
analog Astable multivibrator frequency mismatch Electrical Engineering Stack Exchange
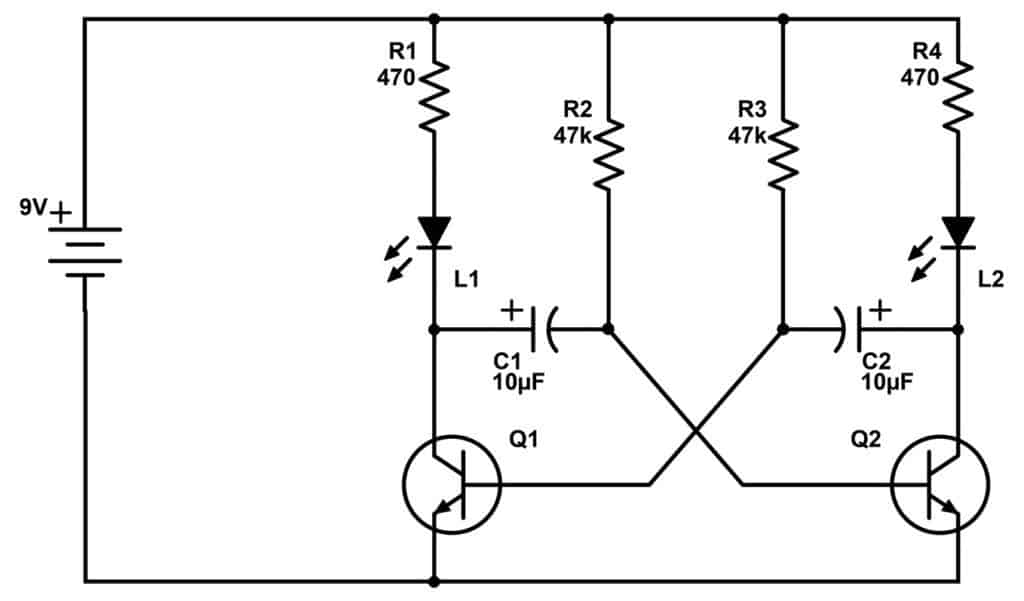
Frequency of Oscillations The ON time of transistor Q 1 or the OFF time of transistor Q 2 is given by t 1 = 0.69R 1 C 1 Similarly, the OFF time of transistor Q 1 or ON time of transistor Q 2 is given by t 2 = 0.69R 2 C 2 Hence, total time period of square wave

555 Variable Duty Cycle, Constant Frequency Astable Multivibrator Multisim Live
In electronic circuits, astable multivibrators are also known as Free-running Multivibrator as they do not require any additional inputs or external assistance to oscillate.

555 Variable Duty Cycle, Constant Frequency Astable Multivibrator Multisim Live
What Is An Astable Multivibrator Circuit. An astable multivibrator circuit also termed as a regenerative switching circuit, is an electrical circuit that switches between HIGH and LOW states continuously. The output of the astable multivibrator circuit is a square wave that goes on indefinitely. As simple as it is, the astable multivibrator is.

Astable Multivibrator (using opamp) Explained YouTube
Example 1. The Astable Multivibrator The first example is an astable multivibrator shown by its conventional circuit diagram in Figure 8-1. The idealized wave forms on the collectors and bases of transistors Q1 and Q2 are shown in Figure 8-2. At time t0 transistor Q1 is in saturation, and its collector voltage is close to ground.

Astable Multivibrator Frequency Derivation OPAMP Astable Multivibrator Frequency of
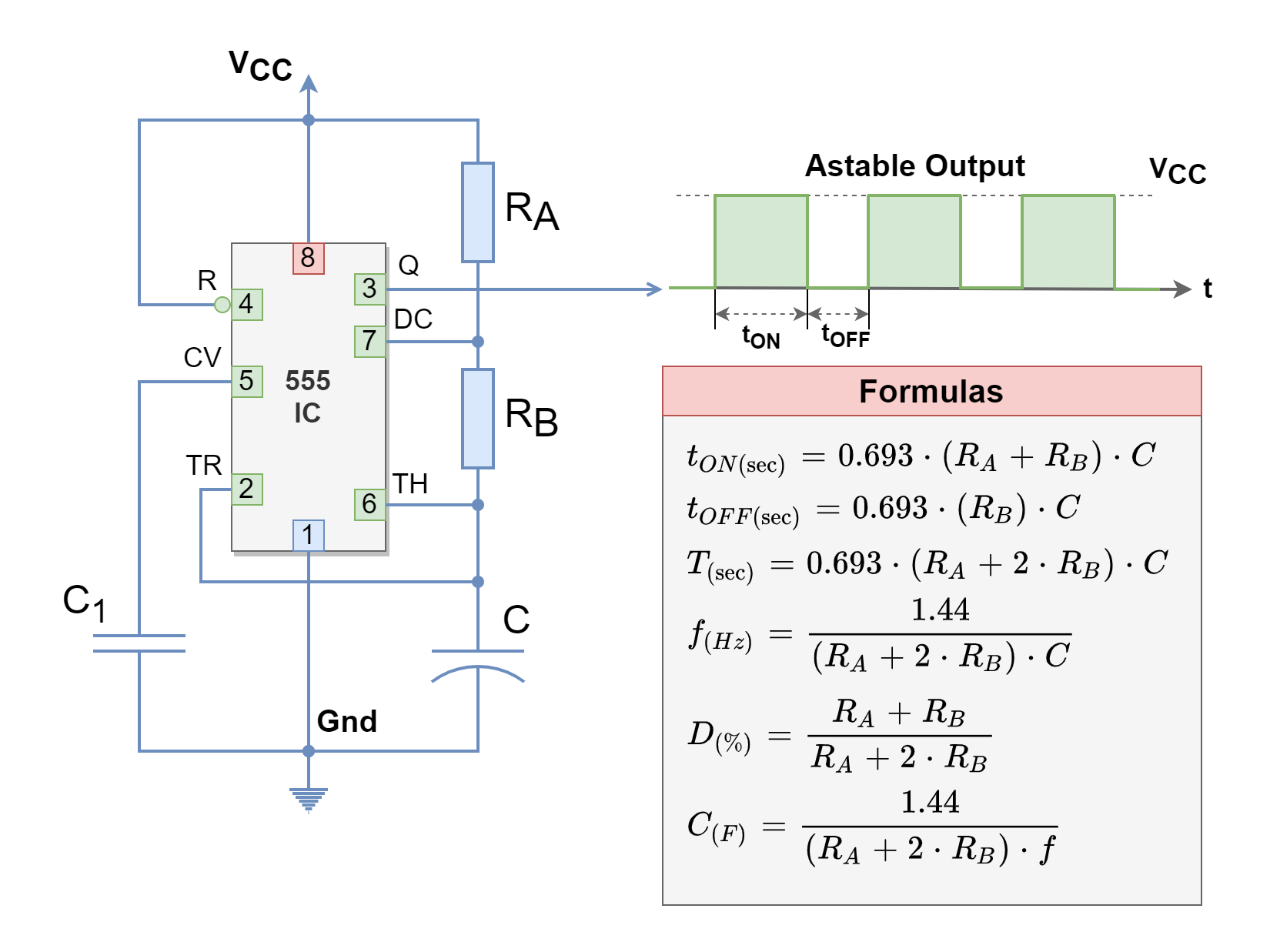
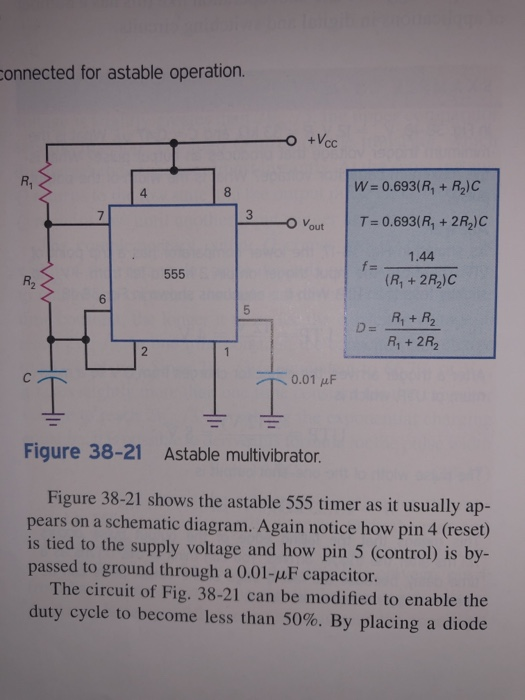
Astable multivibrator is also called as Free Running Multivibrator. It has no stable states and continuously switches between the two states without application of any external trigger. The IC 555 can be made to work as an astable multivibrator with the addition of three external components: two resistors (R 1 and R 2) and a capacitor (C).

555 Variable Duty Cycle, Constant Frequency Astable Multivibrator Multisim Live
A voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is one in which the frequency of oscillations varies as a function of voltage. The same circuit is also called a voltage-to-frequency converter (VFC) because a given voltage gives rise to a specific frequency. An astable multivibrator is used as voltage-controlled oscillator [see Fig. 7.13 (a) ].
555 Variable Duty Cycle, Constant Frequency Astable Multivibrator Multisim Live
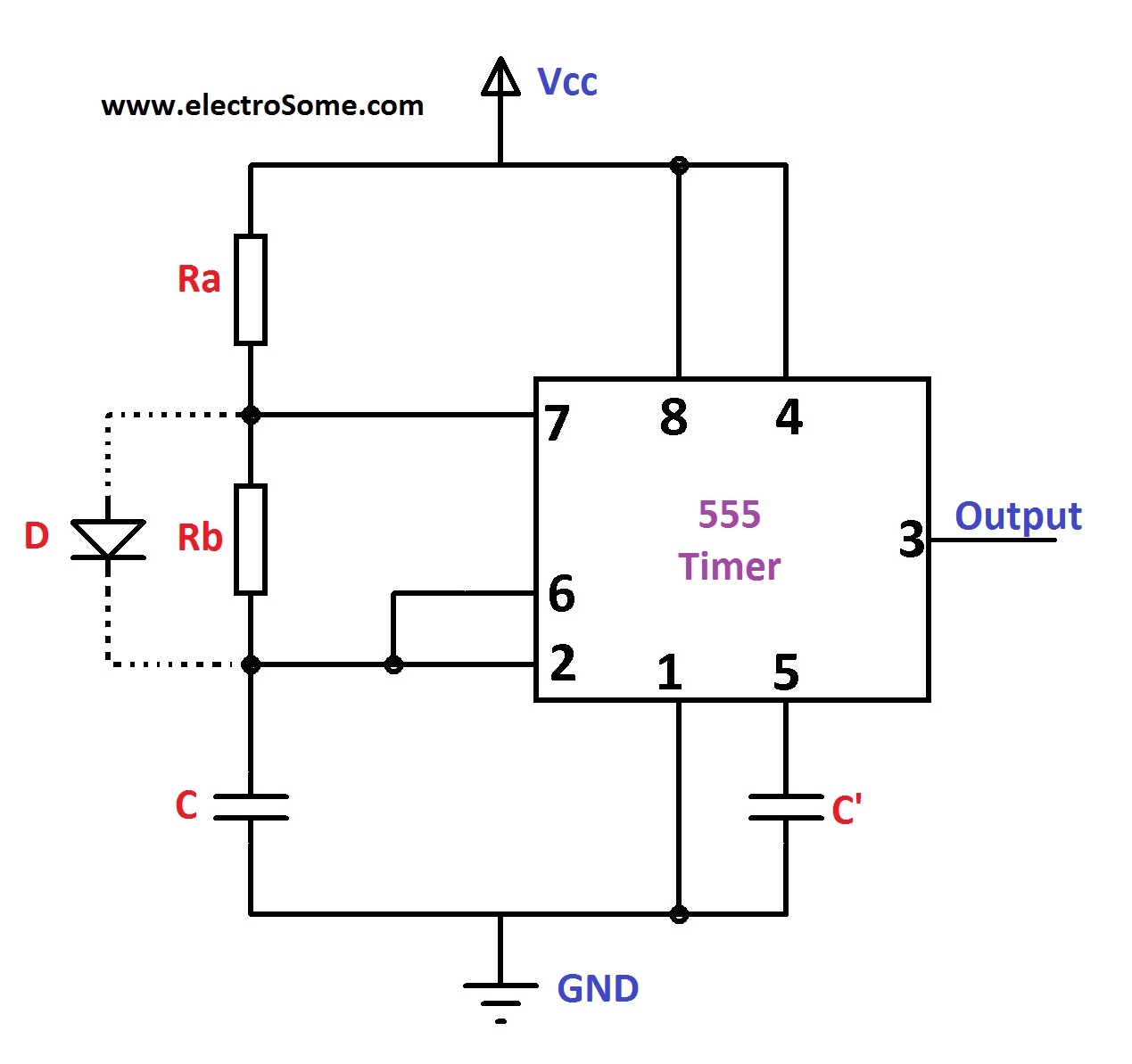
The 555 Oscillator is another type of relaxation oscillator for generating stabilized square wave output waveforms of either a fixed frequency of up to 500kHz or of varying duty cycles from 50 to 100%.

Astable Multivibrator Circuit Using 555 Timer Output Frequency 8.32Hz Elektrotechniek
555 Astable Multivibrator Calculator #1 This calculator takes R1 resistor, R2 resistor and Capacitor C as inputs and provides frequency and duty cycle as outputs. Resistance (R1) in K-Ohm (Input-1) : Resistance (R2) in K-Ohm (Input-2) : Capacitance (C) in µF (Input-3) : Frequency of AMV (output-1) : Duty Cycle of AMV (output-2) :
Astable multivibrator calculator
Astable - A free-running multivibrator that has NO stable states but switches continuously between two states this action produces a train of square wave pulses at a fixed known frequency. Monostable - A one-shot multivibrator that has only ONE stable state as once externally triggered it returns back to its first stable state.

Adjusting Frequency of an Astable Multivibrator Skinny Research and Development
• Calculate the frequency of an astable multivibrator. • Understand methods for varying the frequency and mark to space ratio of the output wave. BJT Astable Multivibrators Fig. 4.1.1 Basic BJT Astable Multivibrator
astable définition C'est quoi
Astable oscillators produce a continuous square wave from its output or outputs, (two outputs no inputs) which can then be used to flash lights or produce a sound in a loudspeaker. The basic transistor circuit for an Astable Multivibrator produces a square wave output from a pair of grounded emitter cross-coupled transistors.
555 Variable Duty Cycle, Constant Frequency Astable Multivibrator Multisim Live
Circuit Explanation The Astable multivibrator consists of two cross-coupled RC amplifiers. The circuit has two unstable states o When V1 = LOW and V2 = HIGH then Q1 ON and Q2 OFF o When V1= HIGH and V2 = LOW then Q1 OFF and Q2 ON In this R1 = R4 , R2 = R3, R1 should be greater than R2 C1=C2
Solved RI 555 Timer R2 Output Astable Multivibrator 5 01 uF
The astable multivibrator circuit is a classic circuit for flashing two LEDs. It doesn't have to flash two LEDs though. It can blink just one LED. Or it can create a tone to play on a speaker. First, let me show you the circuit in action: Astable Multivibrator Circuit demo Watch on Want to know the theory behind how the circuit works?
How Astable Multivibrator Circuits Work
The frequency of oscillation f = 1/ T. Duty cycle is the ratio of ON time (duration of HIGH state or pulse width) to the total time period of a cycle. The duty cycle of an Astable multivibrator = TON/ TON + TOFF. Working of astable multivibrator Circuit. Initially, the voltage across the trigger and threshold input is below 1/3Vcc.

ISF Robotics astable multivibrator mode of 555 timer ic
My first observation was that the conventional (i.e., often quoted) formula for the frequency, F, of oscillation of the canonical STAM, F = 1/ {2 ln (2) RC} with R = RO and C = CO, does not accurately predict the observed flash rate, with the model calculation being in error by more than 50% to as much as a factor of three, or more, depending up.
555 Variable Duty Cycle, Constant Frequency Astable Multivibrator Multisim Live
The output frequency of an astable multivibrator can be calculated using the formula: f = 1 / T = 1.44 / ( (R1 + 2R2) * C1) Here, R1, R2 are the resistors and C1 is the capacitor. The '1.44' is a constant derived from the natural logarithm base ( e ), showing the integral role of exponential growth in the circuit's function.