
Human Tongue Anatomy Human tongue, Tongue health, Anatomy
Lips and Tongue: Anatomy. The lips are the soft and movable most external parts of the oral cavity. The tongue, on the other hand, is a complex muscular structure that permits tasting and facilitates the process of mastication and communication. Together, these structures play an important role in each of these vital processes.
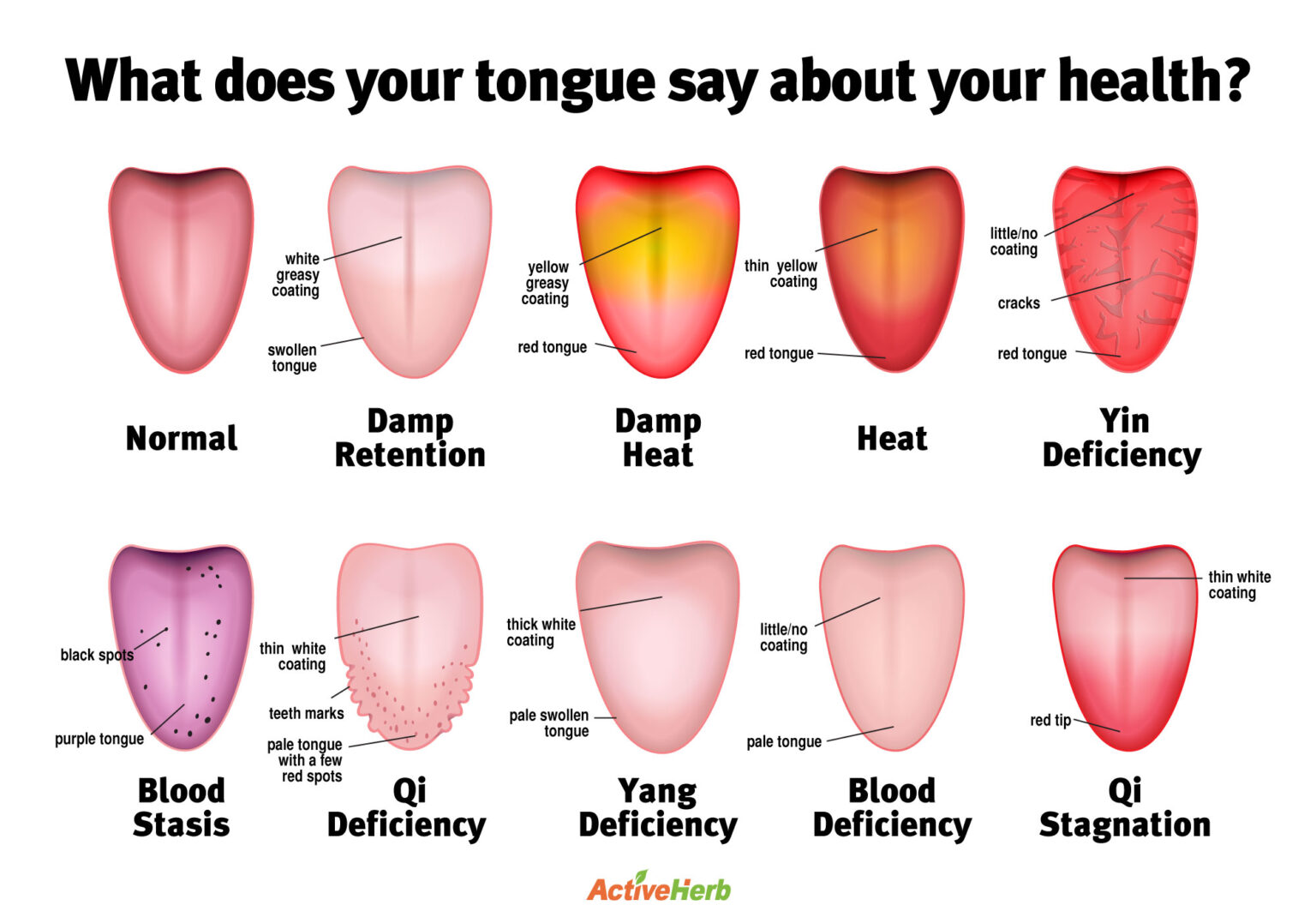
tonguediagram Activeherb Blog
Anatomy Anterior two thirds Posterior third Muscles Histology The lingual papillae Taste buds Blood supply and lymphatic drainage Arteries Veins Lymphatic drainage Innervation Motor innervation

Adult Frenectomy For Pain Relief Osteopathic ConsiderationsOsteopathy New York, P.C.
Your tongue runs from your hyoid bone (located in the middle of your neck) to the floor of your mouth. Advertisement What is the tongue made of? Your tongue is mostly made of muscles. It's anchored inside of your mouth by webs of strong tissue and it's covered by mucosa (a moist, pink lining that covers certain organs and body cavities).
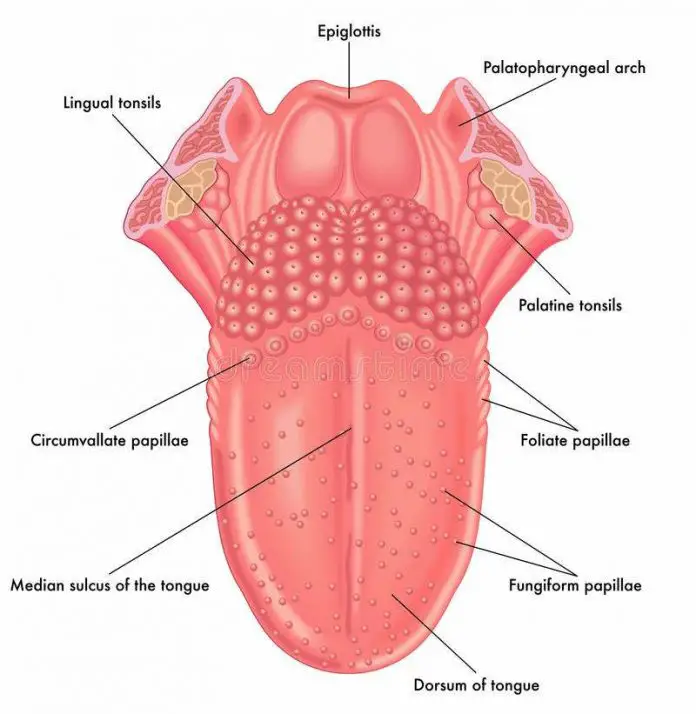
Diagram of tongue
Many parts make up your mouth anatomy. These parts work together harmoniously to help with chewing, speaking and breathing. The outside of your mouth creates a boundary that holds food in place and helps you form sounds and words. It includes your cheeks and lips. The inside of your mouth contains your: Teeth. Gums.
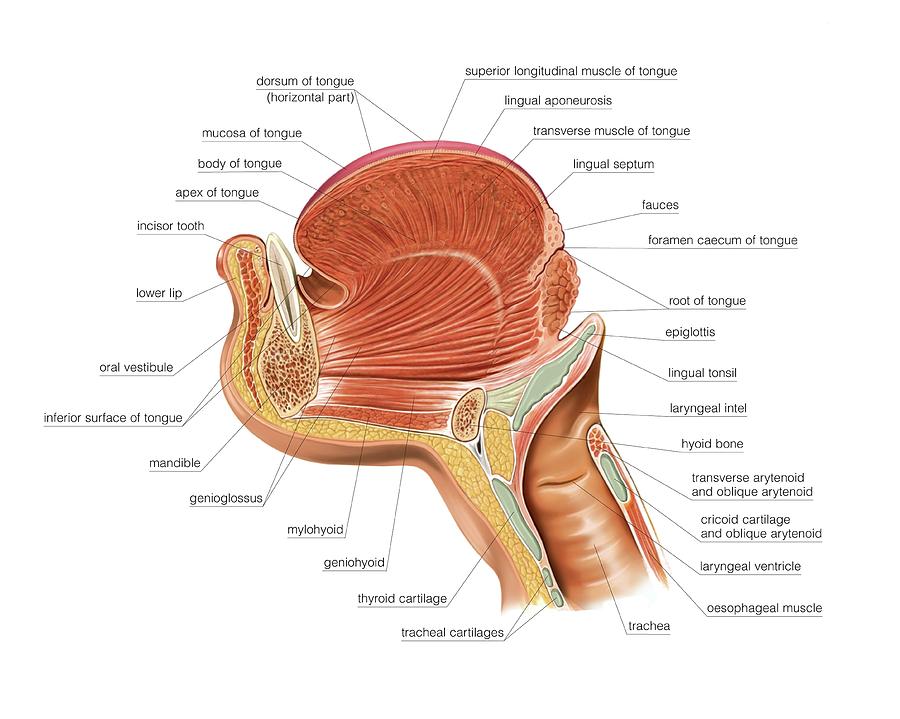
Tongue Anatomy Diagram Anatomical Charts & Posters
Human Tongue Diagram Table of Contents: Human Tongue Well-labelled Diagram of Human Tongue Tongue Structure Frequently Asked Questions Human Tongue The tongue is a muscular structure situated in the mouth and is a part of the oral cavity floor. It also forms a part of the anterior wall of the oropharynx.

Tongue Anatomy QA
Oral Tongue Oral tissues: Tongue Anterior surface of the tongue. The tongue is a mass of interlacing skeletal muscle , connective tissue with some mucous and serous glands, and pockets of adipose tissue, covered in oral mucosa. A V-shaped line (shallow groove)- the sulcus terminalis, divides the tongue into an anterior 2/3 and a posterior 1/3.
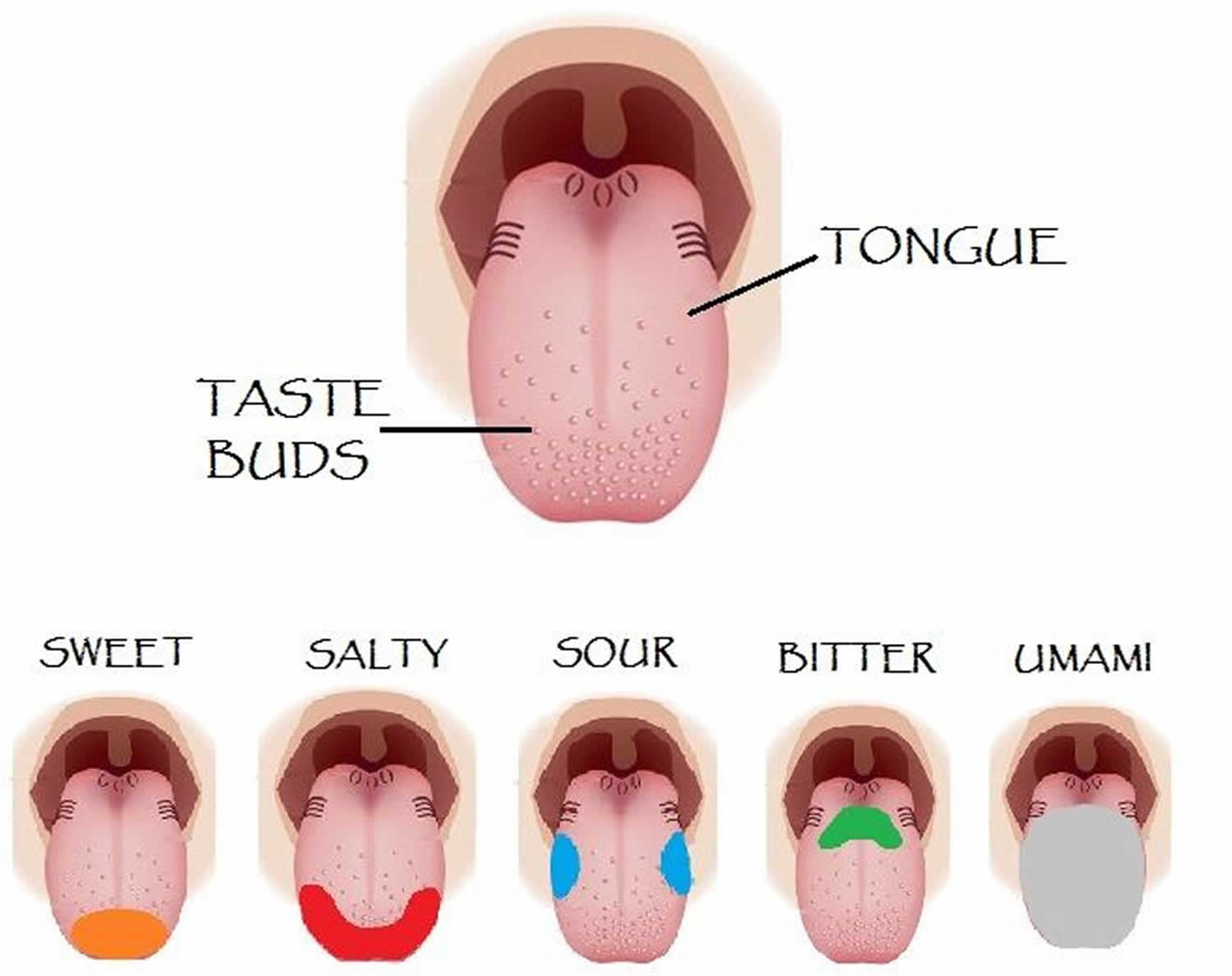
Hypogeusia definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis
1/2 Synonyms: none The tongue is a muscular organ situated in the oral cavity, and an accessory digestive organ. Its main functions include sensation of taste, mastication (chewing), deglutition (swallowing), speech, and clearing the oral cavity. The rich motor and sensory innervation of the tongue is carried by four cranial nerves

Anatomy of Tongue Biology Ease
What's a muscular hydrostat, you ask? Essentially, it's a strong, flexible biological structure that contains a whole bunch of muscle fibers but no skeletal structure. If you need a non-tongue example, think elephant trunks and octopus tentacles. Octopuses, slugs, and the roundworm C. elegans also have muscular hydrostat bodies. Cool, right?
The Tongue
The root of the tongue is posterior and slightly vertical, forming the posterior one third of the tongue. It extends from the hyoid, epiglottis, and soft palate, to the mandible. The body forms the anterior ⅔ of the tongue, and the apex of the tongue is the most anterior end of the body. The entirety of the tongue rests on the mouth's floor.
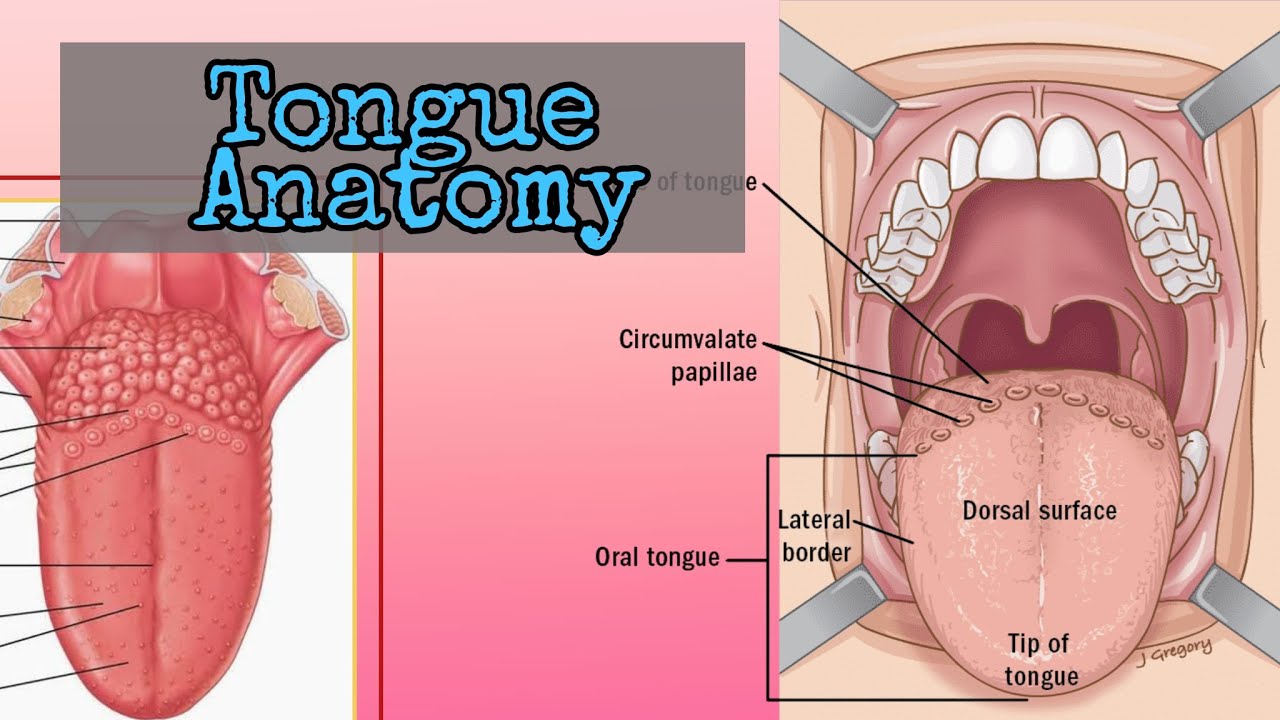
Tongue Surface Anatomy of the Tongue Head and Neck Human Anatomy YouTube
Review of the tongue Embryology. The tongue begins to develop at the end of the fourth gestational week.It arises from the first, third and fourth pharyngeal arches of the pharyngeal apparatus. Initially, the first pharyngeal arch gives rise to a central tuberculum impar (also called the median lingual swelling) and the bilaterally paired lateral lingual swellings.

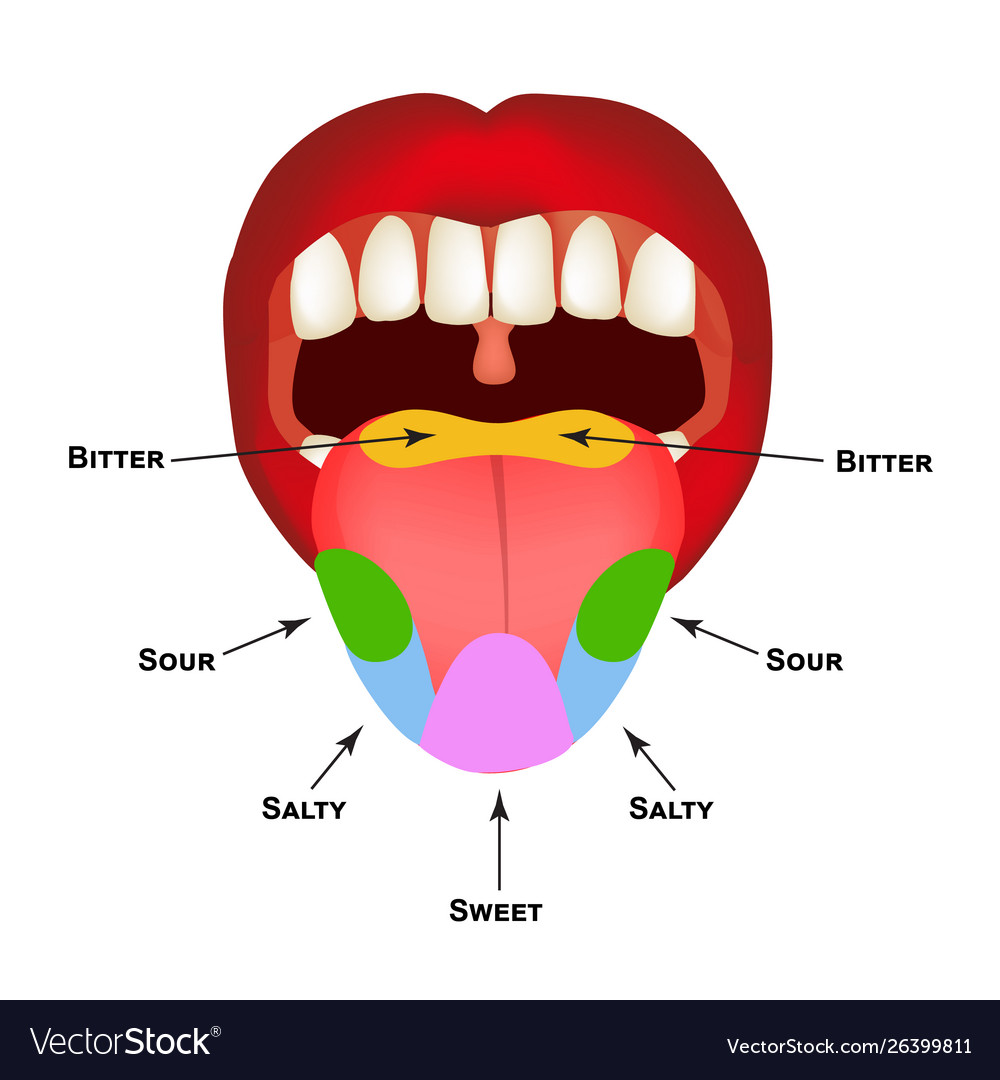
Cartoon of human tongue anatomy Royalty Free Vector Image
The tongue is a muscular structure in the mouth covered by mucosa whose primary functions are in mastication, taste, and speech. It can be divided into the anterior two-thirds which makes up part of the oral cavity and the posterior-third, part of the oropharynx. 1 The tongue consists of a tip, dorsal surface, ventral surface, and root.

Anatomy and Physiology Sensory Perception
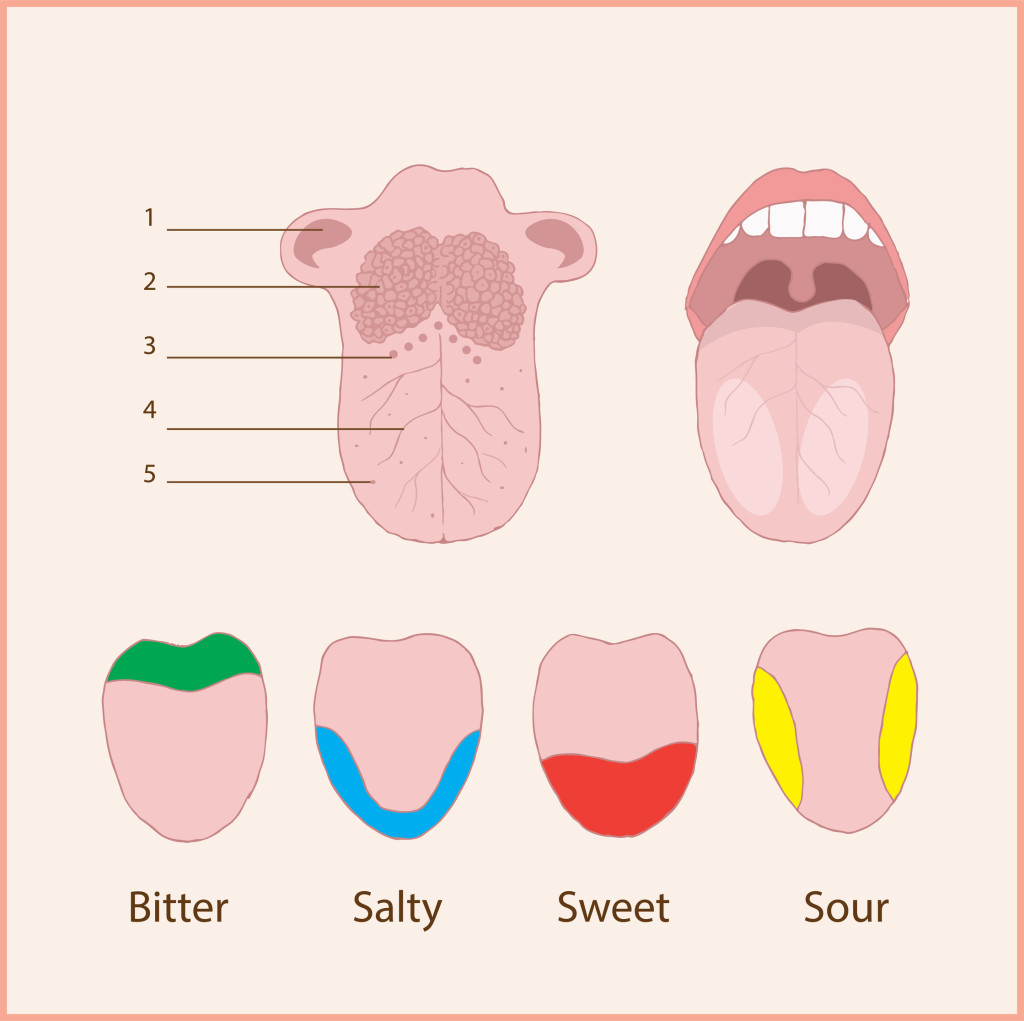
Tongue (Fig. 9.5) is made up of three elements; epithelium, muscles and glands. The epithelium is stratified and non-cornified. Two types of special structures are seen on it; the papillae (Fig. 9.6) and the taste buds. The taste buds (Fig. 9.7) are the sense organs of taste. These buds are lined by stratified squamous epithelium and are flask.

Print of Diagram illustrating the anatomy of the tongue, front view Anatomy of the tongue
The taste buds are bulb-shaped structures responsible for taste perception, located within the lingual papillae and in the surface mucosa of the soft palate, oropharynx, epiglottis, and upper esophagus. It is the only extrinsic muscle of the tongue that is not innervated by the hypoglossal nerve but by the vagus nerve (CN X). Contraction of the.

The Mouth, Pharynx, and Esophagus Anatomy and Physiology II
Human body Digestive System Tongue Tongue The tongue is unique in that it is the only muscle that isn't connected to bone at both ends. It is connected on one end to the hyoid bone, which is.
Anatomical structure tongue taste buds Royalty Free Vector
3 min read Image Source © 2014 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth. The tongue is covered with moist, pink tissue called mucosa. Tiny bumps called.

The Tongue Diagram Quizlet
Read about the human tongue and view a tongue diagram. Learn about the parts of the tongue, which includes taste buds, and learn about the tongue's function. Updated: 09/13/2022 What is.