
Divergent Boundary Easy Science Divergent boundary, Plate tectonics
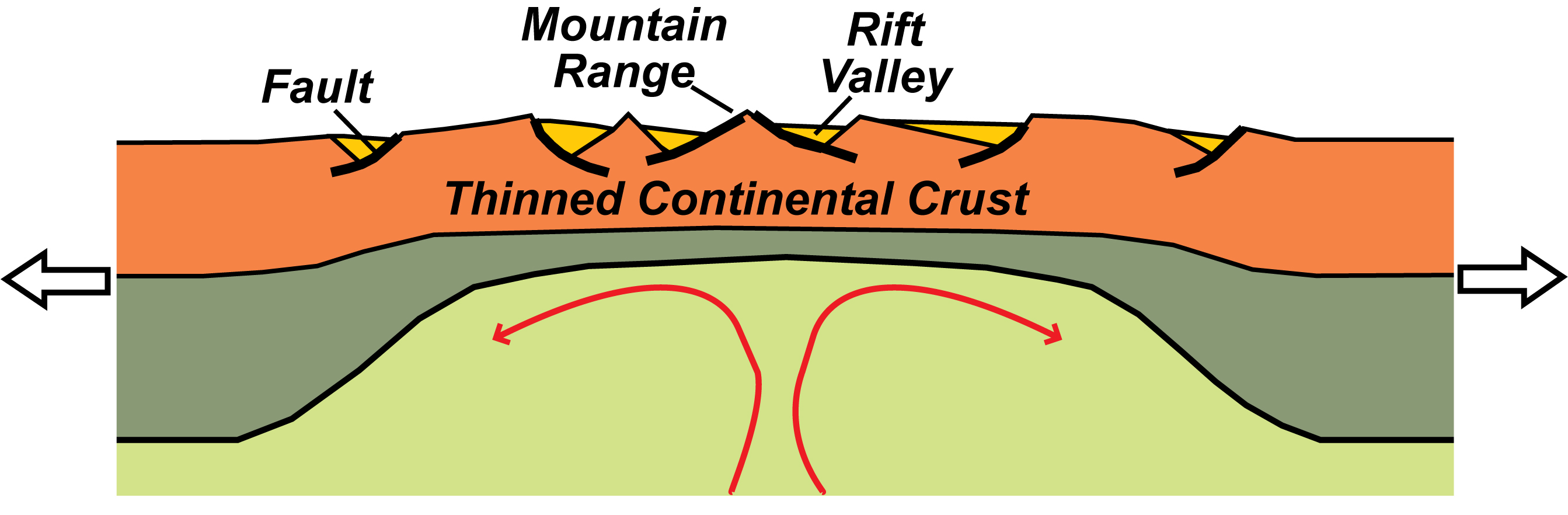
Divergent Plate Boundary—Continental Rift - Geology (U.S. National Park Service) Like other continents, North America has thick crust, compared to the thin crust beneath the adjacent Atlantic and Pacific oceans. In the western part of the continent, divergent plate boundary forces are beginning to rip the continent apart, forming the Basin.
IHSL Monica Ahtamova March 2013
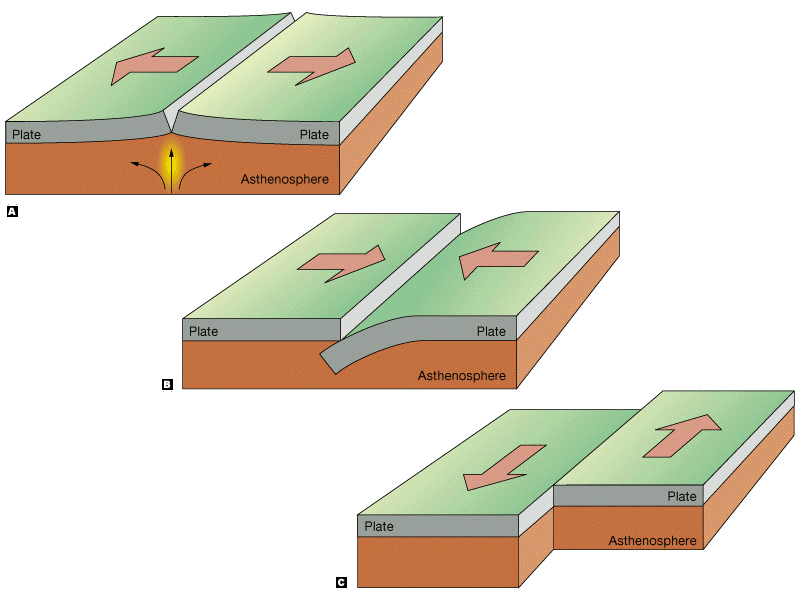
There are three types of plate boundaries: convergent, divergent, and transform. Created by Khan Academy. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Top Voted mmfinley2 a year ago What would happen if the plates stop moving • ( 7 votes) Upvote Flag Mark a year ago
Divergent Plate Boundary—Continental Rift Geology (U.S. National Park
In plate tectonics, a divergent boundary or divergent plate boundary (also known as a constructive boundary or an extensional boundary) is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. Divergent boundaries within continents initially produce rifts, which eventually become rift valleys.

6a) different stages of development of the divergent boundary, starting
Facts About the Divergent Plate Boundary Explained with a Diagram Divergent plate boundaries are those tectonic borders where tectonic plates pull away from each other and form a new crust. ScienceStruck takes you through some interesting facts about these divergent boundary zones on this Earth.

Pin on Earth Science
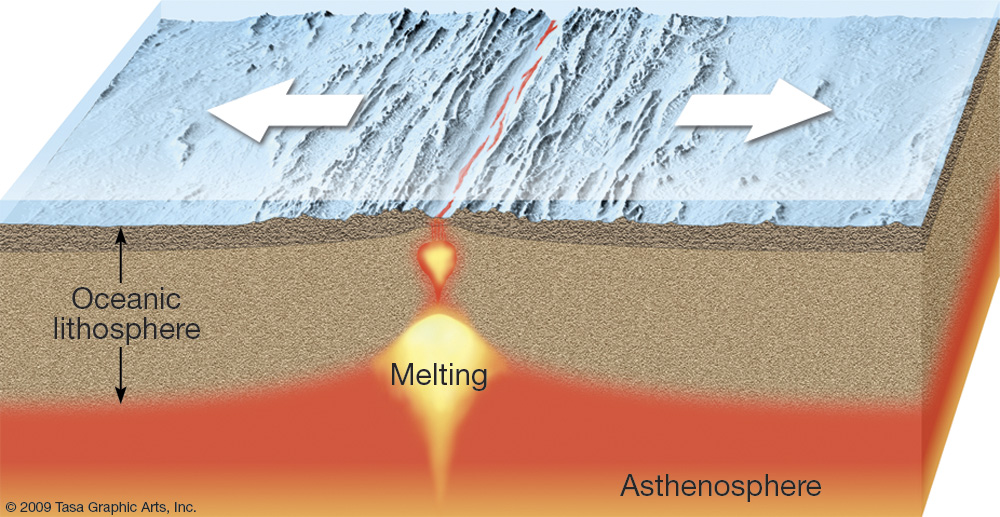
Divergent plate boundaries are locations where plates are moving away from one another. This occurs above rising convection currents. The rising current pushes up on the bottom of the lithosphere, lifting it and flowing laterally beneath it. This lateral flow causes the plate material above to be dragged along in the direction of flow.
Divergent Plate Boundaries Geology (U.S. National Park Service)
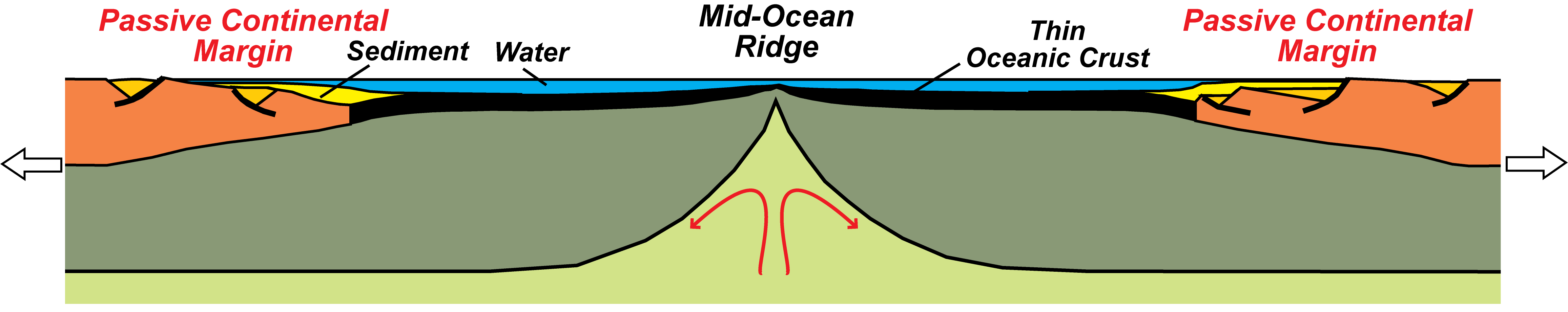
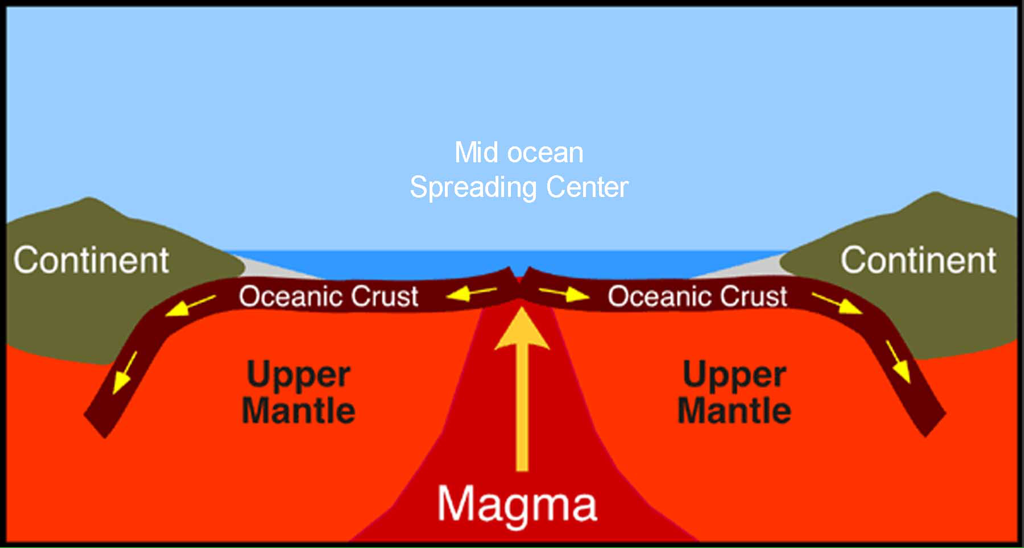
Spreading Centers along Divergent Plate Boundaries. A spreading center is a linear area where new crust forms where two crustal plates are moving apart, such as along a mid-oceanic ridge. Spreading centers are typically seismically active regions in ocean basins and may be regions of active or frequent volcanism (Figure 4.7).
Divergent Boundaries Tectonics Website
Now, with that out of the way, let's draw a little diagram of what happens in the early stages of these divergent plate boundaries. So you might have your just your crust, and maybe it's continental crust. So this right here is the Earth's crust. And then you have the solid part of the mantle, and the combination of them is the lithosphere.
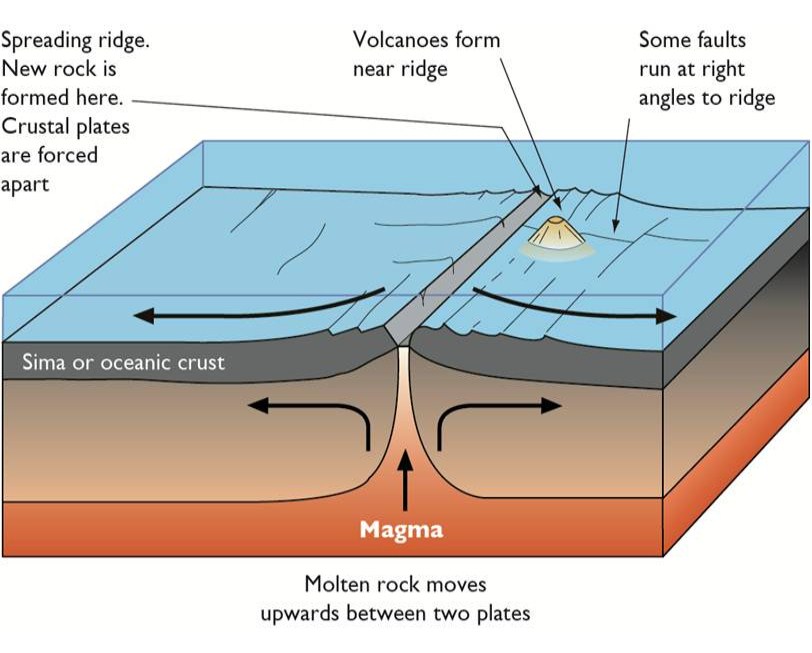
Plate Tectonics September 2012
Divergent boundaries occur along spreading centers where plates are moving apart and new crust is created by magma pushing up from the mantle. Picture two giant conveyor belts, facing each other but slowly moving in opposite directions as they transport newly formed oceanic crust away from the ridge crest.

divergent boundary
A convergent plate boundary also known as a destructive plate boundary , usually involves an oceanic plate and a continental plate. The plates move towards one another and this movement can.
Divergent Boundary GrickArnure Inc.
Divergent boundaries are spreading boundaries, where new oceanic crust is created to fill in the space as the plates move apart. Most divergent boundaries are located along mid-ocean oceanic ridges (although some are on land). The mid-ocean ridge

Divergent Boundary Definition & Examples Video & Lesson Transcript
Figure 2.4.1 2.4. 1: Faulting that occurs in divergent boundaries. In places where the continental plates are very thick, they reflect so much heat back into the mantle it develops strong convection currents that push super-heated mantle material up against the overlying plate, softening it.

At What Type Of Plate Boundary Do Shallow Focus Earthquakes Occur
In the oceans, plates move apart at mid-ocean ridges. Lava rises upward, erupts, and cools. Later, more lava erupts and pushes the original seafloor outward. This is seafloor spreading. Seafloor spreading forms new oceanic crust. The rising magma causes the ridge to be buoyant. This is why there are mountain ranges running through the oceans.

divergent Boundary
A generalized diagram showing the lithospheric situation associated with the formation of convergent, divergent, and transform plate boundaries. Illustration prepared by the United States Geological Survey.. The boundary between the North America Plate and the Eurasian Plate is an example of a divergent boundary at a mid-ocean ridge. All of.
Divergent Boundary Plate Boundaries
Most divergent boundaries are located along mid-ocean oceanic ridges (although some are on land). The mid-ocean ridge system is a giant undersea mountain range, and is the largest geological feature on Earth; at 65,000 km long and about 1000 km wide, it covers 23% of Earth's surface (Figure 4.5.1 4.5. 1 ). Because the new crust formed at the.

At divergent plate boundaries, plates move
. Tensional stress operates between the tectonic plates at a divergent boundary, which causes the lithosphere at these locations to stretch and pull apart. Divergent boundaries slowly grow ocean basins within continental lithosphere. The process of divergence breaks up continental landmasses and supercontinents .

Labeled Divergent Plate Boundary Diagram
Figure 10.4.1 10.4. 1 A map showing 15 of the Earth's tectonic plates and the approximate rates and directions of plate motions. 10.04: Plate Plate Motions and Plate Boundary Processes#fig10.4.1. Rates of motions of the major plates range from less than 1 cm/y to over 10 cm/y. The Pacific Plate is the fastest, followed by the Australian and.