
6 How to create swap file in Ubuntu Server YouTube
The Open Event Android App generator runs on a DigitalOcean. The deployment runs on a USD 10 box, that has 1 GB of RAM, but for testing I often use a USD 5 box, that has only 512mb of RAM.. The steps to create a swap file and allocating it as swap are. sudo fallocate -l 1G /swapfile sudo chmod 600 /swapfile sudo mkswap /swapfile.
Create a Linux Swap File Linuxize
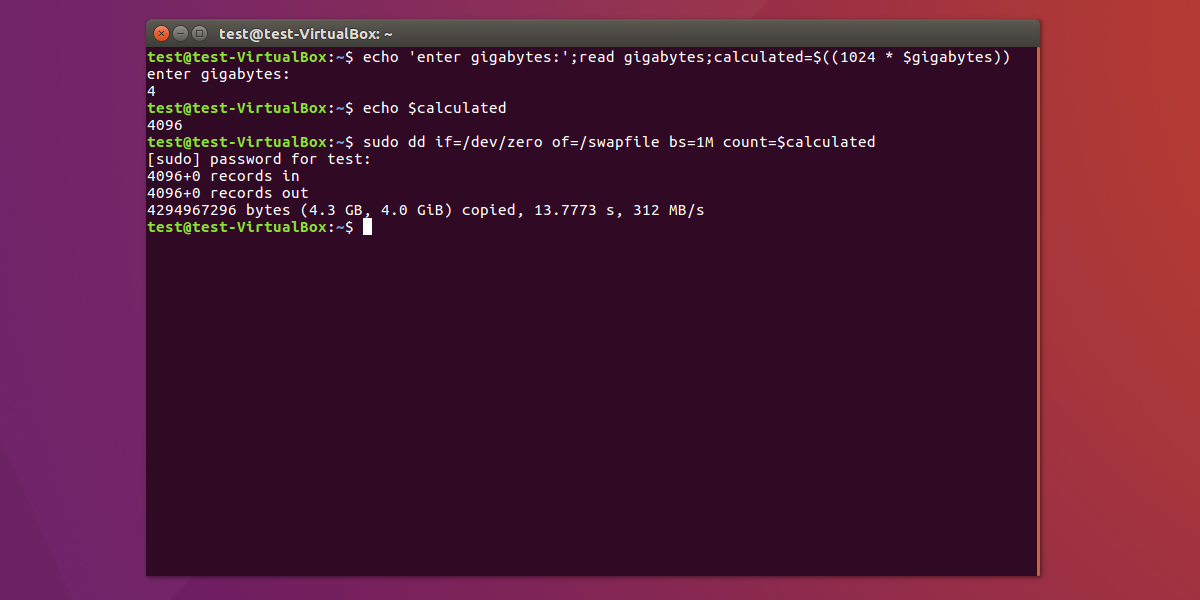
Preallocated swap files are . supported on XFS since Linux 4.18. The most portable solution to create a swap file is to use dd(1) and /dev/zero. So, although fallocate is faster, we'll use dd to create the swap file. The machine used to research this article has two GB of RAM. We're going to create a one GB swap file. The options are: if: The.

How to Create a Droplet from the DigitalOcean Control Panel DigitalOcean Documentation (2022)
Creating a Swap File First, we will verify that you have available hard drive space on the system, then we can create a swap file on our filesystem. We will further allocate a file of the size that we want calling swapfile in our root ( /) directory.

How do I upload a file to DigitalOcean droplet?
1- Use DigitalOcean's 1-Click Install DigitalOcean makes it pretty easy to initially install WordPress onto a VPS. In fact, they have a pretty easy - to - follow guide on their own website which you can read here. It's a good starting point that we don't need to rehash. A few notes, though:
How To Set Up A Swap File On Linux
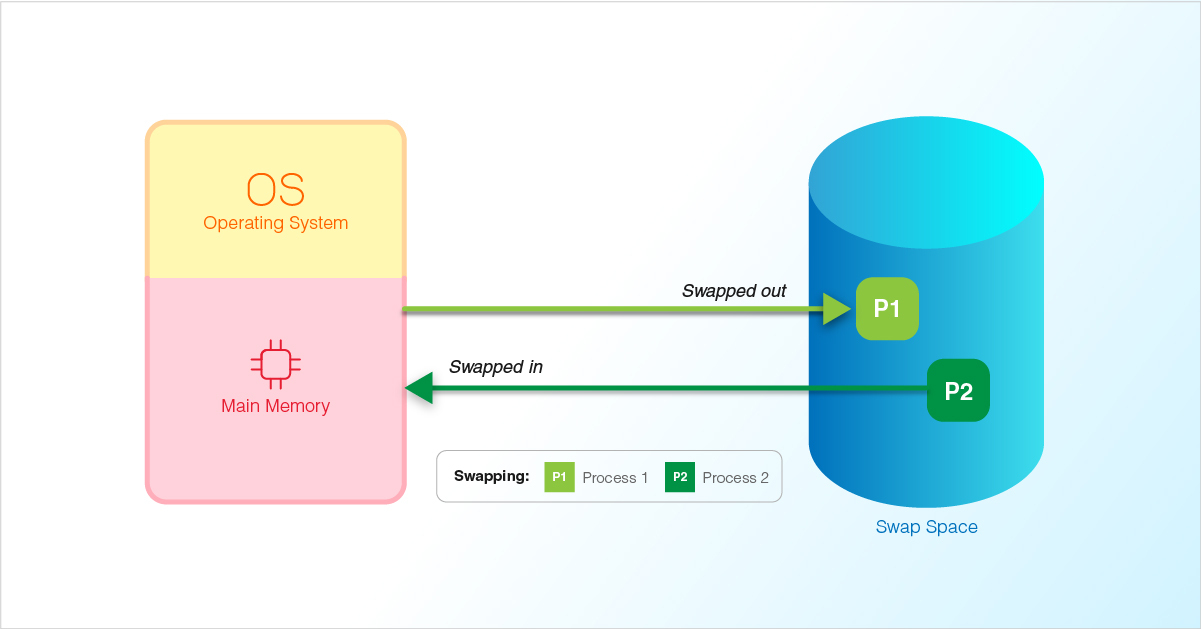
Introduction One of the easiest ways to make your server more responsive, and guard against out-of-memory errors in your application, is to add some swap space. Swap is an area on a storage drive where the operating system can temporarily store data that it can no longer hold in memory.

how to create and extend swap partition and swap file in linux ? part 2 swap swapon
Step 1 - Checking the System for Swap Information Before we begin, we can check if the system already has some swap space available. It is possible to have multiple swap files or swap partitions, but generally one should be enough. We can see if the system has any configured swap by typing: sudo swapon --show
Understanding Swap Space in Linux A Practical Guide Knoldus Blogs
Follow the below steps to create and enable Swap memory on your Ubuntu system. 1. Check Current Swap Before working make sure that the system has already swap enabled. If there is no swap, you will get the output header only. ADVERTISEMENT sudo swapon -s 2. Create Swap File Let's create a file to use for swapping in the system of the required size.

Discourse Memory on DigitalOcean Droplet Swap Jason Loong
Robust web-based PDF editing solution for businesses of all sizes. Start Free Trial! Save Time Editing Documents. Fast, Easy & Secure. Edit PDF Files on the Go. Try Now!

How do I upload a file to DigitalOcean droplet?
How to Upload, Download, and Delete Files Upload files from your local computer to make them available in a Spaces bucket, download files from a bucket to your local computer, and delete files from a bucket to stop serving them. How to Organize Files with Folders Use folders to organize files in a Space and make them conceptually easier to manage.
Install & Configure WordPress in DigitalOcean WPExplorer
Navigate to the File tab in the top menu and then select Site Manager. This action opens up a new prompt, where you can press the New site button in the bottom left under Select entry. Once you do this, name the site DigitalOcean and press Enter. Navigate to the General tab and press the drop-down menu for Protocol.
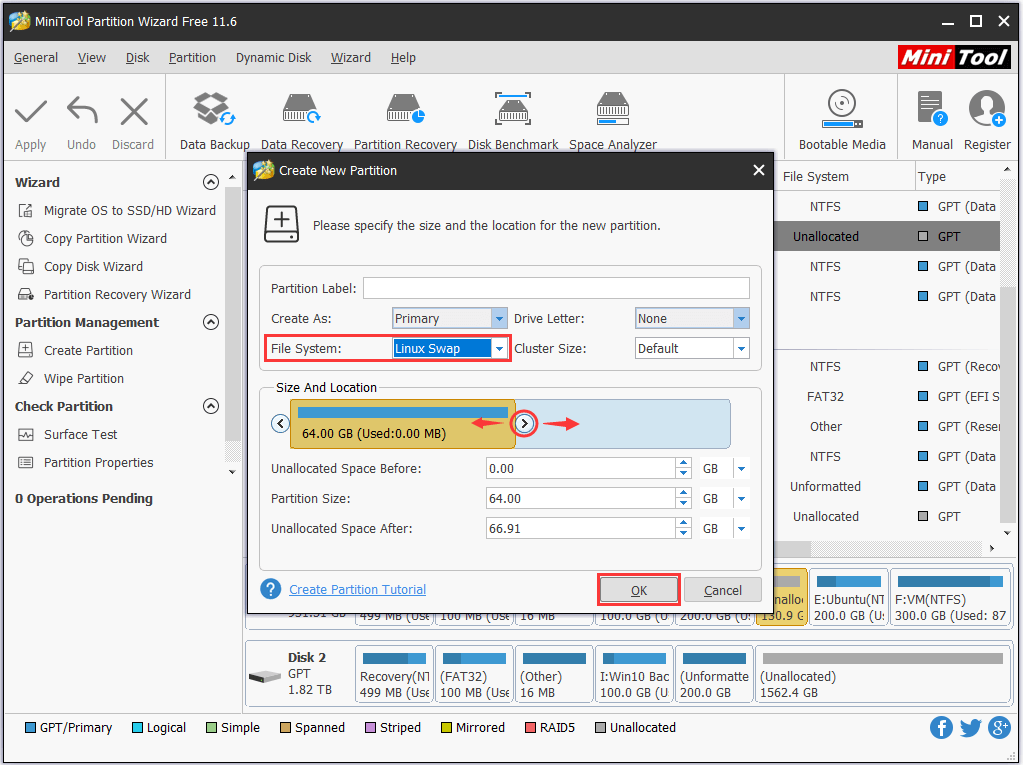
The Best Way to Free Create Swap Partition in Linux MiniTool Partition Wizard
How To Configure Virtual Memory (Swap File) on a VPS | DigitalOcean // Tutorial // How To Configure Virtual Memory (Swap File) on a VPS Published on November 15, 2013 Linux Basics Server Optimization By Jai Boudreau Table of Contents & Preface Introduction - Requirements and Why Pros & Cons - Droplet Check if Enabled on your VPS

How to create a swap file in GNU/Linux Tutorial MARKO NTECH
Swap is an area on a hard drive that has been designated as a place where the operating system can temporarily store data that it can no longer hold in RAM. Basically, this gives you the ability to increase the amount of information that your server can keep in its working "memory", with some caveats.

DigitalOcean Reviews 2020 Details, Pricing, & Features G2
Create swap file on digitalocean ubuntu droplets Raw. swap.sh This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters. Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters.
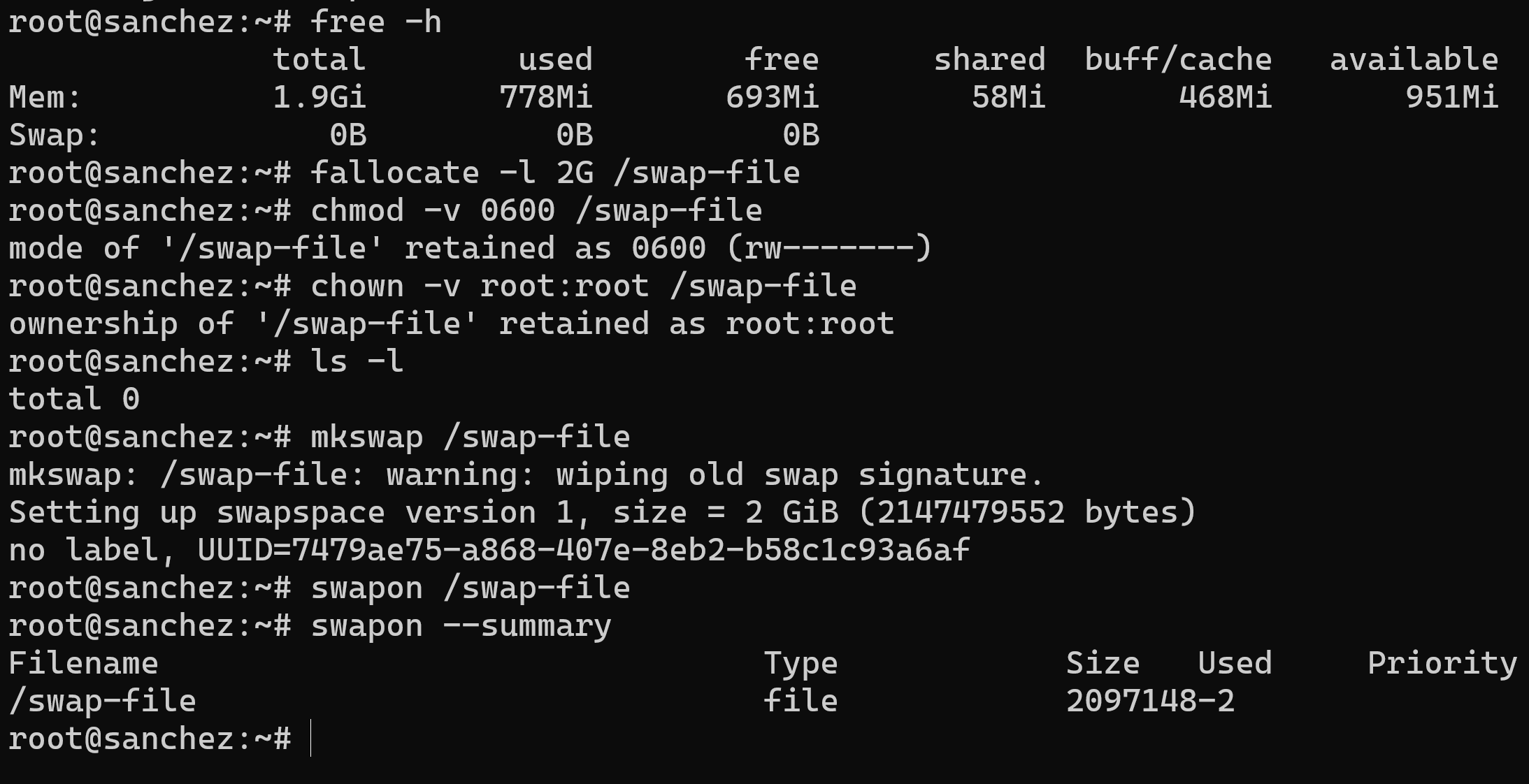
Linux Swap File blog.adminintelligence.de
Step 1 - Checking the System for Swap Information Before we begin, we can check if the system already has some swap space available. It is possible to have multiple swap files or swap partitions, but generally one should be enough. We can see if the system has any configured swap by typing: sudo swapon --show

How to Create Swap File, Adjust Swappiness Value & Delete Swap file in Ubuntu Linux
If you have a smaller droplet on DigitalOcean, chances are you will need to create a swap file at some point. A good example of needing a swap file is if you get the following error in your daily cron: /etc/cron.daily/apt: FATAL -> Failed to fork. The error above normally occurs when you run out of RAM needed to run the cron job.

How to Create, Resize, or Extend a Linux Swap File 2020 Tutorial (Ubuntu)
Swap is an area on a storage drive where the operating system can temporarily store data that it can no longer hold in memory. In this guide, we will cover how to add a swap file to your server. Choose your OS below to get started. CentOS 7 How To Add Swap on CentOS 7 By Josh Barnett 6 How To Add Swap on CentOS 6 By Etel Sverdlov Debian 11