
Cleansing Excess Pitta from the Body Banyan Botanicals
In English, Pitta is roughly translated as "fire", as it shares characteristics with the element of fire, such as heat, light, and transformation. A balanced Pitta dosha is essential for good health, and Ayurveda provides several methods for balancing Pitta and maintaining overall well-being.. Pitta is present in various organs of the.

Ayurveda PITTA Characteristics Learn more about Pitta pitta dosha ayurveda Ayurveda
Ayurveda is an ancient healing science that sets out to create a balance between the mind, body, and spirit. That balance comes when the three doshas— vata, pitta, and kapha —exist in harmony. Each dosha corresponds to different thought patterns, body types, and health profiles. Most of us are dominant in one or two of the doshas.
Pitta Dosha Ayurvedic Human Body Constitution. Combination Of Fire And Water Elements. Vector
Pitta literally means "fire", but is defined by an imbalance of oily, sharp, hot, light, sour, spreading, and liquid biocharacteristics. Pitta characterizes all heat, digestion, and transformation in the body. Pitta reactions include the acid secretion from the stomach, bile from the liver, and inflammation. Pitta sweat is sour, causing body odor.

Sites of Pitta subtypes in the body. Ayurveda yoga, Ayurveda vata, Ayurvedic massage
What Is Pitta Called In English? Pitta is one of the three primary doshas in Ayurveda, with the other two being Vata and Kapha. Each dosha is associated with a combination of elements and has distinct qualities, functions, and effects on the body and mind. Pitta is often described as a combination of the fire (Agni) and water (Jala) elements.

Types Of Pitta (Pitta Subtypes) And Their Roles In Human Body
Introduction Since pitta is said to be a representative of fire in body, the suffix agni is also given to all subtypes of pitta. In this context, pachaka pitta is also called as pachakagni (pachaka + agni), the 'food digesting fire'. I would call it 'digestive pitta'. Pachaka Pitta is one of the five subtypes of pitta.

Pitta Dosha / Ayurvedic Type Diet, Tips, Characteristics,
Ranjaka Pitta is located in the internal organs that are responsible for the formation of plasma and blood cells, and their circulation via the liver, spleen, stomach, and heart. In Sanskrit, ranjaka means "colouring/dyeing agent." This subdosha transforms rasa dhatu (plasma) into rakta dhatu or blood, says Gyawali.
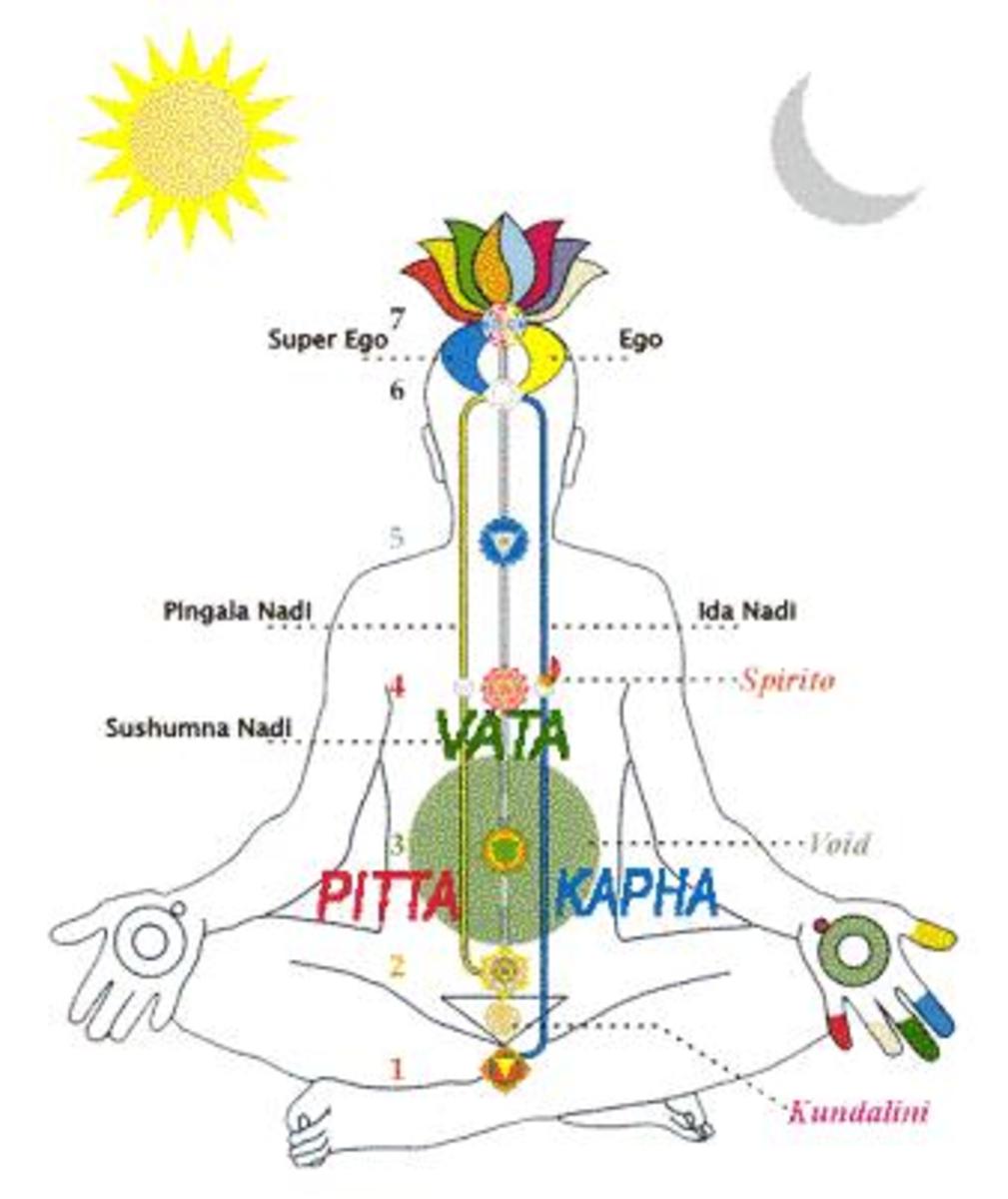
Ayurveda's Three Doshas Vata, Pitta and Kapha HubPages
Imbalanced pitta is often at the root of heat-related disorders, which can affect organs and tissues throughout the body. Imbalanced Kapha When out of balance, kapha triggers emotions of attachment, greed, and possessiveness and can also create stubbornness, lethargy, and resistance to change.

About Pitta
Dictionary Ayurveda Pitta Pitta Last updated: December 21, 2023 What Does Pitta Mean? Pitta is one of the three doshas, or the three fundamental energies that, according to Ayurveda, form every human being. Pitta controls the metabolic system, temperature, heat and transformations of the body and mind.

Body organs vocabulary inner organs Body organs, Body, Vocabulary
It is responsible for digestion, skin texture, vision and many other functions. Let us learn about parts of body where Pitta Dosha is dominant. Pitta is located in the following parts of the body -. Nabhi - umbilicus. Amashaya - stomach. Sweda - sweat. Lasikam - serum / plasma / lymph. Rudhiram - blood. Rasa - blood plasma.

Types Of Pitta (Pitta Subtypes) And Their Roles In Human Body
pitta personality. prakriti. tridosha. vedic medicine. References in periodicals archive. has a brown forehead and buff eyestripe contrasting with a black face, while the hooded has an all-black head. Rare bird sighted after 111 years. In the face of such anthropocentrism, Rocha 's show seemed to put us in our place.

Ayurveda Beginners guide Pitta Vata Khapa Body Types & Dosha Quiz
What Is Pitta? | Ayurveda Explained Watch on What Ayurveda Knows About You While there is undoubtedly no one quite like you out there, it is remarkable how accurate Ayurveda can be in predicting who we are—based simply on the broad strokes of our constitutions.

English Vocabulary Internal Organs of the Human Body Human body vocabulary, English
Article wellness:digestion Understanding the 5 Subdoshas of Pitta According to Ayurveda, the body is governed by three different elemental characteristics, or doshas: Vata (associated with wind and air characteristics of the body) Pitta (associated with fire and water characteristics of the body)

Pin on English Grammar Notes
Foods to Avoid or Reduce Pitta Dosha Precautions Has anyone ever told you, "You're so pitta?" Not sure what it means? Pitta is one of three main "doshas" in Ayurveda. In a way, it's kind of like an ancient system of understanding (and working with) your body and personality type. If Ayurveda medicine is new to you, you're not alone.
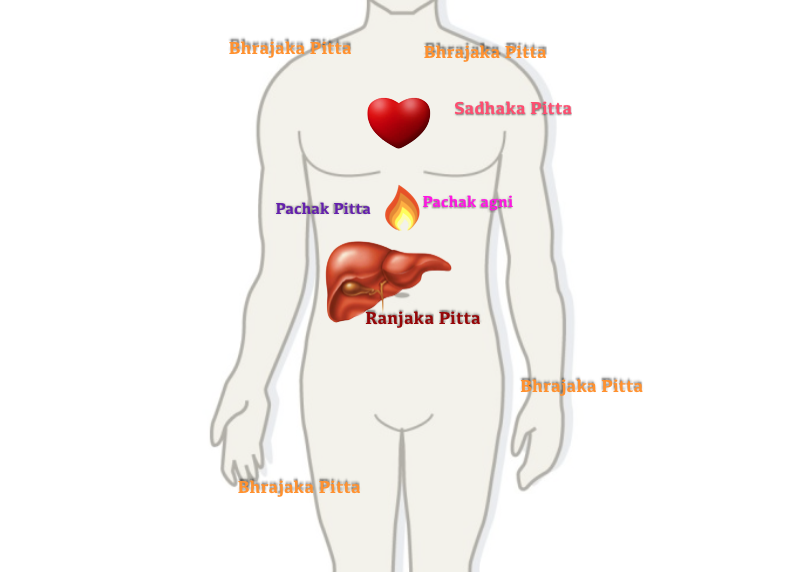
pitta Archives Shaka Vansiya Ayurveda
Pitta translates roughly as fire. However, the term does not mean fire in the literal sense, in the way you might experience or sense it as candlelight or in an open fire. Pitta dosha, the heat energy in the body, is invisible. It manifests itself in your metabolism. When our food is broken down in the stomach and intestine,

What Is Pitta Called In English? Called in English
Excess pitta can manifest in the body as: An uncomfortable feeling of heat in the body. Acid reflux, gastric or peptic ulcers, heartburn. Acute inflammation in body or joints. Indigestion, constipation, or diarrhea. Discomfort or nausea upon missing meals. Anger, irritability, frustration. Bad breath and body odor.
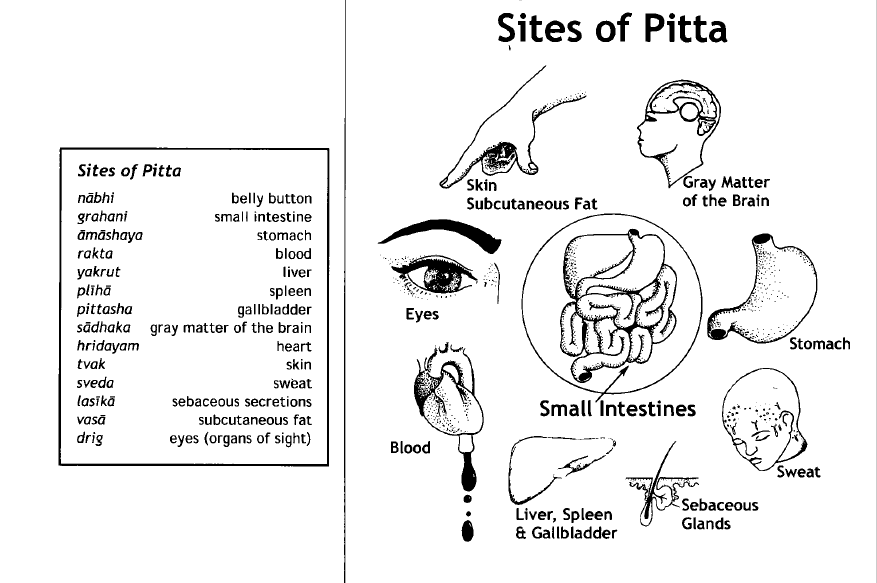
Types Of Pitta (Pitta Subtypes) And Their Roles In Human Body
Pitta (पित्त).—One of the three biological humors ( tridoṣa ).—Pitta is responsible for all aspects of heat, light and color in the body. The one that generates heat in the body is called pitta. Pitta is a source of thermal energy in the body. Sometimes pitta is translated as bile, which is one important aspect of its functions.