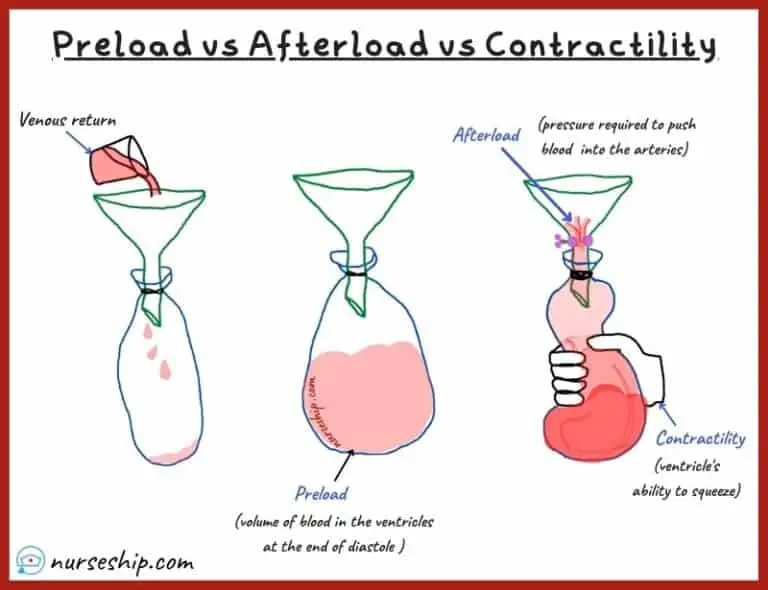
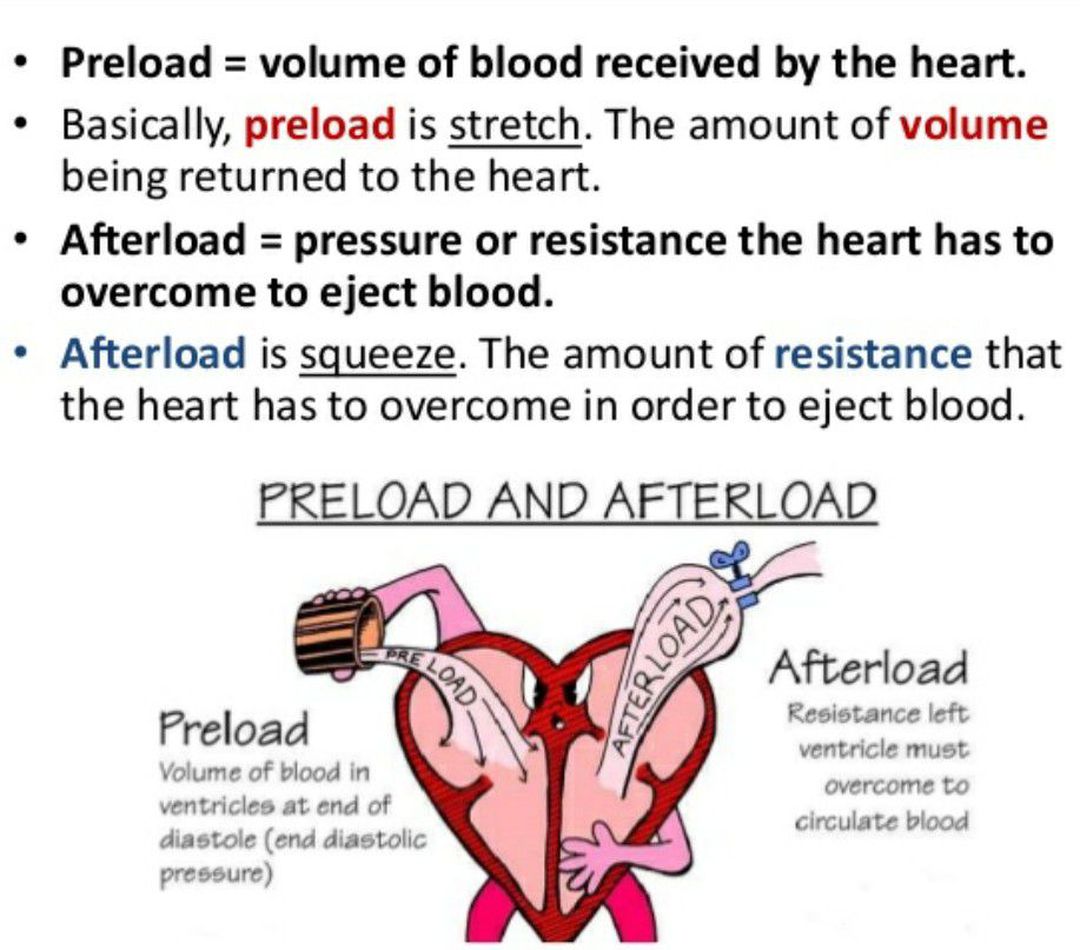
The preload is the amount of stretch or pressure left in the left ventricle at the end of diastole—when the heart is the most relaxed. It is also referred to as the left ventricular end-diastolic pressure or LVEDP. The greater the preload, the more pressure is available for the next cardiac contraction. The afterload is the amount of vascular.
Cardiac Preload vs Afterload vs Contractility With an example
Cardiac output is the volume of blood the heart pumps per minute. Cardiac output is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume by the heart rate; normal cardiac output is about 4 to 8 L/min but varies depending on the body's metabolic needs. Cardiac index is a calculation of the cardiac output divided by the person's body surface area (BSA).
Physiology of the Heart online presentation
Afterload is largely dependent upon aortic pressure. Afterload is the pressure that the heart must work against to eject blood during systole (ventricular contraction). Afterload is proportional to the average arterial pressure. [1] As aortic and pulmonary pressures increase, the afterload increases on the left and right ventricles respectively.

Preload and Afterload Animation (What do they mean? How to measure) YouTube
The heart is an intricate organ that causes quite a bit of bewilderment, especially with nursing students. And one of the topics that bring about such confusion is concerned with preload and afterload. Consider this analogy - the heart is like a slingshot; a slingshot that requires pressure when pulling and energy upon release.

What Are Preload and Afterload? Faculty of Medicine
Check out this Free Hemodynamic Value Cheatsheet To Help You Understand Cardiac https://nursing.com/cheat-sheets/Understanding Preload and Afterload is a lot.

Ventricular PressureVolume Relationship Preload, Afterload, Stroke Volume, Wall Stress & Frank
📝 Find notes here: https://www.nonstopneuron.com/post/preload-and-afterload-for-ventricles-of-the-heartExplore our entire animation video library: https://w.

This is an example of preload and afterload heart hearthealth fitness body design
How Afterload Affects Stroke Volume and Preload. As shown in the figure, an increase in afterload shifts the Frank-Starling curve down and to the right (from point A to B), which decreases stroke volume (SV) and increases left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP). The basis for this is found in the force-velocity relationship for cardiac.

Ventricular PressureVolume Relationship Preload, Afterload, Stroke Volume, Wall Stress & Frank
Preload and afterload are terms you need to know for your next exam — or the next time you're taking care of a patient. So you'll likely be asked to calculate a patient's afterload and preload, along with memorizing other cardiac-related terms.. In this post, we're going to turn complicated, frustrating lectures on cardiac output into effortless, piece-of-cake study systems.
Cardiac Preload vs Afterload vs Contractility With an example
Heart failure can affect your preload and afterload in different ways. Not every person with heart failure will experience these effects. According to 2017 research, the following are the most.
Difference between "PRELOAD "and "AFTERLOAD " MEDizzy
PRELOAD, AFTERLOAD AND CONTRACTILITY. Preload is the initial stretching of the cardiac myocytes (muscle cells) prior to contraction.It is related to ventricular filling. Afterload is the force or load against which the heart has to contract to eject the blood. Contractility is the intrinsic strength of the cardiac muscle independent of preload, but a change in preload will affect the force of.

preload and afterload Nursing mnemonics, Nursing school survival, Icu nursing
In this video, Dr Mike explains all the factors that contribute to cardiac output. This includes the complex terms PRELOAD and AFTERLOAD!

Cardiomyopathy Preload vs Afterload YouTube
Edema can be caused by: 1. high arterial blood pressure. 2. venous obstruction. 3. leakage of llama proteins into interstitial fluid. 4. myxedema (excessive production of certain glycoproteins in the extracellular matrix caused by hypothyroidism) 5. decreased plasma protein concentration.

Interdependent Effects of Preload, Afterload and Inotropy on Ventricular PressureVolum
This wall stress is what causes the distention in the cardiac myocyte. Another definition of preload is that "preload is the pressure on the ventricular wall prior to contraction (i.e. at the end of diastole). Afterload = "LV wall stress during ejection". Unlike preload which is the wall stress at a specific point in time, the afterload.