
Image result for internal jugular vein Brain Anatomy, Human Body Anatomy, Human Anatomy And
Introduction. Internal jugular vein (IJV) drains blood from the head and neck district. It originates from the sigmoid sinus after it exits from the cranial cavity through the jugular foramen, then descends in the carotid sheath, and unites within the subclavian vein to form the brachiocephalic vein, which enters the thorax to join vena cava superior .

VEINS CAPILLARIES SINUSOIDS POSTCAPILLARY VENULES VENULES VEINS TUNICA
Die Vena jugularis interna (innere Drosselvene) ist die Hauptvene des Halses. Sie zieht von der Schädelbasis bis zum Venenwinkel hinter dem Sternoklavikulargelenk . Sie stellt das zentrale Begleitgefäß der A. carotis communis dar und sammelt das Blut aus dem Schädelinneren und den Weichteilen des Kopfes sowie der Schilddrüse .
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/de/vena-jugularis-interna/cOMEyKPJ06WH227w75X4Q_qeM6C1Z6SrZvVqGFjMdPGw_Vena_jugularis_interna_sinistra_02.png)
Vena jugularis interna Anatomie und Klinik Kenhub
The V. jugularis interna reached the ventral surface of the N. vagus after a short course, and these two anatomic structures were contained within the same connective tissue sheath. Then, the V. jugularis interna united with the V. thyroidea caudalis at the subclavian artery level. Thereafter, it opened into the V. subclavian dextra as a single.
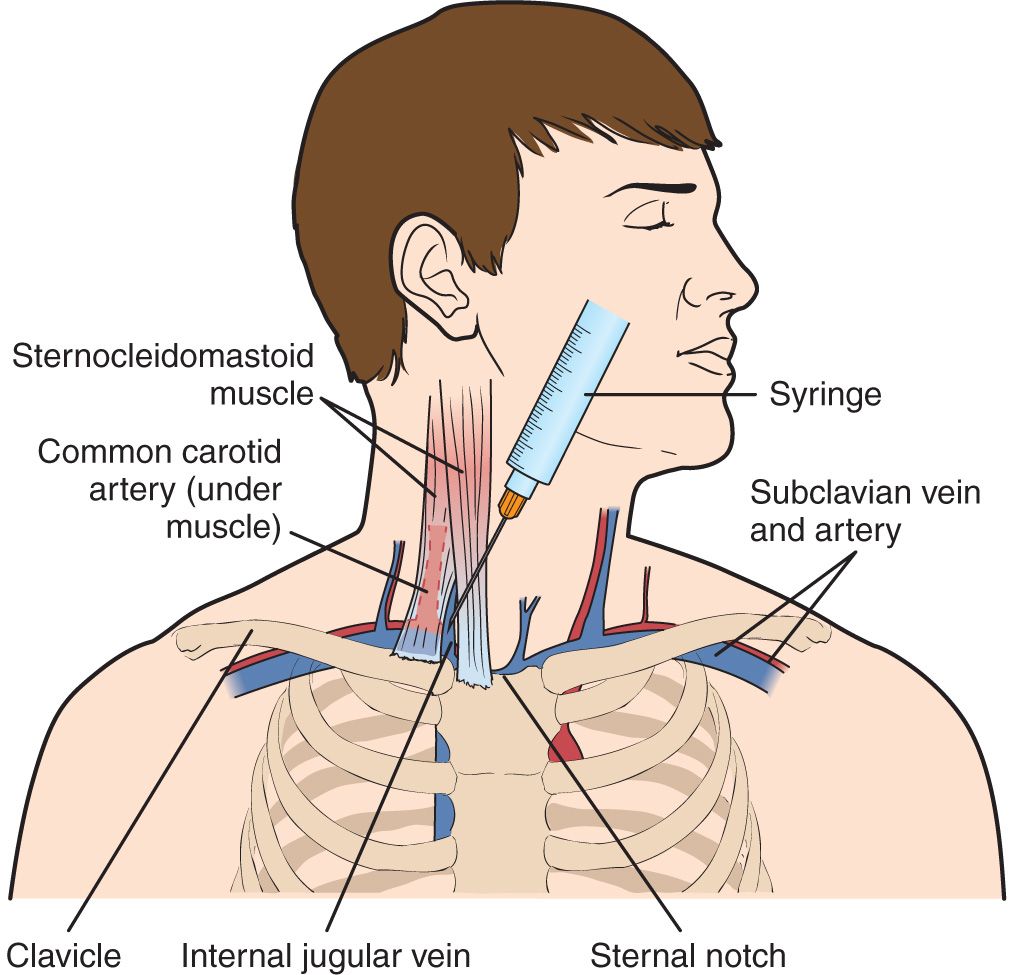
Internal Jugular Vein—Central Venous Access Anesthesia Key
Thrombosen im Kopf-Hals-Bereich und insbesondere der V. jugularis interna (VJI) sind seltene Ereignisse, können aber potenziell ernste Komplikationen nach sich ziehen. Mögliche Ursachen stellen entzündliche, traumatische und (para)neoplastische Veränderungen dar.

Figure 1 from Cerebral venous drainage through internal jugular vein Semantic Scholar
Die Vena jugularis interna weist in ihrem Verlauf zwei Auftreibungen auf, die separat benannt werden: Bulbus superior venae jugularis internae: Auftreibung am Beginn der Vene im hinteren Abschnitt des Foramen jugulare Bulbus inferior venae jugularis internae: Auftreibung hinter dem Sternoklavikulargelenk Zuflüsse
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/de/vena-jugularis-anterior/5Qy8BSRfF9Jrz6SP8j2cw_Bildschirmfoto_2017-10-16_um_20.01.49.png)
Vena jugularis anterior Anatomie, Verlauf und Klinik Kenhub
C+ delayed. Comparison made to CT brain from earlier the same day. There is a filling defect in the right internal jugular vein extending from the jugular bulb 2cm inferiorly. This is consistent with thrombus. No extension above the jugular foramen. The right sigmoid and transverse sinuses opacify normally. No other filling defect identified.

Right internal jugular vein (Vena jugularis interna dextra); Image Yousun Koh Jugular
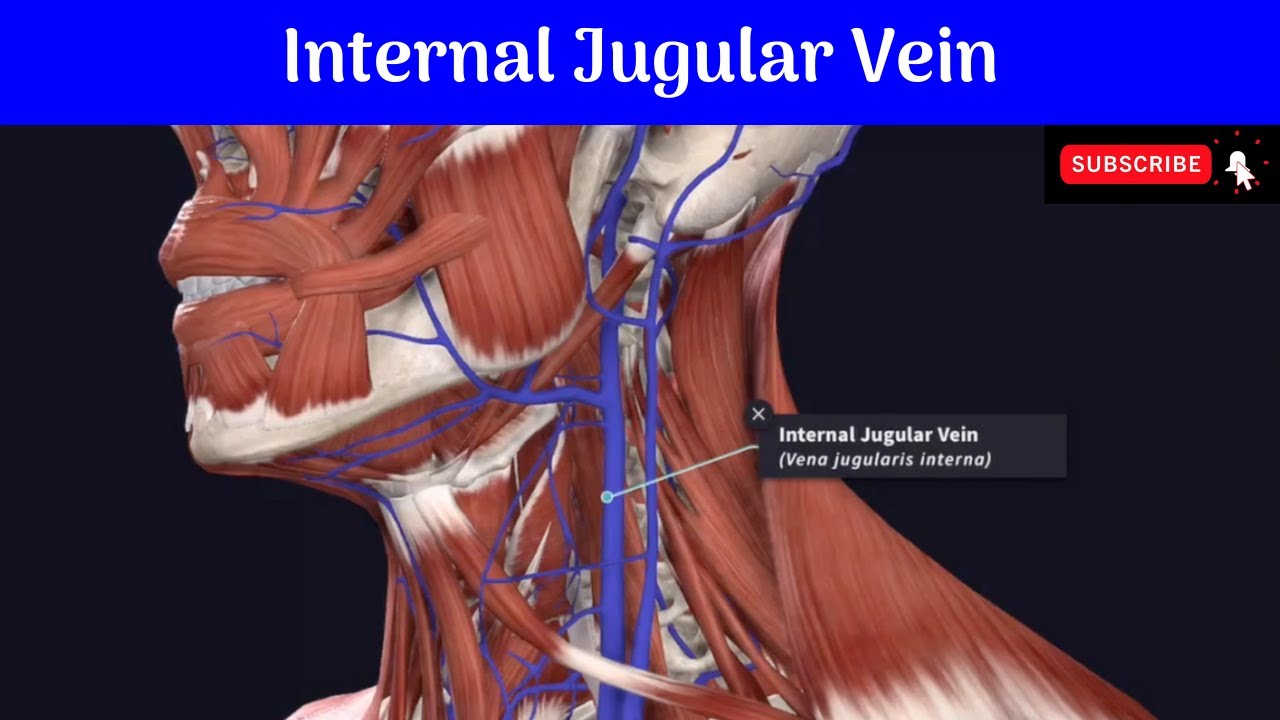
The internal jugular vein is a paired jugular vein that collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck. This vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve. It begins in the posterior compartment of the jugular foramen, at the base of the skull.

The external jugular vein formed by the retromandibular and facial... Download Scientific Diagram
Percutaneous cannulation of the internal jugular vein uses anatomic landmarks to guide venipuncture and a Seldinger technique to thread a central venous catheter through the internal jugular vein and into the superior vena cava. Three approaches (central, anterior, and posterior) are used; the central approach is described here.

Internal Jugular Vein Anatomy ANATOMY
Clinical significance. The external jugular is a large vein used in prehospital medicine for venous access when the Paramedic is unable to find another peripheral vein [4] It is commonly used in cardiac arrest or other situations where the patient is unresponsive due to the pain associated with the procedure.

Internal Jugular Vein Anatomy ANATOMY
The internal jugular vein (IJV) is the major venous return from the brain, upper face and neck. Gross anatomy Origin and course It is formed by the union of inferior petrosal and sigmoid dural venous sinuses in or just distal to the jugular foramen (forming the jugular bulb). It descends in the carotid sheath with the internal carotid artery.
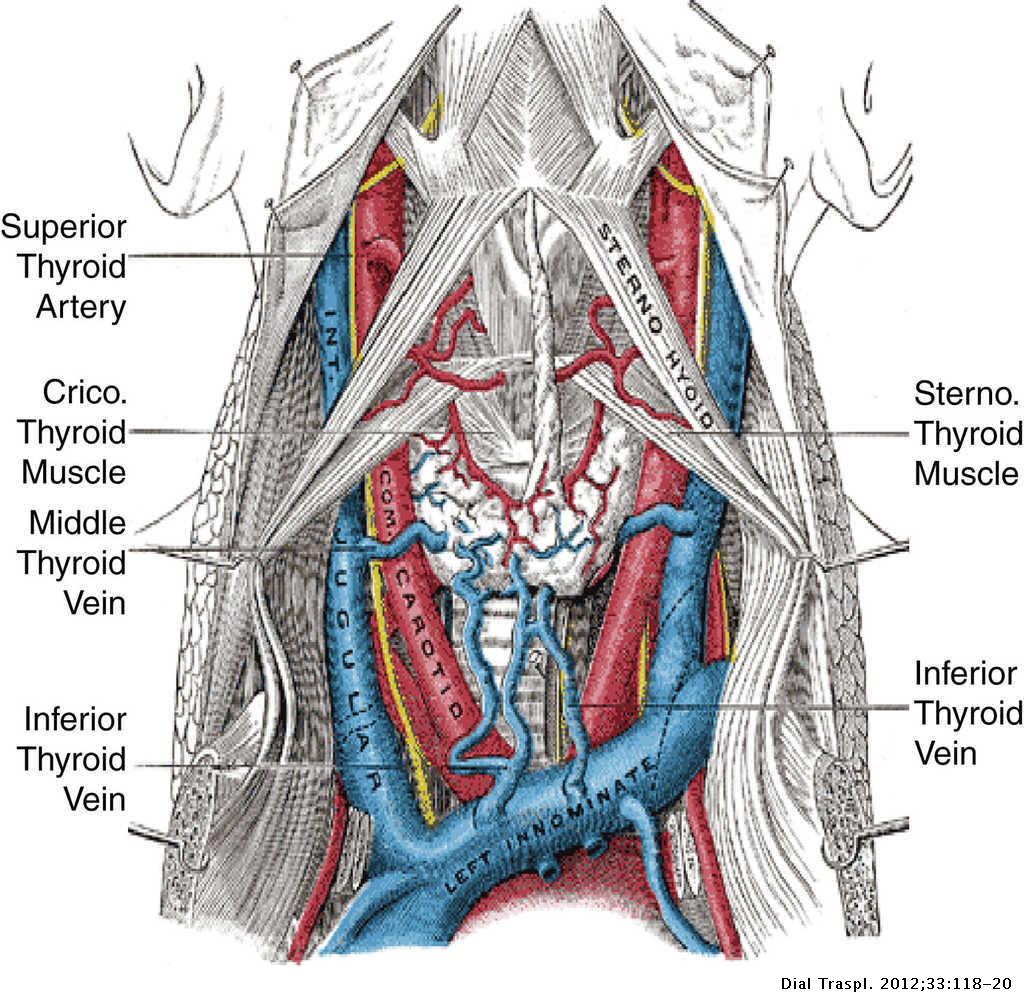
The jugular approach Diálisis y Trasplante
External jugular vein (Vena jugularis externa) The external jugular vein is a vein of the neck that arises from the union of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein and the posterior auricular vein.. The external jugular vein begins near the mandibular angle, just below or within the substance of the parotid gland.It descends obliquely along the neck, superficial to the.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/anterior-jugular-vein/7JgS4AcHZBWoMWteycQA_Anterior_jugular_vein.png)
Anterior jugular vein Anatomy, tributaries, drainage Kenhub
Definition The internal jugular vein ( v. jugularis interna) collects the blood from the brain, from the superficial parts of the face, and from the neck. It is directly continuous with the transverse sinus, and begins in the posterior compartment of the jugular foramen, at the base of the skull.
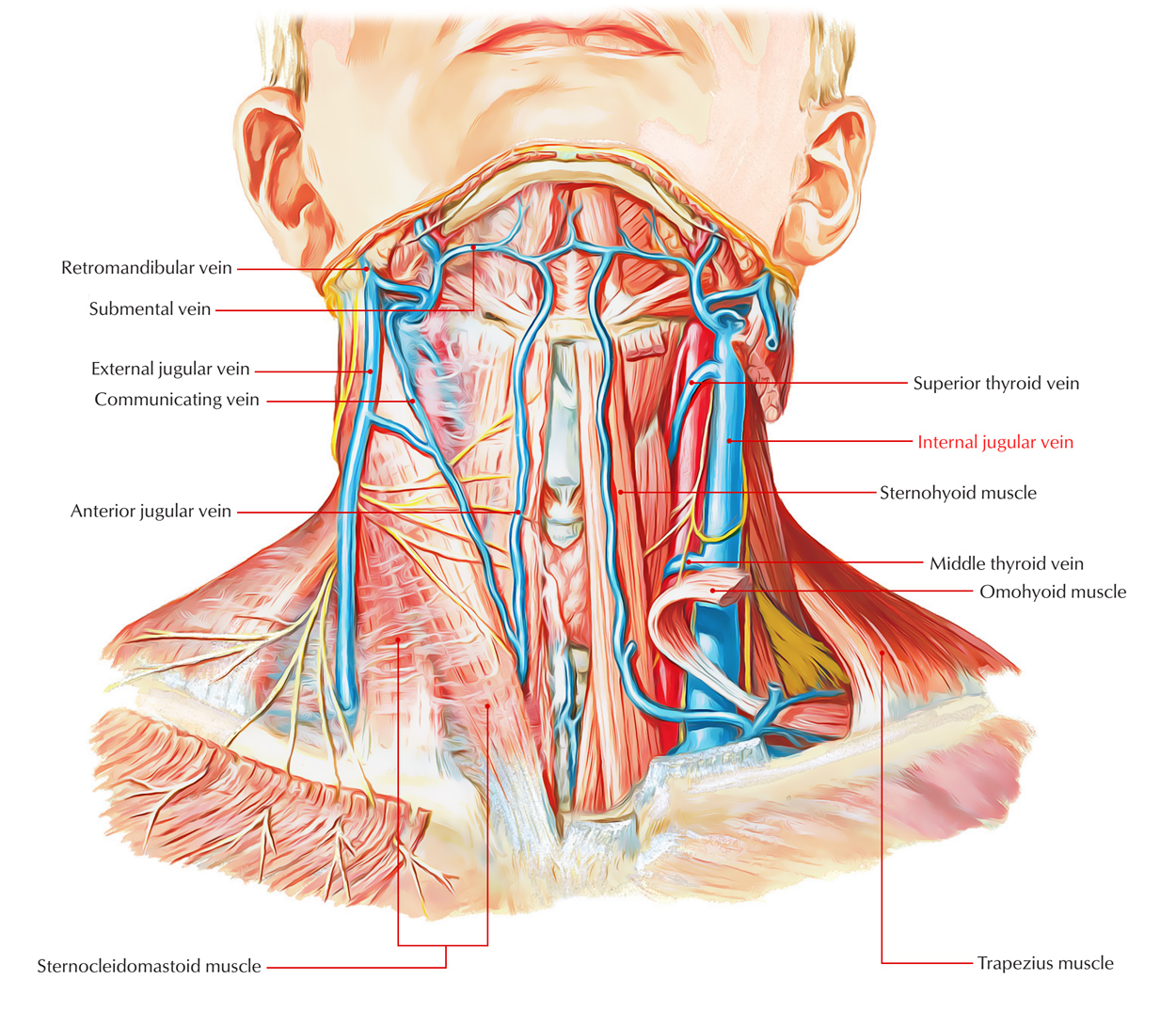
Internal Jugular Vein Earth's Lab
Majdák P., Kubík J., Jr., Harmátová L. Prípad vlajúceho infikovaného trombu v. jugularis interna, septických pneumónií a heparínom indukovanej trombocytopénie [A case of a flapping infected thrombus in the internal jugular vein, septic pneumonias and heparin-induced thrombocytopaenia] Vnitr. Lek. 2011; 57 (1):117-121.
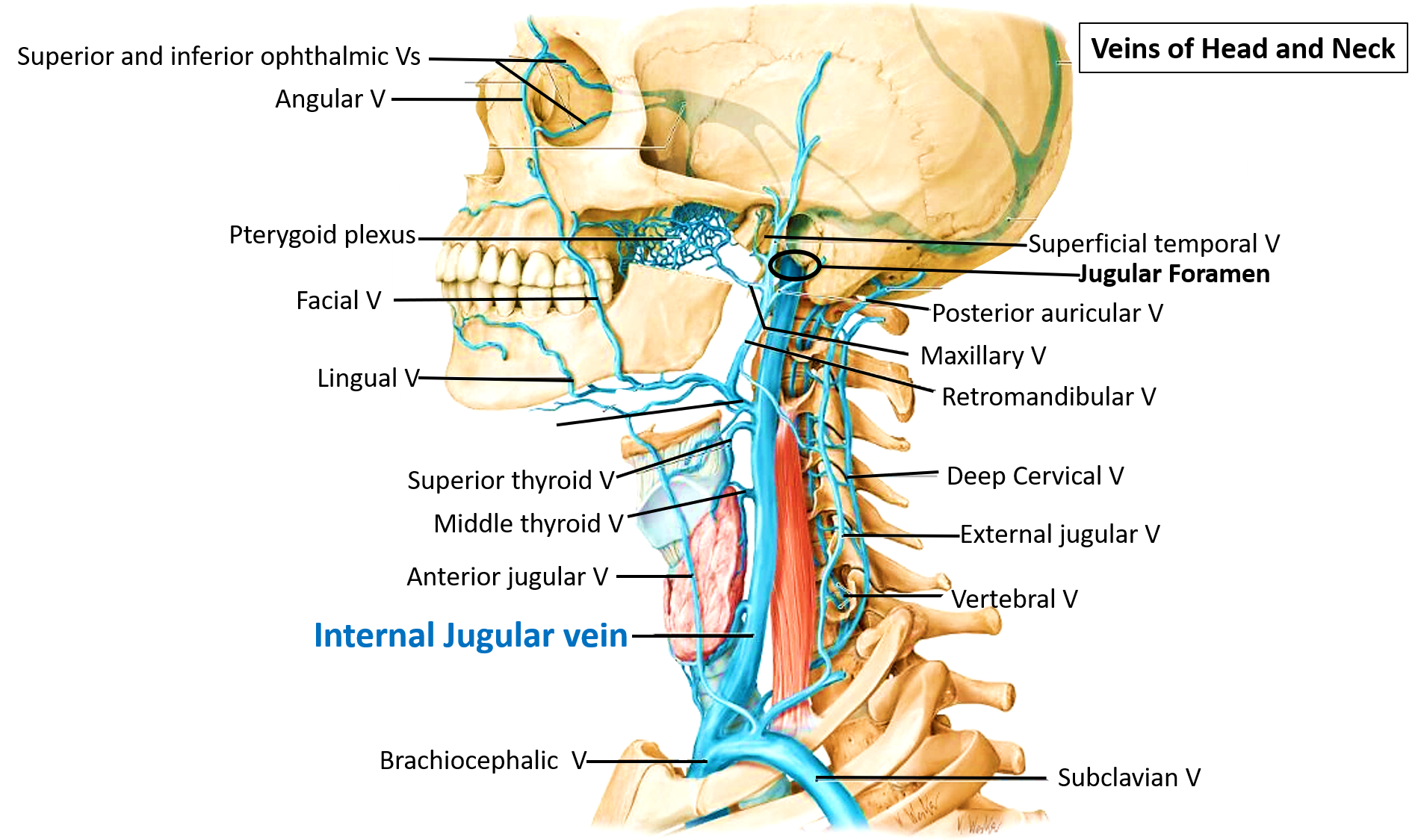
Internal Jugular Vein Course Tributaries Relations AnatomyQA
The internal jugular vein (IJV) is a paired vessel found within the carotid sheath on either side of the neck. It extends from the base of the skull to the sternal end of the clavicle. The internal jugular vein receives eight tributaries along its course.

Internal Jugular Vein Anatomy ANATOMY
The internal jugular vein is formed by the anastomosis of blood from the sigmoid sinus of the dura mater and the inferior petrosal sinus. The internal jugular runs with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve inside the carotid sheath. It provides venous drainage for the contents of the skull .
Internal Jugular Vein Commencement Termination Relations Tributaries Applied Anatomy
Vena jugularis interna. Die Vena jugularis interna („innere Drosselvene") ist eine Vene des Halses. Sie verläuft hinter dem Musculus sternocleidomastoideus (Kopfnickermuskel) parallel zur Arteria carotis communis (Halsschlagader) und zur Luftröhre. Sie beginnt als Fortsetzung des Sinus sigmoideus am Foramen jugulare der Schädelbasis und.